The Internet of Things (IoT) is a network of physical objects—from smartphones to cars to televisions—that are connected to the internet and can collect data from the sensors embedded in them. This data can then be accessed by other devices, including other computers, for analysis.

Physically connecting any object with an onboard computer chip to the internet has enabled it to be accessed remotely using wireless technologies. Connecting these objects sends information about their use back over the internet, helping other connected devices and people to access this information.
There are plenty of IoT devices available on the market nowadays. There are devices to control your home heating, dimming lights with voice command on Amazon Echo, Google’s Nest Thermostat, smart appliances which can talk to each other over the internet.
But how exactly do these things work? Let us break it down for you.
What is IoT?
Internet of things or IoT is the network of physical devices or “things” embedded with electronics, software, sensors, and connectivity to enable it to achieve greater value and service by exchanging data with its manufacturer, other devices, and the internet.
The internet of things extends to wherever there is an internet connection. There are many use cases for IoT. A few examples include smart cities, smart meters, wearable technology, and even traffic lights.
People may be less aware of what is happening in their environment than they were before the advent of the IoT.
Devices connected to the internet are called nodes in IoT that allow sharing information and communicating with each other.
These days, many modern devices can communicate with each other via Machine-to-Machine (M2M) technology. Not only does it help with tasks such as washing or cooking, but also all forms of entertainment.
What are your thoughts on the IoT market? First, let’s discuss some interesting statistics.
- By 2022, 100% of the population is predicted to have LPWAN coverage
- By 2025, there will be more than 75.4B Internet of Things devices worldwide
- 54% of enterprises invested in IoT app development because of its cost-saving factor
- The global internet of things data market size stood at USD 250.72 billion in 2019 and is projected to reach USD 1,463.19 billion by 2027, at a CAGR of 24.9%
- 94% of businesses will use some form of IoT by the end of 2021. Furthermore, 88% believe IoT is critical to their business success among current IoT business adopters
Understanding what IoT devices are and how they work is not enough; we need to know the potential of emerging technologies and concepts in the future. So let’s turn towards why they’re important and how they work!
How IoT works?
The basic structure of IoT is made up of sensors, which transmit collected data to IoT platforms. These centralized devices store the most relevant data through specific tasks – which are also important for understanding how it works.
The data collected in IoT platforms are not all equal. Some of this data is more specific than others, while some are more generalized. This information can be used to detect patterns, make recommendations, and more.
The IoT is enabling many new use cases that were not possible before. For example, the installation of smart streetlights has reduced energy consumption by 80% in some cities. This technology can also be used for security purposes with devices like IoT security cameras.
We can now explore the consequences of IoT technology further.
Major Components of IoT Ecosystem
IoT enables the connection of smart sensors to networked platforms that allow for data collection, automated decision making, and predictive analytics. The main components of an IoT ecosystem are as follows:
Sensors/ Devices: IoT devices are made up of a wide range of sensors. Sensors can be as simple as a button or as complex as a self-driving car. A single device can have multiple types of sensors that work together to perform a specific function or set of functions. One example is the iPhone 5s, which has an accelerometer, proximity sensor, light sensor, and fingerprint scanner all connected to its application processor within the device. This allows for more advanced functionality such as Touch ID authentication and advanced gesture control capabilities.
Connectivity: The second component is connectivity between both people and things. Connections can be enabled through various wireless systems, including mobile broadband networks (3G/4G LTE), Wi-Fi, and Bluetooth. Physical connections can be wired or wireless, depending on the application of that particular device.
Data Processing: Once a connection has been established, the data collected from sensors must be processed to become meaningful information for users. This data needs to have context applied to it to be relevant for decision-making purposes. A car might sense an upcoming obstacle without knowing how fast it will approach or what direction the obstacle is coming from, meaning more processing is required before decision-making capabilities are available. Data processing also occurs within the hardware itself with embedded processors on IoT devices that perform some of this cognitive work while still on the networked platform. The processing power of a device directly affects its cost and complexity, but larger amounts of processing power typically lead to more functionality.
User Interface: The final component of an IoT ecosystem is the user interface, which can be either on-device or on a networked platform. All IoT ecosystems have some type of user interface that allows for human interaction with the device and its collected data. This connection between humans and devices happens through various inputs, including buttons, touch displays, voice recognition interfaces, etc., as well as outputs including digital readouts, lights, speakers, etc. This also includes what are known as virtual user interfaces (VUI)s where the output is not visible but still exists in software form via text commands or audio feedback rather than traditional visual cues.
IoT Ecosystems are built upon the components listed above. As sensors, connectivity, data processing, user interface, and business models are continually evolving, the IoT Ecosystems of tomorrow will likely be built on top of different components than today’s iterations while still adhering to the same functions.
Now that you have understood the major components, let us understand how Cloud computing is required to work IoT.
What is Cloud Computing?
To make it simple, think of a car reservation system where users make reservations through different routes like calling, visiting a customer service center, or booking online.
In this system, there are different servers to deal with thousands of calls, making the system slow and inefficient. On the other hand, when they start using a central server to handle all these requests, it reduces the load on each individual machine and also increases efficiency.
This is Cloud Computing, where you have a single centralized point to store information having access from anywhere in the world through the internet instead of going through different points to get things done.
Why Cloud?
Because IoT devices can connect to a specific server which will communicate with them over the internet instead of communicating with each other directly making the communication secure and reliable.
IoT is an emerging technology that will allow devices to communicate with each other easily and reliably due to its centralized server, which handles all these requests over the internet, making it secure and efficient. Moreover, this time there won’t be any need for human intervention as they can control everything remotely through the internet itself.
Internet of Things (IoT) is an evolving technology that is being rapidly developed into various devices to maximize its potential use. Let us take a look at the different types of IoT device sensors that are available in the market:
What IoT Means to the Business World
IoT devices connected to the internet can communicate with other devices, either wirelessly or over a wired data connection. This concept has been around for decades, but only recently have advances in technology made IoT suitable for many applications.
The future of the Internet of Things is bright. In 2018, there are only 7B IoT devices in the market. But in 2025, there will be more than 64B Internet of Things devices available globally.
The Internet of Things is quite literally transforming business.
New technologies are being developed that make the Internet of Things a reality, allowing devices to communicate with each other in real-time. This communication creates value through new opportunities for businesses and customers alike.
It all begins with data.
The amount of information available on the internet is still growing exponentially, but it’s already too much for humans to make sense of most of it. With IoT devices able to gather, analyze, and act on data in real-time, however, companies can figure out how best to serve their customers at every point during their customer lives – from initial marketing touchpoints all the way through post-sales support.
The result?
A better experience for customers and more efficient business operations for companies.
IoT devices connected to the internet can communicate with other devices, either wirelessly or over a wired data connection. This concept has been around for decades, but only recently have advances in technology made IoT suitable for many applications.
Healthcare

Fitness trackers are one of the best examples of how IoT improves healthcare. They provide immediate feedback on every step you take, recording your activity, heart rate, sleep patterns, and many other metrics on an easy-to-read screen on your wrist.
Not only do they allow users to swipe through this information at their convenience, but these very same fitness trackers are collecting all sorts of interesting analytics that helps medical professionals understand their patients’ lifestyles and health status.
Education
The Internet of Things has made advanced technology more accessible than ever before, making all sorts of interesting applications possible.
One example is how IoT helps schools provide better learning experiences for their students. Students can be equipped with tablets or other devices that allow them to guide field trips using GPS, take pictures and videos of the things they find most interesting, then upload this information into a Cloud database that teachers can access in real-time.
This provides insights into what interests each student, allowing teachers to pursue these areas with greater efficiency while also engaging each student’s curiosity.
“The IoT integrates the interconnectedness of human culture — our ‘things’ — with the interconnectedness of our digital information system — ‘the internet.’ That’s the IoT,” Ashton told ZDNet.
Retail
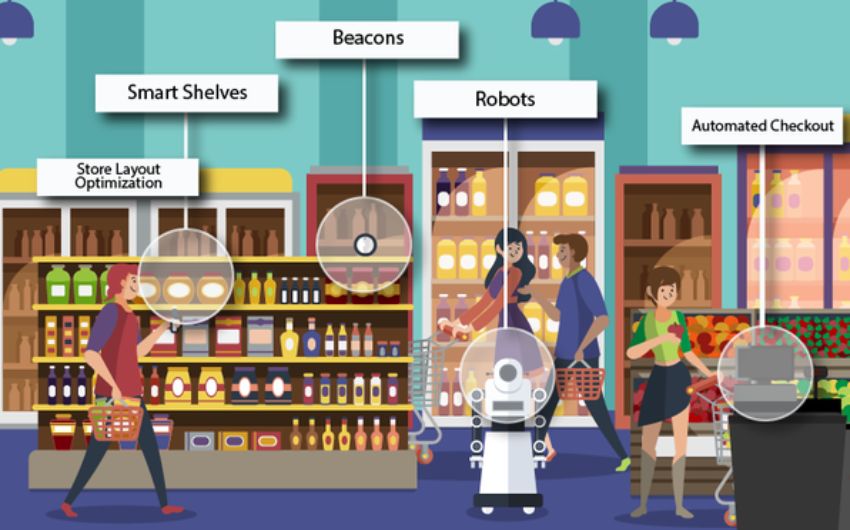
Until recently, retailers have had very limited ability to reach out to customers after the initial point of sale. With the help of IoT, retailers can now send targeted messages to customers’ smartphones, providing information about future discounts and other promotions. This type of communication has proven extremely effective for online retailers like Amazon; by providing automatic notifications about products that are frequently viewed or that might be of interest to the customer, retailers are able to improve click-through rates on their advertisements by over 300%.
Sharing Economy
The Sharing Economy is another area where IoT is making tremendous strides. With the help of IoT, people who don’t own cars – so-called “car sharers” – can find locations where they can rent vehicles when they need them. Similarly, travelers who want to avoid pricey hotel room prices during their trips can rely on home rentals powered by IoT platforms.
Travel
Everything from transportation infrastructure to accommodations for travelers is seeing dramatic changes due to IoT devices. Sensors placed on airport runways allow airport operators to measure tire wear and runway conditions in real-time, providing early warning about any possible problems that need to be addressed. Sensors placed in hotel rooms allow managers to track how often guests open windows, use the entertainment system, or flush toilets, providing valuable insight into how their properties are being used and what kind of experience their visitors are having.
Real Estate
IoT is transforming real estate in many ways. For instance, by placing sensors on fitness equipment like treadmills and bikes, realtors can provide potential buyers with data about how frequently each appliance was used over a given period of time. This information provides great insight into the habits of prior tenants; for example, someone who never fully closes the refrigerator door might constantly be losing cold air, while someone who leaves exercise equipment constantly plugged in might have an electric bill that’s out of control.
To Sum Up
IoT impacts the business world in many ways, each of which is explored in detail within this article. Everything from fitness equipment to real estate can be greatly improved through the implementation of IoT devices that collect data about how these products are being used by customers or tenants. Furthermore, the rate at which IoT adoption has grown shows no signs of slowing down, so now is a great time for companies to start looking into how they can benefit from implementing new IoT technologies.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Industrial IoT?
Industrial IoT refers to the application of IoT technologies in industrial settings, primarily as instruments and control of sensor and device interaction using Cloud technologies. See the Titan application cases PDF for an excellent case study of IIoT. Recently, the industry has incorporated the M2M method in automation and control. However, a new generation of automation tools can create new income streams by using Cloud technologies. IoT has been referred to as the fourth wave of the industrial revolution.
Why is IoT important?
Using technology, we can make smart choices and take control. IoT also helps businesses with automation. IoT gives businesses in-depth insight into the way their products work — from machine efficiency to supply chain and logistics functions. IoT helps organizations streamline processes and reduce labor costs. It also reduces waste by making the process more cost-efficient to produce and ship and also offers transparency in customer transactions.
Related Articles
-
Make Healthcare Industry Smarter with Internet of Things
The experts have always tried to enhance the process of treating human health. They put all their efforts to cure patients with new treatments and technology. These things are developed
-
A More Personal & Interactive Fitness Industry – Thanks to IoT
IoT, or the Internet of Things, has found its rightful place in nearly all walks of life. Right from smart farming to smart homes, the list is endless. One major
-
Why is eSports Evolving as a Business Model with a 40 Percent Year-on-Year Growth?
eSports (electronic sports) has attracted the attention of gaming franchises and the younger audience in the past few years and continues to do so. If industry reports are to be



