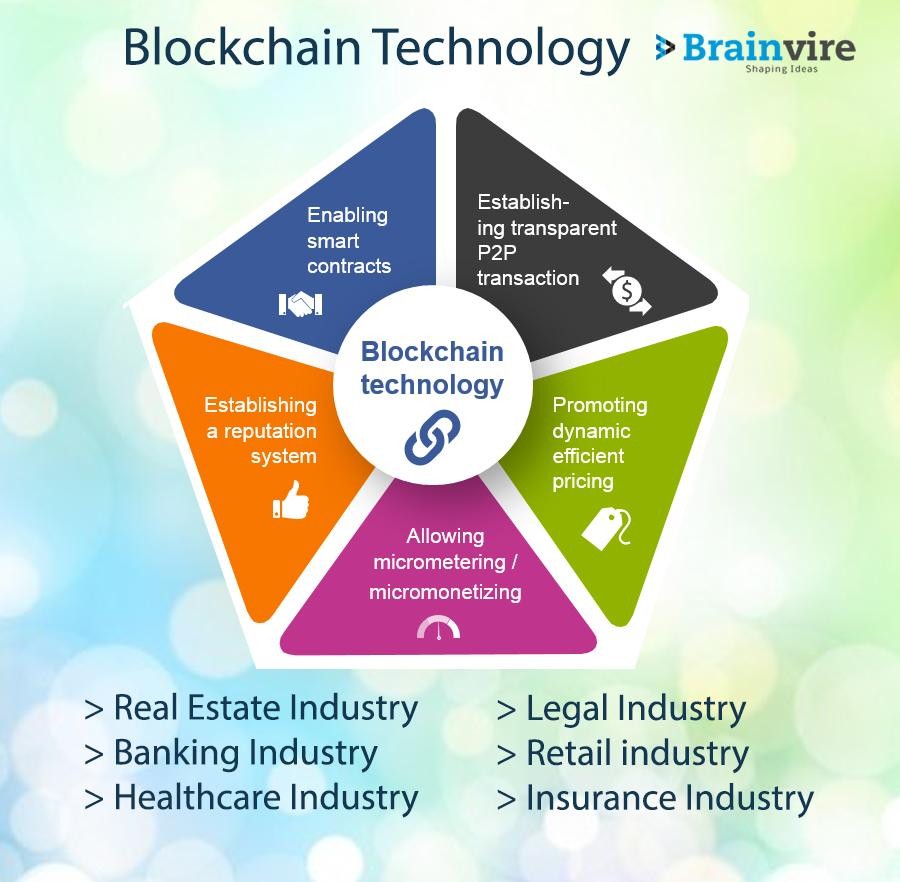
Imagine a world where supply chains are as clear as crystal, products can be traced from their birth to your doorstep, and transactions are safe and secure. Sounds like a dream, right? Well, thanks to blockchain, this dream is becoming a reality.
According to Mordor Intelligence, the global blockchain market size is expected to reach USD 195.7 billion by 2027, growing at a CAGR of 67.7% from 2021 to 2027. In the age of Industry 4.0 today, technology is transforming how we make things. It’s like a digital revolution, turning factories into smart, connected hubs. And blockchain is playing a starring role in this transformation.
But what exactly is blockchain? Think of it as a digital ledger that records transactions across a network of computers. What makes it special is that it’s decentralized, meaning no single entity controls it. This decentralization also makes it super secure and transparent.
Why is blockchain so important for Industry 4.0?

- Security: It’s like having a fortress around your data, keeping it safe from hackers.
- Transparency: Imagine a world where you can track every step of a product’s journey.
- Efficiency: Smart contracts automate processes, saving time and money.
- Trust: Blockchain builds trust between businesses and their customers.
Let’s dive into the details.
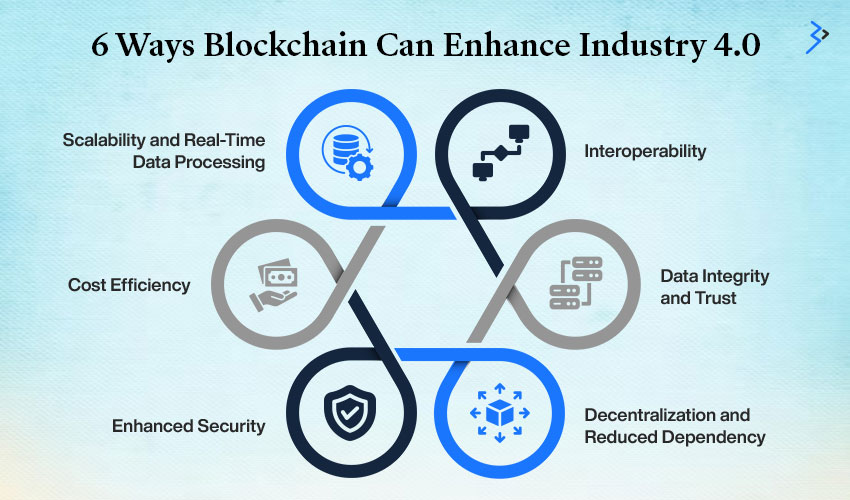
6 Ways Blockchain Can Enhance Industry 4.0
Blockchain has the potential to significantly enhance Industry 4.0 by providing a strong foundation for digital transformation. Its decentralized nature, immutable records, and smart contract capabilities offer numerous benefits:
01 | Interoperability
Blockchain can create a unified digital ecosystem by seamlessly integrating with other Industry 4.0 technologies such as the Internet of Things (IoT), artificial intelligence (AI), and big data. This interoperability enables seamless data sharing and collaboration across different systems.

02 | Data Integrity and Trust
Blockchain ensures data integrity and transparency by creating an immutable ledger of transactions. This assurance eliminates the risk of data tampering and builds trust among stakeholders, which is crucial for Industry 4.0 operations.
03 | Decentralization and Reduced Dependency
Blockchain reduces dependency on centralized systems, making operations more resilient to failures and attacks. This decentralization also promotes a more equitable and democratic approach to data management.
04 | Enhanced Security
Blockchain’s cryptographic principles and immutable records offer a high level of security against cyber threats. This security is particularly important in Industry 4.0, where sensitive data and critical operations are increasingly vulnerable to attacks.
05 | Cost Efficiency
By eliminating intermediaries and streamlining processes, blockchain can reduce operational costs. Smart contracts, for example, can automate workflows and reduce the need for manual intervention.
06 | Scalability and Real-Time Data Processing
Blockchain’s decentralized networks can handle large volumes of data and transactions in real time, making it suitable for the demanding requirements of Industry 4.0.
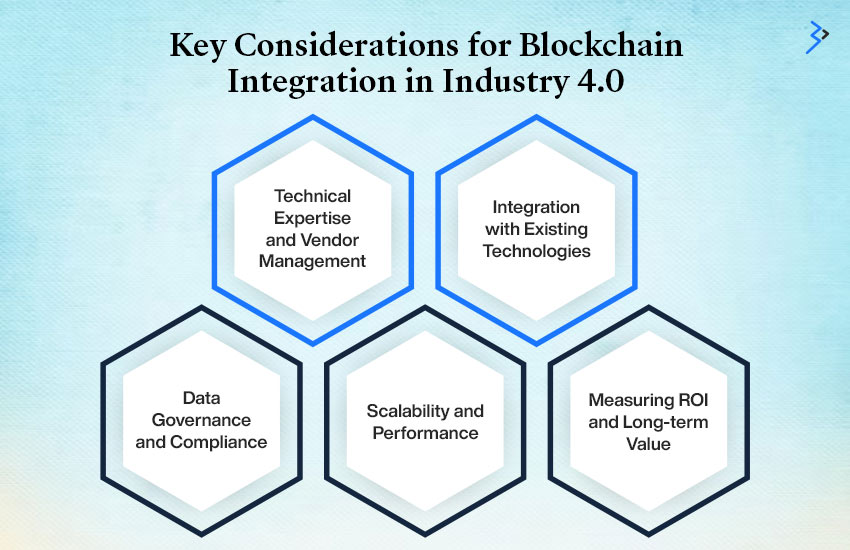
5 Key Considerations for Blockchain Integration in Industry 4.0
While blockchain offers numerous benefits, you need to carefully consider several factors for a successful integration:
01 | Technical Expertise and Vendor Management
Implementing blockchain requires technical expertise in areas such as cryptography, distributed systems, and smart contract development. You may need to partner with vendors or consult with experts to acquire the necessary skills.
02 | Integration with Existing Technologies
Integrating blockchain with existing Industry 4.0 technologies like IoT and AI requires careful planning and technical expertise to ensure seamless interoperability and data consistency.
03 | Data Governance and Compliance
Establishing clear data governance frameworks is essential to ensure compliance with industry regulations and data protection laws. This governance includes defining data ownership, access controls, and data retention policies.
04 | Scalability and Performance
Blockchain systems can face scalability challenges as the number of transactions increases. Evaluate different blockchain platforms and consider scalability solutions to ensure your organization’s systems can handle future growth.
05 | Measuring ROI and Long-term Value
Assessing the ROI of blockchain integration requires careful planning and analysis. Define key performance indicators (KPIs) and track the impact of blockchain on cost savings, efficiency improvements, and overall business value
[ Read More: Android App Development with Blockchain Integration ]
Future Trends and Opportunities in Blockchain and Industry 4.0
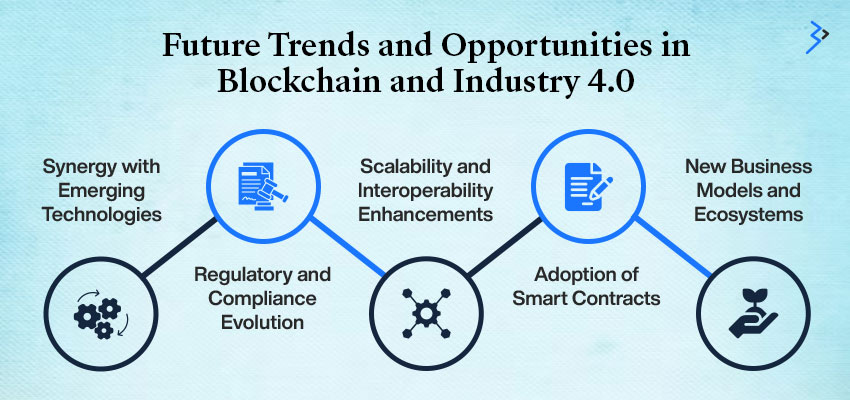
Imagine a world where machines talk to each other, sharing data seamlessly; AI analyzes vast amounts of information to predict the future; smart contracts automate processes, reducing paperwork and errors.
While it may sound like science fiction, blockchain and Industry 4.0 are close to making it a reality.
Here’s a sneak peek into what the future holds:
Synergy with Emerging Technologies
Blockchain can be combined with AI, IoT, and big data to create even more powerful solutions. For example, AI can be used to analyze blockchain data and identify patterns, while IoT devices can generate data that is stored and verified on a blockchain.
Regulatory and Compliance Evolution
As blockchain technology gains prominence, regulatory frameworks are evolving to address its unique characteristics. Staying informed about the latest regulations and ensuring compliance can help you avoid legal and financial risks. This information includes understanding privacy laws, data protection regulations, and industry-specific requirements.
Scalability and Interoperability Enhancements
Blockchain’s scalability and interoperability have been areas of focus for researchers and developers. Efforts are underway to improve the performance of blockchain networks, so they can handle larger volumes of transactions and integrate seamlessly with other systems. This enhancement is crucial for large-scale Industry 4.0 deployments where scalability and interoperability are paramount.
Adoption of Smart Contracts
Smart contracts, self-executing contracts with terms directly written into code, are becoming increasingly popular in industrial processes. They automate workflows, reduce the need for intermediaries, and ensure transparency and trust. Smart contracts can be used for various applications, such as supply chain management, payments, and asset-tracking solutions.
New Business Models and Ecosystems
Blockchain is enabling the creation of new business models and ecosystems that were previously not feasible. For example, blockchain-based marketplaces can facilitate peer-to-peer transactions, reducing the need for intermediaries and empowering individuals and businesses. Additionally, Blockchain Development Services can enable new forms of collaboration and value creation across industries, fostering innovation and growth.
Blockchain vs. Traditional Industry Approaches: A Comparative Analysis
In the realm of Industry 4.0, the choice between traditional centralized systems and blockchain-based solutions can significantly impact operational efficiency, security, and scalability. Let’s explore the key differences and advantages of each approach.
Traditional Industry Approaches
Traditional industrial approaches often rely on centralized systems to manage data, processes, and operations. While these systems have been in place for decades, they come with certain limitations:
- Centralized Control: Centralized systems require a single entity to manage and control all aspects of operations. This factor can create bottlenecks and increase the risk of data breaches.
- Limited Scalability: Traditional systems may struggle to handle large volumes of data and transactions, especially as businesses grow and expand.
- Security Concerns: Centralized systems are vulnerable to single points of failure and cyberattacks, as all data is stored in a single location.
Blockchain Integration in Industry 4.0
Blockchain, on the other hand, offers a decentralized and immutable approach to data management and process automation. Key advantages of blockchain integration include:
- Enhanced Security: Blockchain’s cryptographic principles and decentralized nature make it highly resistant to cyber threats.
- Improved Transparency: Blockchain provides a transparent and auditable record of all transactions, reducing the risk of fraud and increasing trust.
- Automated Processes: Smart contracts can automate various industrial processes, reducing manual intervention and errors.
- Real-Time Data Access: Blockchain enables real-time access to data, facilitating faster decision-making and improved operational efficiency.
- Scalability: Blockchain’s decentralized architecture allows it to handle large volumes of data and transactions, making it suitable for rapidly growing businesses.
Comparing Key Features
| Feature | Traditional Industry Approaches | Blockchain Integration in Industry 4.0 |
| Concept | Centralized systems managing all aspects of industrial operations | Decentralized systems leveraging blockchain technology |
| Pros | Established processes, easier regulatory compliance | Enhanced security, transparency, automation, real-time data |
| Data Management | Centralized databases | Distributed ledger |
| Scalability | Limited by centralized systems | Scalable through decentralized networks |
| Security | Vulnerable to single points of failure | Highly secure due to cryptographic principles and decentralization |
Blockchain in Action: Real-World Case Studies
Let’s see how blockchain has transformed industries from supply chain to finance and eCommerce:
01 | Supply Chain Revolution:
Think of a global logistics giant grappling with the complexities of managing a vast supply chain. Blockchain can provide a solution. With a decentralized platform, the company can:
- Track shipments in real-time
- Verify product authenticity
- Ensure compliance with regulations
These capabilities can result in a more efficient and transparent supply chain, reducing fraud and delays.
Real-Life Examples:
- Walmart: A pioneer in blockchain adoption, Walmart has used blockchain to track food products from farm to fork. It ensures transparency, traceability, and safety throughout the supply chain.
- Maersk: This global shipping giant has implemented blockchain to streamline its logistics operations, reducing paperwork and improving visibility into shipment status.
02 | Financial Services Reinvented:
Take a leading financial institution seeking to modernize its cross-border transactions. Blockchain can offer a breakthrough. By creating a decentralized ledger, they can:
- Reduce transaction processing time
- Enhance security and transparency
- Improve customer trust
This transformation can streamline operations and lower costs.
Real-Life Examples:
- Ripple: This fintech company has leveraged blockchain to enable faster and cheaper international payments, challenging traditional banking systems.
- Hyperledger Fabric: This open-source blockchain platform is used by banks and financial institutions for various applications, including trade finance and securities settlement.
03 | eCommerce Trust Restored:
An online marketplace faces challenges with fraud and counterfeit products. Blockchain can come to the rescue. By implementing a decentralized platform with smart contracts, they can:
- Reduce fraud
- Ensure product authenticity
- Increase customer trust
This transformation can revitalize the marketplace and create a safer eCommerce shopping environment.
Real-Life Examples:
- VeChain: This blockchain platform is used to track luxury goods, ensuring authenticity and preventing counterfeit products from entering the market.
- Provenance: This blockchain-based platform provides traceability for food products, empowering consumers to make informed choices.
Now that we have a clearer understanding of the various capabilities of blockchain, let’s discuss a few more real-life examples:
- IBM Food Trust: This blockchain-based platform tracks food products from farm to table, ensuring safety and reducing foodborne illnesses.
- Medchain: This platform uses blockchain to secure medical records and facilitate data sharing among healthcare providers.
- Grid Ledger: This blockchain-based platform enables peer-to-peer energy trading, promoting renewable energy adoption and optimizing grid efficiency.
- Authorship: Blockchain can be used to verify the authenticity of digital content and protect intellectual property rights.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What technical expertise is required for blockchain integration in Industry 4.0?
Successful blockchain integration in Industry 4.0 requires a diverse set of technical skills. Professionals need a deep understanding of blockchain protocols, consensus mechanisms, and smart contract development. Expertise in data management, cleaning, and integration is also crucial. Additionally, knowledge of distributed systems and network architecture is essential. To address security concerns, a strong understanding of blockchain security principles and best practices is necessary. Finally, familiarity with the specific processes and technologies used in the target industry is vital for effective integration.
2. How do I manage relationships and support with multiple vendors in a blockchain-integrated architecture?
The best way to manage relationships with multiple vendors in a blockchain-integrated architecture is with careful planning and coordination. Establish clear contracts outlining roles and responsibilities. Assign a dedicated project manager to oversee the integration process. Maintain open communication with vendors to address issues and ensure alignment. Regularly evaluate vendor performance and consider alternative options if necessary.
3. How do I integrate blockchain with existing Industry 4.0 technologies?
You can integrate blockchain with Industry 4.0 technologies with careful planning and technical expertise. Begin by identifying specific use cases where blockchain can add value. Select a blockchain platform that aligns with your needs and scalability goals. Develop APIs to facilitate data exchange between blockchain and existing systems. Thoroughly test the integration to identify and address any issues before full-scale implementation.
4. How do I ensure data consistency across all components in a blockchain-integrated architecture?
To ensure data accuracy and integrity across all components in a blockchain-integrated architecture, you can implement validation rules. Synchronize data across different system components using appropriate mechanisms. Regularly audit the system to verify data consistency and identify any discrepancies.
5. How can I measure the return on investment (ROI) of blockchain integration in Industry 4.0?
You can measure the ROI of blockchain integration with careful analysis. Consider quantifying cost savings from automation and reduced intermediaries. Evaluate the increase in revenue from improved processes, customer satisfaction, or new business models. Assess the reduced risk of data breaches, supply chain disruptions, and fraud. Finally, measure the time and resource savings achieved through streamlined processes.
6. What steps should I take to get started with blockchain integration?
To get started with blockchain integration, follow these steps: First, assess the potential benefits and challenges in your specific context. Then, select a blockchain platform that aligns with your technical needs. Assemble a skilled team with expertise in blockchain, data engineering, and your industry. Begin with a small-scale pilot project to test the waters and gradually expand blockchain integration across your organization based on its success.
7. What resources are available to help me learn more about blockchain integration in Industry 4.0?
Numerous resources are available to help you learn more about blockchain integration in Industry 4.0. Online platforms like Coursera, edX, and Udemy offer informative courses. Industry conferences and events provide opportunities to learn from experts and network with peers. Academic research and industry publications offer valuable insights into the latest trends and developments. Engaging with online communities and forums can connect you with other professionals for advice. And for comprehensive guidance, consider consulting with blockchain experts.
Want to know how you can integrate Blockchain in Industry 4.0? Connect with us today for Blockchain Solutions!
Related Articles
-
The Blockchain is the Talisman Larger Enterprises Have Anticipated!
Think Bitcoin? Think Blockchain technology! The reported potential of Blockchain for reducing bank infrastructure costs by 30%. Reported annual savings (potential) for banks deploying Blockchain technology is $8-$12 billion. The
-
Feel the Power of Robust Security with Blockchain and Cloud
When you hear the word Blockchain, most individuals correlate it to Bitcoins and Cryptocurrency. Several myths revolve around Blockchain technology and its association with Cryptocurrency. Financial software solutions have noticed
-
Blockchain For Different Industries
Blockchain, a future-vision technology, works in the distributed environment and on the highly-secured platform with a huge amount of information across the network. Blockchain service providers that connect the world