Artificial Intelligence (AI) is reshaping industries worldwide, and manufacturing is no exception. Recent statistics reveal that over 60% of manufacturers have integrated AI-driven solutions, leading to increased operational efficiency and product quality. The manufacturing sector can address challenges like production bottlenecks, quality inconsistencies, and resource inefficiencies by harnessing AI.
The industrial manufacturing business is the leading adopter of artificial intelligence, with 93% of the CEOs reporting that their companies use AI at least substantially.
Manufacturers encounter several obstacles, such as unexpected machinery breakdowns or poor product delivery. Manufacturers may use AI and machine learning to accelerate their digital transformation to increase operational efficiency, introduce new goods, personalize product designs, and forecast future financial activities.
Artificial intelligence is transforming every business in the world, from healthcare and geology to cybersecurity and self-driving cars to everyday human use cases. With all firms fully committed to digital transformation, AI is also fast developing in the manufacturing industry.
Simply, artificial intelligence (AI) in the industrial business simulates human cognitive processes taught by very complex computer systems. The benefits include increased productivity, lower costs, improved quality, and reduced downtime.
According to an Accenture analysis, organizations that use artificial intelligence in manufacturing might raise profit margins by an average of 38% by 2035. This rise might result in an economic benefit of up to $14 trillion across 16 industries and 12 economies.
This blog delves into AI’s transformative potential in manufacturing, critical applications, benefits, challenges, and future outlook, illustrating why AI is indispensable for staying competitive in today’s tech-driven world.
What is AI in Manufacturing?
AI in manufacturing refers to the use of ML (Machine Learning) solutions and DL (Deep Learning) neural networks to automate complicated activities and reveal previously unknown patterns. This, in turn, optimizes manufacturing processes through enhanced data evaluation and decision-making.
Every firm conducts data-driven transactions and eventually becomes a data company. With so much data industrial firms generate via connected industrial devices, advanced sensors, and individual artificial intelligence (AI) applications in manufacturing, new efficiency, customization, and productivity levels are enabled. Embedding AI in industry is called 4IR, or the fourth technological revolution (Industry 4.0).
As reported by McKinsey, a leading management consulting firm, 4IR technologies are anticipated to be worth up to $3.7 trillion by 2025. AI alone can add $1.2 to $2 trillion in value to the supply chain management and manufacturing industries.
Exploring AI and Its Key Capabilities in Manufacturing
Artificial Intelligence (AI) transforms manufacturing by replicating human intelligence in machines to learn, reason, and make data-driven decisions.
In this context, AI combines advanced technologies like machine learning (ML), computer vision, natural language processing (NLP), and robotics to optimize operations, reduce costs, and enhance product quality. By bridging the gap between traditional manufacturing processes and cutting-edge innovation, AI empowers manufacturers to achieve unprecedented efficiency and productivity.
AI’s Impact on the Future of Manufacturing Industry
AI’s application in manufacturing revolves around its ability to interpret data, identify patterns, and execute tasks traditionally performed by humans. Unlike conventional automation, which relies on preprogrammed instructions, AI continuously learns and adapts, enabling dynamic responses to real-world challenges.
This adaptability makes AI invaluable for industries aiming to scale production, improve flexibility, and meet evolving market demands. Core components like ML enable machines to process and learn from data, allowing predictive analytics to identify trends and improve decision-making.
Computer vision revolutionizes quality control by automating defect detection, while NLP enhances communication in production systems, such as enabling voice commands or interpreting maintenance logs. AI-powered robots represent the pinnacle of intelligent manufacturing, combining precision, speed, and reliability to handle complex processes.
Key Capabilities of AI Transforming Manufacturing Processes
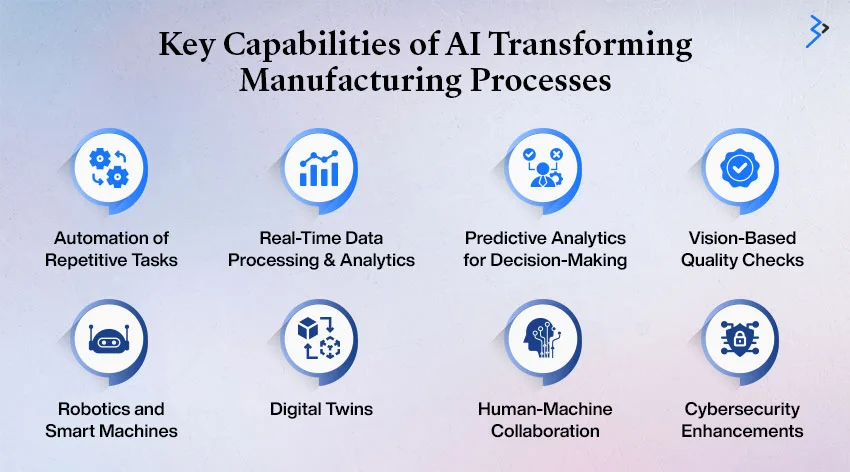
- Automation of Repetitive Tasks
AI systems excel in automating routine, repetitive tasks, from assembling components to processing documentation. This reduces human error and allows workers to focus on more strategic and creative roles, enhancing productivity. For example, AI-powered robotic arms can seamlessly handle assembly-line tasks, ensuring accuracy and speed without fatigue. - Real-Time Data Processing and Analytics
In the era of Industry 4.0, manufacturing generates immense volumes of data. AI enables real-time analysis of this data, transforming raw information into actionable insights. Whether tracking inventory levels or monitoring machine performance, AI ensures quick, informed decisions to prevent bottlenecks and optimize workflows. - Predictive Analytics for Decision-Making
Predictive analytics is a cornerstone of AI’s role in manufacturing. By analyzing historical data and identifying patterns, AI can forecast potential outcomes. This capability helps manufacturers anticipate demand fluctuations, optimize production schedules, and proactively address maintenance needs, reducing downtime and avoiding costly disruptions. - Vision-Based Quality Checks
AI-powered computer vision systems elevate quality assurance by inspecting products for defects with unparalleled precision. Unlike manual inspections prone to fatigue or oversight, these systems operate continuously, ensuring consistent quality while reducing waste. Such technologies have become critical for industries requiring stringent quality standards, like aerospace or pharmaceuticals. - Robotics and Smart Machines
Robots enhanced by AI are redefining manufacturing. From assembly lines to packaging, AI-driven robots handle intricate tasks quickly and precisely. Collaborative robots, or cobots, work alongside human employees, fostering a safer and more productive environment. These machines are versatile and scalable, with minimal intervention, adapting to diverse manufacturing requirements.
AI’s capabilities extend beyond mere automation; they represent a paradigm shift in manufacturing. By leveraging AI’s power, manufacturers can meet rising consumer expectations, navigate complex supply chains, and achieve sustainable growth in a competitive landscape, just as a catering delivery service must adapt to demand and logistics challenges to deliver fresh, timely meals.
Exploring Key AI Applications Transforming the Manufacturing Industry
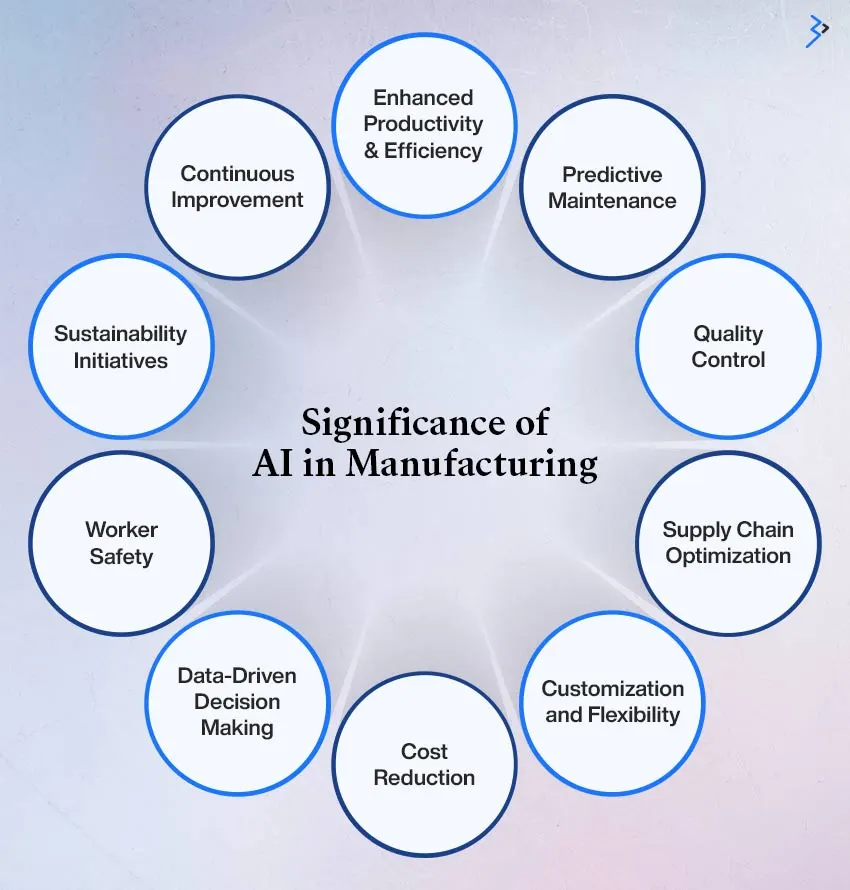
Predictive Maintenance
AI enhances maintenance strategies by analyzing historical and sensor data to predict equipment failures. This approach minimizes unplanned downtime, extends machinery life, and reduces maintenance costs.
Quality Control and Inspection
AI-powered computer vision systems excel in defect detection and quality assurance. These systems offer real-time monitoring, ensuring consistent production standards and significantly reducing waste.
Supply Chain Optimization
AI optimizes inventory management, demand forecasting, and logistics, ensuring supply chains are agile and responsive to market demands. Key AI use cases in logistics such as real-time route optimization and dynamic inventory adjustments help prevent stockouts and reduce inefficiencies.
Robotics and Automation
AI-powered robots are transforming manufacturing with advanced capabilities:
- Cobots (Collaborative Robots): Cobots are designed to work alongside humans and improve productivity and safety.
- Precision Automation: AI robots execute intricate tasks like material handling and assembly with unmatched accuracy.
Top Advantages of AI Integration in Manufacturing Processes
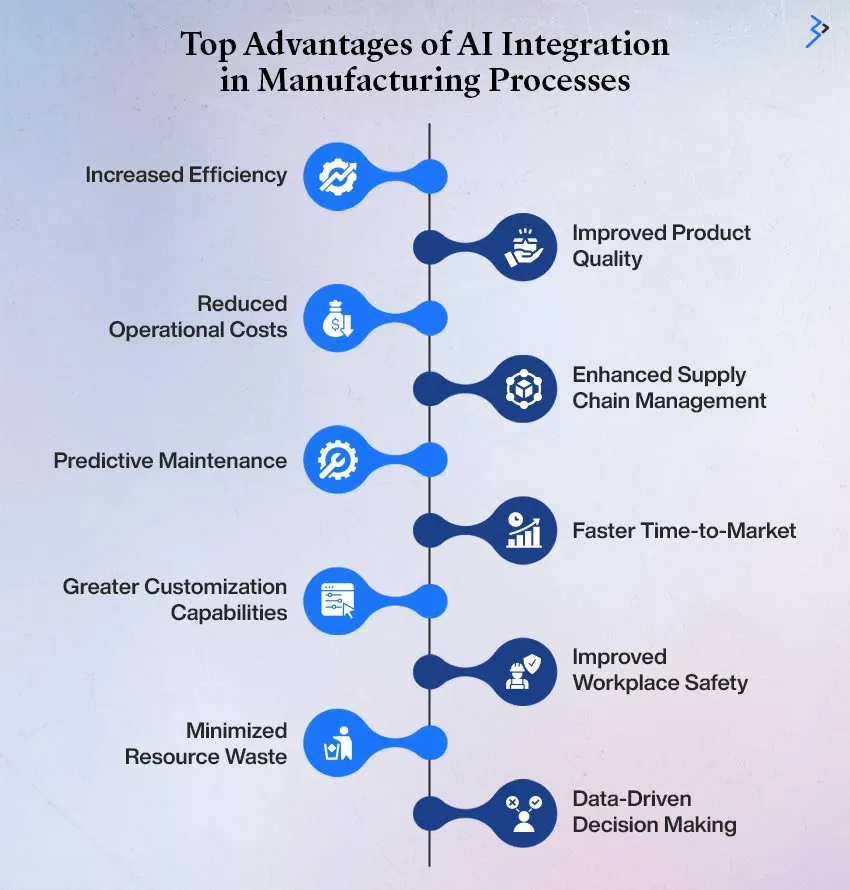
AI technology has revolutionized the manufacturing industry, delivering benefits that enhance efficiency, reduce costs, improve product quality, enable scalability, and promote sustainability. Below are the key advantages of adopting AI-driven solutions in manufacturing, along with detailed insights into each benefit.
Efficiency
AI optimizes manufacturing processes by automating workflows, improving throughput, and minimizing cycle times. Advanced systems analyze real-time data to detect bottlenecks and optimize production schedules, ensuring smooth operations.
- Forecasting: Identifies potential equipment failures before they occur, reducing downtime.
- Workflow Automation: Streamlines repetitive tasks to enhance productivity and operational speed.
- Optimized Production: AI fine-tunes production schedules for higher efficiency and resource utilization.
Cost Reduction
AI helps manufacturers reduce production costs by minimizing waste, lowering labor expenses, and preventing equipment failures. By optimizing energy consumption, AI also contributes to significant operational savings.
- Labor Cost Reduction: Automation frees up human resources for strategic roles, cutting labor expenses.
- Waste Minimization: AI-driven analytics identify inefficiencies, reducing material waste.
- Energy Optimization: Intelligent systems manage energy use, lowering utility bills and carbon emissions.
Improved Product Quality
AI ensures precision and consistency in production, enhancing product quality and minimizing defects. Vision-based quality control systems identify flaws that might go unnoticed by human inspectors, boosting customer satisfaction.
- Defect Detection: AI-powered systems identify imperfections during production to ensure high-quality output.
- Consistency: Maintains uniformity in product quality across large-scale manufacturing.
- Customer Satisfaction: Fewer defects lead to reduced returns and improved brand reputation.
Scalability and Flexibility
AI allows manufacturers to scale operations and adapt to changing market demands. Flexible manufacturing systems (FMS) powered by AI allow for customization and quick adjustments to production processes.
- Custom Orders: AI-driven systems handle diverse product requirements with ease.
- Rapid Adaptation: Adjusts production schedules based on demand fluctuations.
- Scalable Solutions: AI expands capabilities as business grows without compromising efficiency.
Sustainability
AI supports environmentally sustainable manufacturing by optimizing resource usage and waste management. Intelligent systems contribute to reducing carbon footprints and promoting greener production practices.
- Energy Efficiency: AI enhances energy utilization, lowering overall consumption.
- Reduced Waste: Identifies and mitigates wasteful processes, promoting sustainability.
- Carbon Footprint Reduction: AI-driven practices align with global environmental standards.
AI’s transformative impact on manufacturing addresses modern challenges while paving the way for future advancements. With its ability to improve efficiency, reduce costs, enhance product quality, enable scalability, and support sustainability, AI is an indispensable tool for manufacturers seeking to stay competitive in an ever-evolving market.
Challenges and Considerations for Adopting AI in Manufacturing
| Challenges | Description | Examples/Implications |
| High Initial Investment | Significant hardware, software, and workforce training costs can strain resources, particularly for SMEs. | SMEs may delay AI adoption due to affordability concerns, missing out on potential efficiency gains. |
| Data Management and Integration | Integrating AI with existing infrastructure requires managing vast datasets. Data quality is critical for AI performance. | Consistent data could result in accurate predictions or improved automation processes. |
| Workforce Transition and Upskilling | Workforce displacement requires reskilling employees to operate AI systems effectively. Training programs help ease the transition. | Workers may only resist AI implementation with clear training initiatives, affecting productivity. |
| Cybersecurity and Ethical Concerns | AI systems interconnected with IoT are vulnerable to cyberattacks. Ethical concerns, like algorithmic bias and lack of transparency, may undermine trust. | A security breach in an AI-powered smart factory could disrupt operations and compromise sensitive data. |
The Evolving Role of AI in Manufacturing
As more sectors and manufacturing units migrate to digital transformation, the market for AI in manufacturing is likely to expand rapidly. Manufacturing units in a variety of end-user industries around the world are implementing services that provide artificial intelligence-based solutions in response to shifts in consumer tastes, increasing requirements for better supply chain and logistics services, and the need to maintain regulations in manufacturing activities.
The US AI in manufacturing market is anticipated to be USD 1.41 billion in 2024 and USD 56.17 billion by 2034, increasing at a CAGR of 44.55% between 2024 and 2034.
AI-Powered Smart Factories
AI continues to redefine the manufacturing landscape, shaping a future where automation, collaboration, and innovation drive efficiency and competitiveness. Below, we explore key trends and advancements, complete with examples, to understand how AI will influence manufacturing in the years ahead.
AI-Powered Smart Factories
Smart factories represent the pinnacle of modern manufacturing, where AI integrates seamlessly with IoT (Internet of Things) and big data to create self-optimizing, autonomous systems. These facilities operate with minimal human intervention, offering unparalleled efficiency, precision, and reliability.
- Real-Time Process Adjustments: AI-powered smart factories can monitor operations in real-time. For example, Siemens’ MindSphere uses AI to collect and analyze data from production lines, enabling instantaneous adjustments to improve efficiency.
- Smart Maintenance: Smart factories equipped with AI can predict equipment failures before they occur. General Electric employs AI-driven factory maintenance systems to reduce downtime and prolong machinery lifespan.
- Industry 4.0 Applications: Industry 4.0 showcases AI’s potential in creating interconnected ecosystems where machines communicate autonomously. For instance, Bosch uses AI to integrate robotics and IoT, achieving seamless automation.
Collaborative Robots and Human-AI Interaction
The future of manufacturing emphasizes harmonious collaboration between humans and robots. Known as collaborative robots or “cobots,” these AI-powered machines enhance productivity while prioritizing worker safety and comfort.
- Improved Productivity: Cobots assist in repetitive tasks, allowing workers to focus on complex, value-driven activities. For example, Universal Robots’ cobots assemble components alongside human workers in electronics manufacturing.
- Enhanced Safety: Cobots are designed with safety features like proximity sensors to prevent accidents. BMW uses AI-powered cobots to assemble car parts, ensuring a safe environment for human employees.
- Reduced Manual Strain: Cobots minimize worker fatigue and injury by handling heavy lifting and repetitive motions. Amazon’s fulfillment centers employ cobots to sort and move inventory, reducing manual labor intensity.
AI in Product Design and Customization
AI-assisted design tools revolutionize product development by enabling manufacturers to efficiently create innovative, customized solutions. These tools harness AI’s ability to analyze vast datasets and generate optimized designs.
- Generative Design: AI suggests design options based on specific parameters. Autodesk’s generative design software has created lightweight, durable parts for Airbus aircraft.
- Customization: AI personalizes product designs to meet individual customer requirements. Nike uses AI to enable customers to design bespoke shoes on its platform, reflecting specific preferences and measurements.
- Reduced Development Time and Costs: AI-driven simulations identify potential design flaws early, saving resources. For example, Tesla uses AI for virtual crash testing, significantly speeding up vehicle development cycles.
Advanced AI Capabilities
Emerging AI technologies like reinforcement learning and deep learning further enhance manufacturing processes by enabling autonomous decision-making and improving predictive accuracy.
- Reinforcement Learning: AI systems learn optimal actions through trial and error, enhancing process efficiency. For example, Google DeepMind applies reinforcement learning to optimize energy use in data centers, a model that can be adapted for energy-intensive manufacturing.
- Deep Learning: This subset of AI processes complex patterns in large datasets to enable precise predictions. Samsung employs deep learning in its chip manufacturing process to detect and rectify defects at a microscopic level.
- Autonomous Decision-Making: AI systems can make real-time adjustments without human intervention. Fanuc, a leader in industrial robotics, uses AI for autonomous quality control, ensuring consistent output without delays.
Wrap Up
AI undeniably transforms the manufacturing industry, offering unparalleled efficiency, cost savings, and quality enhancements. Despite challenges like high initial investments and workforce adaptation, the benefits far outweigh the hurdles. The future of manufacturing lies in AI-driven smart factories, collaborative robotics, and innovative design solutions. By embracing AI, manufacturers can stay competitive, sustainable, and creative in an ever-evolving market.
Are you ready to revolutionize your manufacturing processes with AI? Start today to gain a competitive edge and future-proof your business. Connect with Brainvire’s AI experts to explore customized solutions tailored to your needs.
FAQs
AI enhances manufacturing by automating processes, improving efficiency, reducing costs, and ensuring quality control. It enables predictive maintenance, optimizes supply chains, and supports robotics and automation, making production faster and more reliable.
Predictive maintenance uses AI to analyze sensor data and historical trends to forecast equipment failures before they happen. This helps reduce downtime, extend machinery life, and minimize maintenance costs.
While AI implementation may require a high initial investment, there are scalable AI solutions tailored for SMEs. Cloud-based AI services and modular AI tools allow smaller businesses to adopt AI incrementally without overwhelming costs.
Key challenges include high implementation costs, integrating AI with legacy systems, data management, workforce reskilling, and addressing cybersecurity and ethical concerns.
The future involves smarter, more autonomous factories driven by AI, including enhanced robotics, AI-driven supply chains, and greater use of digital twins. These advancements will make manufacturing more agile, efficient, and sustainable.
Related Articles
-
Prominence of Business Intelligence in the Success of Any Business
The world today is demanding smarter processing and use of technologies that can possibly automate or ease out every possible task. And many companies have started adopting business intelligence in
-
The Role of AI-Driven Plugins in WordPress to Enhance User Experience
In the dynamic world of website development using artificial intelligence driven for plugin has emerged as a revolutionary force in the wordpress ecosystem. These intelligent plugins are changing the user
-
Preparing Your Enterprise for AI Integration: A Step-by-Step Guide
We live in a time when AI is no longer just a futuristic idea; it’s a key player in achieving business success today. Companies across all industries are realizing that




