Artificial Intelligence (AI) has revolutionized industries worldwide, with machine learning (ML) driving automation, predictions, and data analysis. Traditional ML models rely on structured data to identify patterns and make decisions, but a groundbreaking advancement is reshaping the AI landscape—Generative AI.
Unlike traditional AI, Generative AI doesn’t just recognize patterns; it actively creates them. From generating realistic images and composing music to crafting human-like text and accelerating drug discovery, this transformative technology is pushing the limits of innovation. A J.P. Morgan Research even predicts that Generative AI could boost global GDP by 10%, highlighting its tremendous economic potential.
In this article, we’ll dive into the key differences between Generative AI and Traditional AI, exploring how generative models overcome the constraints of rule-based learning. We’ll also uncover how this cutting-edge technology is reshaping creativity, automation, and decision-making across industries. Get ready to explore the future of AI!
Understanding Generative AI vs. Traditional Machine Learning
Traditional machine learning development services follows predefined tasks, where models are trained on labeled datasets (supervised learning) or attempt to find structures in unlabeled data (unsupervised learning). These models typically focus on classification, clustering, and predictive analytics. Generative AI, on the other hand, creates entirely new content, generating outputs that did not previously exist.
Key Differences:
| Feature | Traditional ML | Generative AI |
| Learning Approach | Learns from labeled/unlabeled data to make predictions or classifications | Learns patterns and generates novel data resembling the training set |
| Primary Task | Regression, classification, clustering | Text, image, and audio generation |
| Model Types | Decision Trees, SVMs, Neural Networks | GANs, VAEs, Transformers |
| Example Use Cases | Fraud detection, recommendation systems, medical diagnosis | AI-generated art, chatbot text generation, synthetic voice creation |
Traditional ML is more about recognizing and understanding data, whereas generative AI is about creating data. This distinction makes Generative AI particularly valuable for creative tasks, content synthesis, and automation of various domains.
How Generative AI is Transforming Creative Processes Today
Generative AI development services is a powerful branch of artificial intelligence that creates new content by learning patterns from vast amounts of data. It leverages deep learning techniques, including Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), Variational Autoencoders (VAEs), and transformer-based models like Generative Pre-trained Transformers (GPT). These architectures enable AI to generate realistic images, text, music, and even synthetic data for various industries. Let’s explore how each of these models functions and their applications.
1. Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs)
Developed by Ian Goodfellow in 2014, Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) feature two opposing neural networks: the generator and the discriminator. The generator creates synthetic data that mirrors real-world examples, while the discriminator evaluates authenticity. This ongoing competition enhances the generator’s abilities, yielding increasingly realistic outputs and advancing the field of artificial intelligence development services across various applications, including image generation and style transfer.
Applications of GANs:
- AI-generated artwork – Tools fueled by GANs, like DeepDream and DALL·E, produce stunning digital art and illustrations.
- Deepfake videos – These models can manipulate video content by superimposing faces or modifying voices, raising both ethical concerns and entertainment possibilities.
- Synthetic medical images – GANs help generate high-quality synthetic medical images for research, enabling medical professionals to train AI models with diverse datasets without privacy concerns.
2. Variational Autoencoders (VAEs)
VAEs are another class of generative models that encode input data into a compressed representation (latent space) and reconstruct new variations from it. Unlike GANs, which rely on adversarial training, VAEs use probabilistic sampling to generate smooth and controlled variations of the original data. This makes them particularly useful for applications requiring structured and interpretable data generation.
Applications of VAEs:
- Image synthesis and style transfer – VAEs can generate new images based on learned representations, facilitating applications like artistic style transfer and photo enhancement.
- Drug discovery – Researchers use VAEs to simulate molecular structures, accelerate drug development, and identify promising chemical compounds.
- Data augmentation – VAEs generate additional training data in machine learning, improving model accuracy by providing diverse examples.
3. Transformer-Based Models (e.g., GPT, BERT, T5)
Transformers have revolutionized natural language processing (NLP) and AI-generated content. Unlike traditional models, transformers use self-attention mechanisms to process vast amounts of text, capturing long-range dependencies and contextual relationships. Models like GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) are trained on massive datasets and fine-tuned for specific tasks, making them highly versatile for various AI-driven applications.
Applications of Transformer-Based Models:
- AI chatbots – GPT-based models, including ChatGPT and Bard, enable human-like interactions, assisting with customer support, content creation, and conversational AI customer contact solutions.
- Automated code generation – Tools like GitHub Copilot leverage transformers to suggest code snippets, improving developer productivity.
- AI-generated content – AI-powered models are increasingly producing News articles, reports, and creative writing, enhancing efficiency in media and publishing.
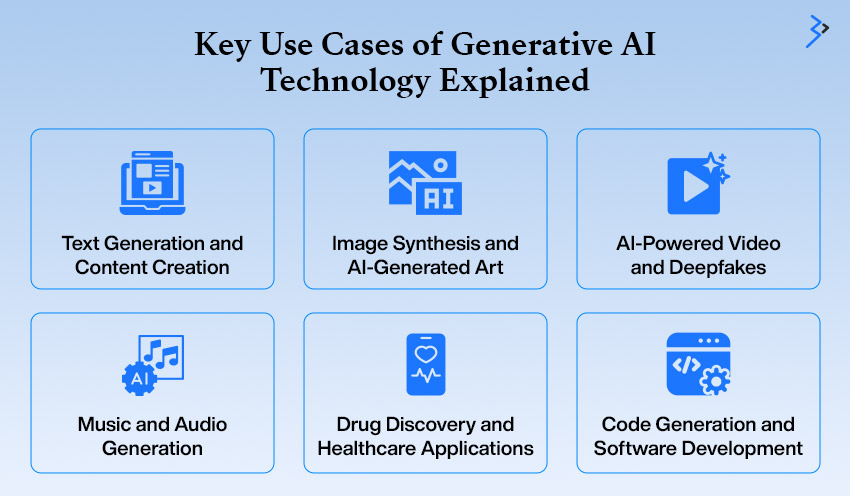
Key Use Cases of Generative AI Technology Explained
Generative AI has revolutionized multiple industries by enabling automation, enhancing creativity, and solving complex problems. From content creation to scientific research, its impact is profound and ever-expanding. Below are some of the most significant use cases that showcase its transformative potential.
1. Text Generation and Content Creation
One of the most well-known applications of generative AI is natural language processing (NLP)-driven text generation. Advanced models like GPT-4 and Bard enable businesses and individuals to automate content creation, enhancing productivity and efficiency. AI-generated text can be tailored for various industries, from marketing to entertainment, making it an essential tool for writers, journalists, and businesses.
Examples:
- Automated blog writing and news article generation
- AI-generated scripts for movies, TV shows, and video games
- Personalized marketing copy and chatbot responses for enhanced customer engagement
2. Image Synthesis and AI-Generated Art
Generative AI can create stunning visuals, illustrations, and digital artwork, effectively blurring the lines between human creativity and machine-generated content. Tools such as DALL·E, MidJourney, and Stable Diffusion empower users to generate high-quality images from simple text prompts. Today, AI is extensively utilized in design, advertising, and entertainment, enabling the rapid creation of unique visual assets.
Examples:
- AI-assisted graphic design and concept art creation
- Virtual influencers and synthetic media for marketing and social media
- Style transfer and photo enhancement for artistic and commercial applications
3. AI-Powered Video and Deepfakes
AI-generated video technology has advanced significantly, enabling realistic video synthesis, deepfake applications, and even AI-assisted film production. While deepfakes raise ethical concerns, this technology also has legitimate uses in entertainment, education, and media.
Examples:
- AI-generated film and game animations, reducing production time and costs
- Virtual avatars for customer service, providing interactive AI-powered assistance
- AI-enhanced video editing and restoration for old or damaged footage
4. Music and Audio Generation
Generative AI extends beyond visuals and text into music and audio production. AI models can compose songs, generate realistic voiceovers, and create adaptive sound effects for video games and films. This technology is reshaping the music industry by offering artists new tools for creativity.
Examples:
- AI-generated music compositions using tools like AIVA and OpenAI’s Jukebox
- AI-assisted podcast editing and voice synthesis for audiobooks and narration
- Personalized soundtracks and adaptive game music that change based on gameplay
5. Drug Discovery and Healthcare Applications
In the medical field, generative AI accelerates drug discovery, enhances medical imaging, and assists in creating personalized treatment plans. By generating synthetic patient data and simulating molecular structures, AI helps researchers develop new treatments faster and more efficiently.
Examples:
- AI-generated protein structures for pharmaceutical research, aiding in drug design
- Synthetic patient data for training medical AI models without privacy concerns
- AI-powered radiology image enhancement for improved diagnosis and treatment
6. Code Generation and Software Development
Generative AI is transforming software development by assisting developers in writing, debugging, and optimizing code. AI-driven code generators streamline workflows, helping businesses build applications more efficiently.
Examples:
- AI-powered code completion with tools like GitHub Copilot and OpenAI Codex
- Automatic bug detection and fixes, improving software quality
- AI-generated game design elements, reducing manual coding effort in game development
Read More-: Top Generative AI Content Writing Tools for 2025
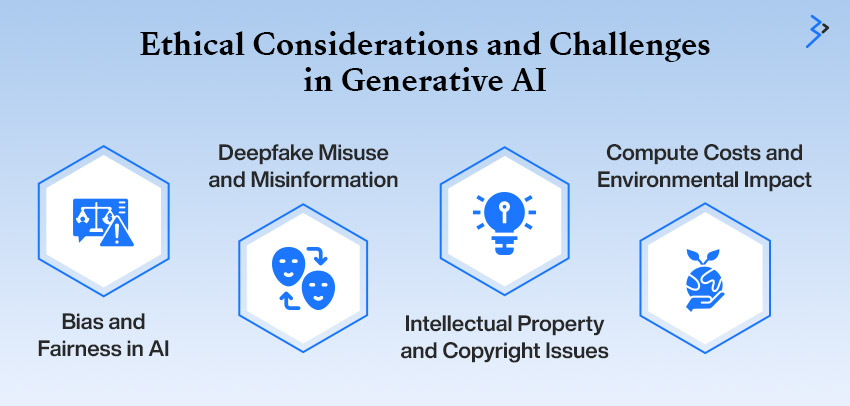
Ethical Considerations and Challenges in Generative AI
While Generative AI has unlocked groundbreaking possibilities, it also presents profound ethical and technical challenges. Addressing these issues, from biases in AI models to deepfake misuse and environmental concerns, is crucial to ensuring responsible AI development and deployment.
1. Bias and Fairness in AI
AI-generated content is only as unbiased as the data it learns from. Since large language models (LLMs) and image generators are trained on vast datasets sourced from the internet, they often inherit societal biases, leading to discriminatory or misleading outputs. A 2023 study by Stanford University found that major AI models exhibited gender, racial, and cultural biases in 38% of generated outputs.
Unchecked bias in AI can lead to:
- Reinforcement of harmful stereotypes in generated content
- Discriminatory AI decisions in hiring, finance, and legal systems
- Spread of misinformation through AI-generated news and articles
Solution: To mitigate these issues, continuous bias audits, diverse training datasets, and ethical AI governance frameworks are necessary.
2. Deepfake Misuse and Misinformation
Deepfake technology has become alarmingly sophisticated, enabling the creation of hyper-realistic fake videos, voices, and images. Onfido’s 2024 deepfake crime statistics reveal a concerning trend. As generative AI tools evolve, deepfake technology grows increasingly advanced and accessible. Alarmingly, incidents of phishing and fraud related to deepfakes skyrocketed by 3,000% in 2023.
Key risks include:
- Political disinformation: AI-generated deepfakes have been used to manipulate elections and public opinion.
- Financial fraud: Voice-cloning AI has been exploited in scams, costing businesses millions.
- Privacy concerns: Personal images and videos can be manipulated for blackmail or defamation.
Solution: AI watermarking, stricter deepfake regulations, and AI detection tools can help counter misuse.
3. Intellectual Property and Copyright Issues
The legal landscape surrounding AI-generated content is murky. Who owns an AI-created painting, song, or article—the AI developer, the user, or the data source? A recent US Copyright Office ruling denied copyright protection for AI-generated artworks, stating that “creativity must be human-driven.”
Key intellectual property concerns include:
- Plagiarism risks: AI models trained on copyrighted material may generate derivative works.
- Ownership disputes: Companies and creators are contesting AI-generated content rights.
- Fair use debates: AI scraping publicly available data raises legal and ethical concerns.
Solution: Updated copyright laws and clear AI content attribution policies are essential to navigate this evolving landscape.
4. Compute Costs and Environmental Impact
Training large-scale AI models requires immense computational power. For example, training GPT-3 consumed 1,287 MWh of electricity and produced 552 metric tons of CO₂ emissions—equivalent to driving 1.24 million miles in a car.
Challenges include:
- High operational costs: AI model training costs can exceed millions of dollars for cloud computing and GPU resources.
- Carbon footprint concerns: The AI industry’s energy consumption is projected to increase by 2030 unless sustainable practices are adopted.
- Accessibility gap: Only tech giants with vast resources can afford cutting-edge AI, widening the digital divide.
Solution: Researchers are developing low-power AI models, energy-efficient algorithms, and renewable-powered AI data centers to address sustainability concerns.
Read More-: How to Use Generative AI to Its Full Potential in Your Adobe Commerce Store
Exploring the Future of Generative Technology and Innovation
Generative AI is poised to reshape industries by enhancing creativity, automation, and decision-making. As research progresses, we can expect more sophisticated models with improved efficiency and ethical safeguards. Future developments may include:
- AI-generated virtual assistants with advanced reasoning capabilities
- More realistic and controllable AI-generated content
- Enhanced interpretability and transparency in generative models
- Sustainable AI frameworks reducing energy consumption
With continuous advancements, generative AI will continue to expand its influence, driving innovation across technology, healthcare, entertainment, and beyond.
Wrap Up!
Generative AI is revolutionizing how we interact with technology by moving beyond traditional machine-learning approaches to create new and innovative content. Its applications are vast and transformative, from text and images to music and medical breakthroughs.
While challenges remain, responsible AI development and ethical considerations will shape a future where Generative AI coexists with human creativity to unlock unprecedented possibilities.
Related Articles
-
How AI is Transforming and Revolutionizing the Manufacturing Industry for the Future
Artificial Intelligence (AI) is reshaping industries worldwide, and manufacturing is no exception. Recent statistics reveal that over 60% of manufacturers have integrated AI-driven solutions, leading to increased operational efficiency and
-
NLP Solution Use-Cases Redefining the Business Sector
Natural Language Processing or NLP, as it commonly called, is gaining a lot of momentum these days. Organizations are using this piece of technology in various manners depending upon the
-
AI Impact On Medical Diagnostics And Treatment
The medical industry has witnessed a significant transformation due to the remarkable impact of Artificial Intelligence (AI). When doctors successfully save a patient’s life, they are elevated to a status




