Design is an essential part of every app. It is the first thing people see when they open an app. A good design can make your app stand out in the crowded app market.
Android and iOS have their unique design language, but UI design still has many similarities and differences.
iOS apps are typically designed with a more minimalistic approach, while Android apps are designed with a more colorful and complex process.
They each take a distinct approach to app development and design. This post compares the two platforms while highlighting some of the main UI design distinctions that you should keep in mind while designing for either.
Android vs. iOS – Market Data
The Android platform was the largest platform for the smartphone industry globally. In 2020, Apple sold 3.7 million iPhones.
According to Gartner’s figures, Android sold more than 1.3 million devices in 2020.
Google Play Store had 2.8 million app downloads in December, compared with Apple App Store having 2 million apps.
App Downloads: According to the App Annie data, the App downloads in 2018 reached 284.7 billion. Google has downloaded over 20 billion apps in its first year of operation.
Flat/Human Interface Design vs. Material Design-Difference Between Apple and Android
Flat interface designs, also known as human interface guidelines, consist of three basic tenets: Clarity, Deference, and Depth. This approach supports minimalism, uses clean elements, and emphasizes typography and flat colors. Apple’s Design rules have been dubbed its Flat Design rules. Apple mostly has a balanced design that offers fewer shadows, adding textured texture to the elements. In general, the Android Material Design is believed to be an enhanced version of Flat design with hints of Skeletomorphism. The most effective Android interface design rule is known as Material Design Languages.
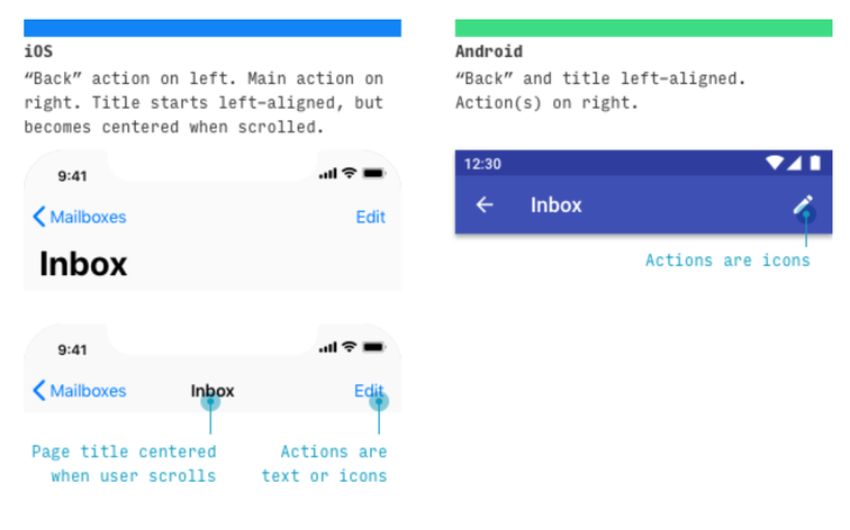
The navigation between screens is one of the most popular operations consumers perform on mobile apps on both platforms. The bottom of Android has a navigation bar. According to the device, back, home, and overview routes are controlled by a set of three buttons (physical or digital).
The Drawer menu, which extends out from one side of the screen and comprises drop-down list components, is Android’s core element for browsing across applications. In addition, tabs, which appear just beneath the page title and switch between pages within an app, are standard on Android.
In iOS apps, the previous tab’s name appears in the top-left corner, beside the back button. The current tab’s name appears in the center, with the option to “Edit” or “Done” (Control button) appearing in the extreme right corner in some circumstances.
In addition, it has a tab bar at the bottom of the screen that allows users to flip between many screens. Back navigation is accomplished by swiping from left to right or using the back button in the top left corner of the screen.
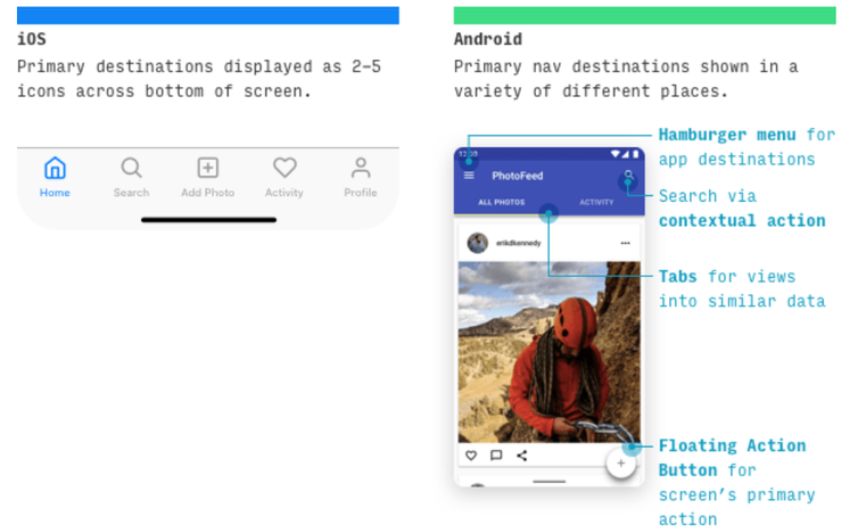
The core in-app navigation behaviors in iOS applications always follow the fore front, and the hamburger menu is utilized to store rarely used features. When comparing the UI designs of Android and iOS, you’ll notice that the former has the primary navigation in the hamburger menu or is scattered throughout the interface in the form of the search bar, floating action buttons, and other elements.
A navigation drawer is a menu open from the left of the screen when a menu icon appears. All tabs positioned beneath a screen name allow users to switch between views, data sets, and functional features of apps. Unfortunately, Apple has no navigation controls that replicate drawer navigation menus.
Instead, you will be able to navigate the world using an icon in the tabs of any iOS application, which is displayed at the bottom of the app screen. You can access these two navigation options in the section “more.”
The Android app design includes a back-like gesture that allows you to return to the previous tab in certain circumstances. However, using the Material design back button in the navigation bar is the most frequent and easiest method.
In iOS apps, there are four ways to use the “back” function —
- Swiping from left to right in apps to return to the previous screen.
- It’s as simple as pressing “back” on your keyboard.
- For non-editing modal displays, press the “Done” option
- Fullscreen and modal views can be accessed by swiping down on the screen
iOS vs. Android Comparison: Buttons
The only variation between the two platforms in button design is string capitalization and aesthetic style. There are two types of buttons in Material Design: flat and raised. In addition, on most Material Design buttons, the text is in uppercase. Although iOS occasionally employs uppercase buttons, the content is usually in Title case.
Buttons are helpful for many different tasks. The button edges are flat in iPhones, and there is no shade with title cases. In Android, the buttons are shadowed by uppercase characters. A floating action button is positioned within a tab bar on iOS as a call-to-action button. In Android, it promotes the primary activity, located below the screen.
iOS vs. Android: App icons and Screen resolution
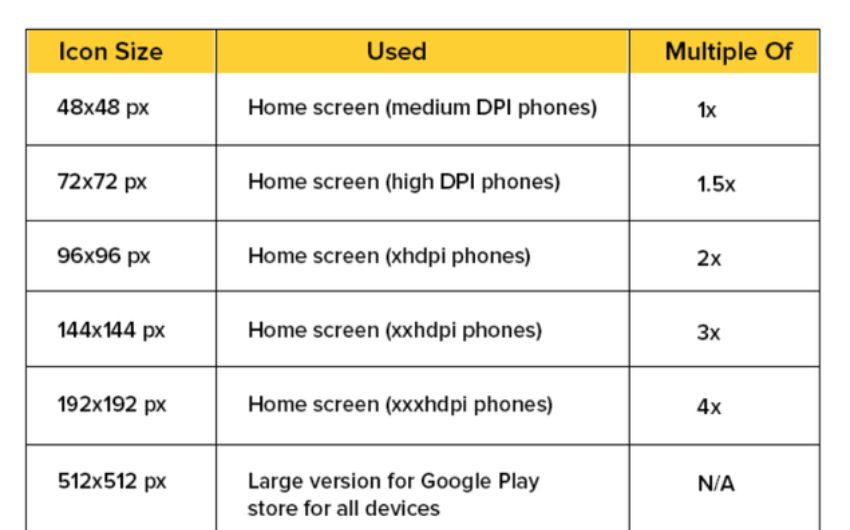
Both systems have an eight dp grid to design their display structures, and the most common margin is 16 dp. Next, it lists some icons intended for iOS applications on various screens. Understandably, some tables may appear intimidating at first, but if you know the base size.
It can check or export at many higher multiples, and everything can be accessible. Finally, the app icons are unique photographs available for both iPhone and Android. Usually, users decide whether they want more information from an application by looking at app icons.
iOS vs. Android: Typography
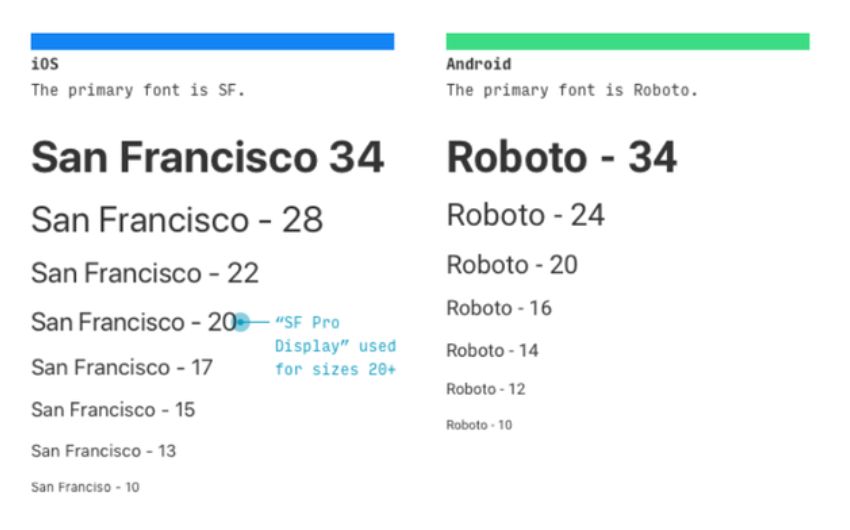
For years, Apple has been an advocate for Helvetica Neue, but in 2015 it changed its strategy and moved to San Francisco. This space-efficient font works best for iPhone, desktop computers, and iOS devices. Android’s main typography has been using Roboto since its inception.
It appears Google doesn’t intend to update this feature quickly. The basic dimensions of these books are similar. However, android vs. iOS has a big difference between the fonts and layout. Android uses white space between texts than iOS does.
iOS vs Android: Control Design
Search
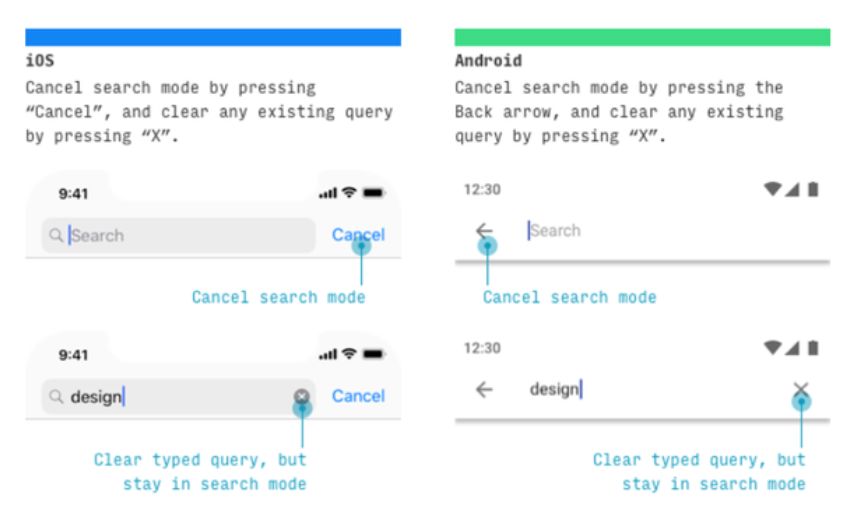
Search functionality on the two systems is vital – as evidenced by the recent Apple iMessage inclusion of search buttons in the messaging app. Apple uses two kinds of searches, visible and hidden. Often search icons are displayed in the upper tab. Sometimes the screen needs a move to reveal a search bar.
To cancel a search, click on cancel and Clear to remove it. Android doesn’t have any hidden inquiries, but there will be some hidden ones on the top of the screen. To stop searching for a particular keyword, click on the “” logo. This search will be removed as Apple did it.
Primary Call-To-Action
The floating action button in Android is considered the primary call/action button and appears at the bottom of the app’s bar. The most commonly used button in iOS applications is in the lower right corner. However, there are certain exceptions: a few iPhone apps may display CTAs in the lower toolbar or Android apps in the upper toolbars.
Action Menu
Action Menu allows for taking specific action for a piece of relevant information on your phone. For example, you can archive the message during a message, mark it as not read, or remove it. Action menu triggering occurs when the user presses any button in the app. The menu slides to its bottom when the user can easily find the menu in his hand.
The latest iPhone feature has context buttons to display related functions if you touch the content or the element. In context mode, a blur is visible. The menu appears in Android when you tap on an icon of 3 dots that indicates “more options” on top. The options pop up in an enlarged box.
Tabs
The results showed that iPhone doesn’t display any controls similar to ‘tab’ graphical controls. You can press the Segment button instead. Android uses a more flat design approach for the same screens as in the iOS/Android design infographic.
Selection Control
On the Android platform, a dropdown menu that appears in-place or a modal dialogue that seems to be centered and darkens the app backdrop is typically used to offer the options.
On the iOS platform, you can utilize picker control to offer a few options. Pickers may appear anchored to the bottom of the screen (as shown in the Android vs. iOS app design infographic).
IOS vs. Android: UX Design
IOS or Android user interfaces depend a lot more on different aspects. For example, if we look at LinkedIn, there’s a difference between iPhone to Android displays. In Android contact, a new connection close to you can be accessed on a screen. On iPhone, the option is displayed, and clicking on it opens a new window that displays all the available options.
In iOS, the mobile application also supports an optional floating button to create contacts with a simple touch of a button.
Content Scrolling
When scrolling in iOS, the navigation bar is smaller, and the toolbars disappear. However, iOS developers may also set the content-specific bar and content alignment when scrolling.
iOS and Android: Cards
Cards contain photos, text, movies, buttons, and comments. IOS cards don’t show shadows with full height or corners. Unlike Android cards, they are the most commonly designed apps with shadowing gutters and square corners.
iOS and Android: Alerts
Android alerting uses the flat button type that the dimensions listed in the materials specifications. Action buttons are located below the Alerts icon. These buttons can only be accessed in text format. In iOS, an alert action is separated by a divider. They can be used as sentences/titles, with the structure gained through each block. Then there are them placed around a popup.
IOS vs. Android – Technical Aspects
Developer complexity: iOS app development has lower complexity than Android. One of the biggest challenges in developing Android apps is fragmentation. There are various mobile devices — mobile phones and tablets — apart from differences in screens, realism, aspect ratio. Development Time. It’s a complicated app development process that can take longer than a standard iOS application. Android app development averages 2-4 percent is slower than iOS apps.
Conclusion
Selecting or using one platform is a choice involving countless factors, including the time of release budget and application size. Why do people use iOS apps to get more customers and earn more money? How does iOS compare to Android apps? While some detail in the article should help answer the question, it is impossible to determine a better solution. TechAhead is an experienced iOS app developer with experience that spans over 300 languages.
Frequently Asked Questions
Which operating system is superior – iOS vs. Android?
The operating system offers both pro and cons. Although Android can easily be customized due to open source functionality it also presents risks related to security, privacy and security controls. IOS developers have less sensitivity towards malware, with stricter privacy and security measures. However, customizations are only available on iOS.
Is it easier to develop an app for iOS or Android?
IOS applications take less effort as they can be written using Apple’s official programming language. Android applications have the ability to code with Java, which takes much longer. The development stage has always had many unknown factors but the release of the app into the store. Apple’s strict security measures mean a long wait to approve the apps, while Android apps can be easily accessed through a single click on the Play store via an ad.
How can I create a native app?
In creating a native app, it should always comply with the iOS user interface design guidelines, as well as the materials design guidelines. This renders an application in sync with a target system. This platform also has different requirements which require your app to comply to be published on the app store.
Is iOS more user-friendly than Android?
These answers are subjective. They depend upon the user’s own individual preferences. Some people find iOS easier than others, but some believe that Android does.
Why do apps look different on iOS and Android?
Differences in brands and ideologies are reflected in how the system works. It became symbolically symbolic for the branding on these sites.
Related Articles
-
30+ Top Uber Statistics To Know
Uber is revolutionizing our journeys. This rideshare app connects passengers to drivers by simply clicking and automatically charging the driver’s account. No money can be traded. Uber offers more comfortable
-
Your All-Purpose Guide for Making Your Mobile Website Accessible
Every web designer in the world is concerned to provide the best kind of website accessibility to its users. After all, accessibility is the key to creating fantastic websites that
-
New Android 11 Features and its Impact on Apps
The new Android 11 release might take some people by surprise with its news line of features, while for others, it will be just about an upgrade. However, there is