In recent years, Cloud computing has grown in popularity. Its exponential growth has accompanied society’s digital transformation in the 21st century.
It is predicted that around 83 percent of company work will be done in the cloud making 54 percent of total CIOs adopt cloud software in the next three years.
Still, professionals and businesses are frequently finding it hard to maintain their sensitive data, projects, and systems safe and running on in-house computer servers.

The solution to this problem is to consider switching your business to the Cloud. Cloud migration has been around almost as long as the internet, but it has only recently gained traction in the business world.

Even so, some business leaders are still reluctant to switch to Cloud migration for their organizations. So, we’d like to walk you through some business benefits of Cloud migration.
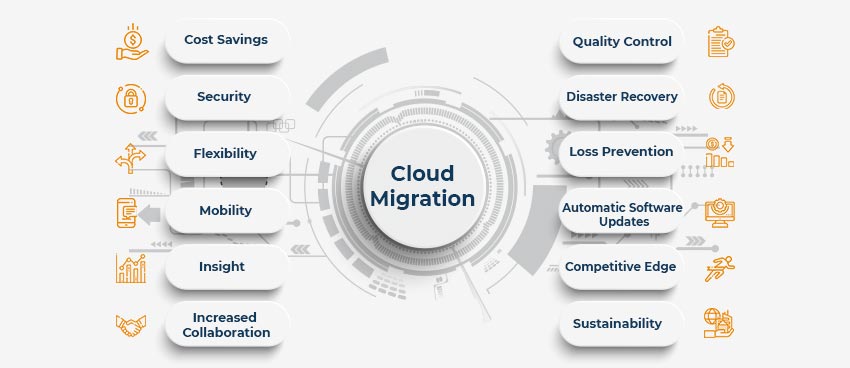
And, if you are aware of the benefits listed above and want to consider migrating your business to the Cloud, be it an application or infrastructure installation, it is more crucial to understand various Cloud services, their benefits, and the differences.
The as-a-service models that are becoming progressively important in the business world are as follows:
- IaaS
- PaaS
- SaaS
In this blog, we will explore the idea, benefits, and differences. Also, we’ll assist you in understanding the significant differences between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS so that you can gain better insights and make informed decisions for your organization.
Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS)
Pay-as-you-go Cloud-based services for storage, networking, and computing resources.
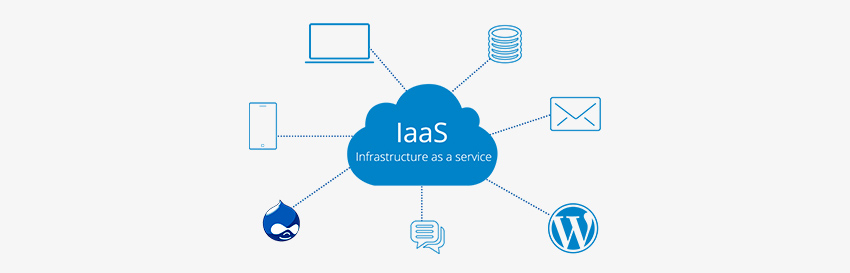
IaaS (Infrastructure as a service) is a kind of Cloud computing service that provides on-demand computing resources over the internet along with storage, networking, and virtualization on a pay-as-you-go basis.
Customers who use IaaS can manage their data infrastructure without having to handle it physically on-site. Instead, they collect data on IaaS providers and connect and utilize their resources through a single dashboard or API.
We can contrast IaaS with the operation of applications in your own data center. The primary distinction is that the IT team is not required to deploy, configure, and maintain the physical equipment that applications rely on. This helps companies to get the product and software they need while spending less on-site resources.
An IaaS model consists of a Cloud provider that hosts all the IT infrastructure components that would normally be found in an on-premises data center. This includes various hardware such as storage, servers, networking, and virtualization, which is also commonly referred to as the hypervisor layer.

Who can use IaaS?
IaaS can profit businesses of all sizes.
Small scale companies or startups that don’t wish to buy hardware or do not have the appropriate resources and enough time, skilled staff, or the ability to host a data center on-premise can use it.
Even larger businesses who wish to keep control of their apps and consume the resources they need can largely benefit from IaaS.
Successfully leading companies experiencing rapid growth appreciate the scalability of IaaS, and then they can easily swap out particular software and hardware as their requirements change.
IaaS Delivery
IaaS products provide businesses with virtual storage systems, networks, and servers. Organizations can connect and operate their data with the help of a dashboard or through a native dashboard and integrate it with the IaaS provider’s API.
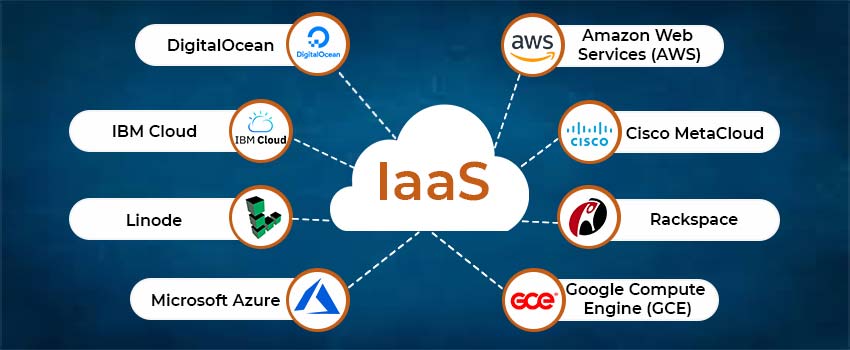
Examples of IaaS
The following are ten companies that offer IaaS platforms for a variety of business needs (some also offer PaaS or SaaS models):
IaaS Advantages
IaaS provides numerous advantages to businesses looking to migrate to the Cloud. The most compelling are highlighted below.
- Minimizes expenditures and optimizes costs
IaaS reduces the expense of setting up and managing physical data centers, as well as lowering hardware costs, allowing your IT team to focus on core business.
- Increases the level and effectiveness of IT workforces
Iaas allows you to produce and deliver IT resources to executives from any part of the world efficiently and improve business processes.
- Maintain Business continuity and reduce the cost of disaster recovery
With the proper SLA in place, IaaS can assist in lowering the cost of achieving full functionality, business continuity, and disaster recovery.

- Better security
IaaS services offer end-to-end security as compared to in-house security.
- Innovate and launch new apps for users faster
IaaS enables you to build and deliver apps to trusted users more quickly. Rather than spending weeks on it, all of the required computing infrastructures can be built in hours or days.
- Enhances stability, dependability, and sustainability
IaaS eliminates the need for regular maintenance and updating of software and hardware. It ensures that your infrastructure is dependable and suffices the terms of the service-level agreement.
IaaS Disadvantages
IaaS also has some significant drawbacks that you should be aware of before deciding on a provider.
- You must ensure that your apps and OS are functioning properly and offering the highest level of security.
- IaaS does not really have the lowest total cost of ownership (TCO); the employees will still be accountable for overseeing the associated IT.
- The responsibility of data is yours. In case data is lost or misplaced, you’ll have to find a way to recover it.
Platform as a Service (PaaS)
Hardware and software tools that create applications are available over the internet.
PaaS (platform as a service) is a Cloud design and implementation environment that provides resources to deliver simple Cloud-based apps to advanced business applications.
PaaS, just like IaaS, includes IT infrastructure components such as storage, servers, and networking along with the middlewares, business intelligence-based services, development tools, DBMS(database management systems), and many other services.
PaaS is designed to power the entire system development lifecycle from development to update.
PaaS streamlines web application development by simplifying all backend management and making developers’ jobs easier.
- Because it is based on virtualization technology, resources can be easily scaled up or down as your business changes.
- Offers a variety of services to help with app development, testing, and deployment.
- Multiple users can access the same development application.
- Web services and databases are integrated.

When to use PaaS?
PaaS is applicable in situations where more than required professional developers are working on the same development project.
It remains flexible throughout all the development phases and even provides you the scope to include other vendors remaining flexible throughout the process.
PaaS is an excellent way to design and develop custom applications swiftly and in a short period of time.
PaaS is a proven method to streamline all business processes.
PaaS services are a feasible solution for businesses that want to reduce their development cost, are first-timers in the application development business, or do not have enough resources.
PaaS Delivery
The PaaS delivery model is similar to SaaS. The only difference is that instead of delivering the application software over the internet, PaaS offers a dynamic platform for software development.
This web-based platform allows developers to focus on developing software rather than worrying about other things such as operating systems, storage, software updates, or infrastructure.
PaaS manages to design and create applications that are built using robust software components. These applications are the middlewares that are highly scalable and readily available as they adapt some Cloud characteristics.
PaaS offers a safe and secure platform for designers to develop software and apps for consumer use. Developers access PaaS toolsPaaS via the web.
PaaS Examples
The following are ten popular PaaS providers that businesses use to build customized apps for their needs.
Paas Advantages
Following are some most significant advantages of using PaaS as a Cloud computing model.
- Quick Time-to-Market – PaaS accelerates the development of software applications, from development to configuration to backend infrastructure. PaaS gives developers immediate access to an entire software development project with sample code and pre-defined components.
- Minimal Development – PaaS reduces the development time by providing rapid development and prototyping. It also provides access to various templates, tools, and code libraries, which lessen and streamline the application development.
- Reduces Development cost – It avoids the necessity to develop applications right from the beginning, making application development a cost-effective process.
- Pressure on Internal Resources – PaaS brings new opportunities for development teams and minimizes the need to hire skilled professionals, outsource experts or services. A platform also reduces the cost as the vendor takes care of managing and maintaining the application software.
- Sophisticated Pre-Built Tools – PaaS provides pre-built software components that reduce the millions of lines of coding in a program. Developers leverage development tools that are typically quite expensive to develop, test, and reiterate in-house.
- Scalable – PaaS allows code reusability. This will not only simplify app development and deployment but also raises the probability of scalability. This enables businesses to efficiently and conveniently expand and customize their products and processes.
- Develop for Multiple Platforms – PaaS vendors provide development opportunities for a variety of platforms, including desktop and mobile apps.
PaaS Disadvantages
There are some disadvantages to using a PaaS Cloud computing model that you should be aware of before signing up.
- Working with third-party vendor-controlled servers is beneficial, but it brings many safety risks.
- A few PaaS solutions aren’t enhanced for your development teams’ specific programming languages or frameworks.
- Every component of the IT system is built for the Cloud; incorporating new programs may introduce some difficulties.
- Customized Cloud applications frequently automate business processes that are incompatible with PaaS software applications, restricting the operational capacity for your customers.
Software-as-a-Service (SaaS)
Allows the software to be accessible over the Internet from third parties.

SaaS(Software as a service) is a type of on-demand software that delivers software applications to end-users over the web. This means that, unlike traditional software, software build on SaaS can be accessed from any device or location with an internet connection and a web browser, instead of just the home PC where it is installed.
There are some ways to describe SaaS :
- It can be managed from a centralized location
- Hosted on a remote server
- Accessible via internet
- Saas is responsible for the regular software and hardware updates.
According to StrategyAnalytics, by 2021, it is predicted that the corporate mobile SaaS market will reach $7.4 billion.
When to use SaaS?
Businesses most commonly use SaaS in the Cloud industry.
Reason being? It’s not difficult to access – all you need is a good internet connection and a fast-running browser, and you’re good to go.
SaaS is also suitable for small businesses or new ventures that lack the resources to develop software applications. SaaS (whether micro SaaS or enterprise-level SaaS) is the fastest and easiest solution for everything from e-commerce solutions to short-term projects if you’re not looking for highly customized software. SaaS is also an excellent choice for infrequently used applications.
SaaS delivery
With SaaS, there is no need to download and install applications on each computer of your IT staff as SaaS is a web-based delivery model. SaaS enables vendors to manage all possible technical problems, like data, middleware, servers, and storage, resulting in optimized business development and support.
SaaS examples
Software-as-a-Service existed long before businesses began to migrate to the Cloud. Internet email systems such as Outlook or Gmail are excellent examples. You’ve probably heard of some of the SaaS providers listed below.
SaaS Advantages
Businesses and their teams benefit from SaaS Service in a variety of ways.
- Accessibility:
It is accessible via any internet browser from any device 24/7.
- Management of Operations:
There is no need for installation, equipment updates, or traditional licensing management.
- Cost-Effective:
SaaS is cost-effective there are no additional hardware costs and payment methods like pay-as-you-go.
- Scalability:
Scalability is easy to achieve.
- Data Storage:
All the Data is saved to the cloud regularly.
- Analytics:
Real-time data reporting and access to intelligence tools.
- Increase Security:
SaaS providers never take a chance with security. Instead, they make sure the maximum amount is invested in security technology and expertise.

SaaS Disadvantages
Before considering a SaaS Cloud computing model, you ought to be aware of the possible disadvantages.
- Data security: large amounts of critical data are swapped with the off servers, security and compliance may be jeopardized.
- Limited customization: Speaking of features and capabilities, SaaS only enables little customization.
- Interoperability: Because of dependencies, implementing SaaS with the other current apps and services may be difficult.
- Lack of control: Users do not have complete control over functionalities, performance, downtime, or how their data is governed.
- Wasted resources: Because of the easy accessibility and scalability of SaaS, an organization’s SaaS stack contains many overlapping, underutilized, or unused apps.
- Shadow IT: Employees purchasing or signing up for new SaaS without the knowledge of IT.
What is the difference between IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS?
The growing demand for IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS is lowering the requirement for on-premise hosting.
The reason being.
These Cloud services models provide users with multiple options, adaptability, and decision to make that on-premise hosting doesn’t.
Some Cloud services models are more challenging to understand than others.
When you go down the scale in this order, the pattern of systems management expertise decreases On-premise > Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) > Platform as a Service (PaaS) > Software as a Service (SaaS).
Here is a visual analysis depicting the difference in each of the Cloud computing server modals.
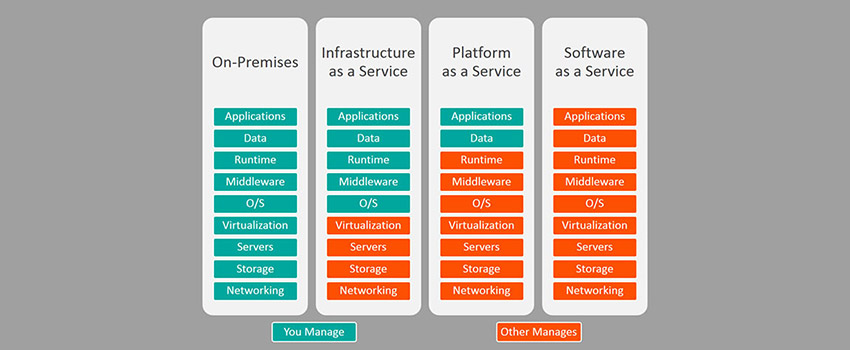
Every Cloud computing model has its advantages and disadvantages, so determining which model will suit your company’s needs the best is critical. For example, IaaS, also known as “the public Cloud,” is rapidly expanding. On the other hand, PaaS is more geared toward developers and has a much more specialized audience. The most popular service- SaaS, hires software systems via the Internet.
IaaS vs. PaaS
IaaS service platforms provide you complete control over your operating systems. It is also the backbone of a Cloud computing system environment. PaaService, on the other hand, allows users to develop applications without having to host them on-premises, giving you more flexibility but relatively more minor control.
Which service model is best for you is determined by the needs of your business. For example, if you want to build a website, an IaaS product like Aws will provide infrastructure for hosting the site and its applications. On the other hand, if you’re going to add custom features, a PaaS product such as Google App Engine not only hosts your site but also allows your developers to design and deploy it.
SaaS vs. PaaS
PaaService, as previously stated, can be used to develop new products on top of your existing network. However, SaaService goes a little bit further. The vendor ultimately manages SaaS products, which are ready for use by your IT teams.
So when should a PaaS product or SaaS product be used? For instance, if you’d like to build a payroll application specific to your HR needs, Platform-as-a-Service provides all of the tools you’ll need to succeed. When your product is completed, it can be classified as SaaS. However, if you would want exceptional simplicity, a payroll app like Quickbooks is a better alternative.
IaaS vs. SaaS
You can receive the most services from your third-party provider regarding software development management and maintenance when you use a SaaS service product. In contrast, with the IaaS service, the provider delivers and establishes core parts such as servers or storage.
Understanding which model is the best for your business is highly dependent on your goals. If you require complete control over your Cloud environment and want to avoid external management data issues that could jeopardize the functionality or security of your data, IaaS is the best choice.
Today, SaaS is the leading Cloud computing service, accounting for 39.4 percent of the Cloud computing market in 2021, followed by IaaS, which is growing at 20.9 percent, and PaaS, which is growing at a rate of 18.7 percent.
The graph below depicts the evolution of the public Cloud computing share of the market over the last three years and its prediction for 2022.
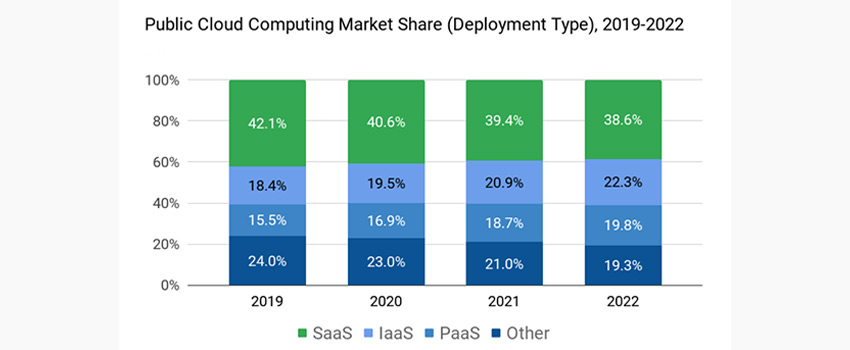
The trend indicates a slight reduction in SaaS and a small rise in IaaS and PaaS, which is expected to increase in the near future. The reason behind this could be businesses recognizing IaaS as more agile and configurable than ready-to-use SaaS solutions.
Conclusion
Most businesses find Cloud-based software servers reliable and straightforward to use, enabling them to handle their organization’s technological infrastructure, application development and access a wide range of tools virtually without purchasing and maintaining a physical server. As a result, these service providers can increase your company’s efficiency and productivity, allowing it to grow more effectively.
In addition to IaaS, PaaS, and SaaS, the following emerging Cloud computing models may also interest you: Monitoring as-a-service (MaaS), Function as-a-service (FaaS), and Communication as-a-service (CaaS) (CaaS). Each of them is aimed at businesses looking for specific services to stay competitive in a Cloud-first market.
FAQs
Infrastructure-as-a-service (IaaS), platform-as-a-service (PaaS), and software-as-a-service (SaaS) are the three primary categories of cloud computing as-a-service, and each provides a different level of control for you.
Briefly, Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) grants access to infrastructure components like virtual machines and storage space, Platform as a Service (PaaS) grants access to runtime environments, application creation, and deployment tools, and Software as a Service (SaaS) grants access to applications.
IaaS is often used as an illustration, such as
– DigitalOcean
– Linode
– Rackspace
– Web Software from Amazon (AWS)
– Cisco Metacloud
– Google Azure
– Computer Processor by Google (GCE)
PaaS instances include Quickbase, AWS Elastic Beanstalk, and Boomi. Discover what PaaS is and how it varies from SaaS and IaaS. The workplace will go virtual in 2020. Meetings shifted from boardrooms to Zooms, watercooler conversations became Slack threads, and IT infrastructure vanished into the cloud.
There are many different types of SaaS (Software as a Service) applications available today, ranging from productivity tools to industry-specific software solutions. Some popular SaaS applications include the following:
A. Google Workspace
B. Salesforce
C. Zoom
D. Shopify
E. HubSpot
Besides, Trello, Canva, Slack, DropBox etc. are other SaaS applications.
IaaS provides virtualized computing resources, enabling businesses to scale and reduce capital expenditures. PaaS offers a complete development and deployment environment, allowing faster time to market and reduced complexity. SaaS provides access to software applications over the internet, reducing costs and improving scalability and flexibility. All three cloud computing services provide various benefits that can help businesses improve their agility and focus on core activities.
The type of cloud service that is best for your business depends on your specific needs, goals, and resources. To determine which type of cloud service is best for your business, consider factors such as your IT expertise, budget, scalability requirements, data security and compliance needs, and the specific applications and services you require. It’s also a good idea to consult with a reputable cloud service provider to help you assess your needs and recommend the best solution for your business.
Yes, there are several risks and disadvantages associated with using cloud services. Some of these include, security risks, data loss, limited control over infrastructure, dependence on the Internet, vendor lock-in, and cost.
Related Articles
-
Top 15 Questions To Ask Before Hiring an Offshore PHP Development Company
In this web world, where businesses just can’t do without websites and applications, everyone knows the importance of bringing their businesses online. As a result, the number of programming languages
-
A Look into Message Brokers: Apache Kafka and RabbitMQ
With devices getting interconnected now, more than ever before, the communication infrastructure needs transformational shifts. The web of connected applications and devices can no longer operate at the backdrop of
-
How Augmented Reality App Development Plays A Crucial Role In Enhancing Apple Vision Pro?
Continual evolution is the only constant, fuelling technological advancements and how humans interact with technology. This becomes even more evident when you evaluate how far we have come in terms



