Have you ever pondered how technology is changing our industrial practices? One effective solution combines ERP (Enterprise Resource Planning) with IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things) technology.
Manufacturing ERP systems have proven excellent tools for managing organizational operations, assisting with inventory control, production planning, and finance administration activities. However, as IIoT emerges, ERPs are developing.
In this article, we will look at how IIoT is transforming ERP in the manufacturing industry and the benefits of integrating IIoT with ERP to assist firms in optimizing production operations. If you are an ambitious manufacturer seeking methods to remain ahead of the competition, read on to find out how this technology might help your operations.
What’s the Distinction Between IoT and IIoT?
Although the Internet of Things and IIoT share many technologies, such as cloud platforms, sensors, connectivity, machine-to-machine interactions, and data analytics, their applications differ.
IoT systems link devices from several industries, including agriculture, healthcare, enterprise, consumer, utilities, government, and cities. IoT technology comprises smart gadgets, fitness bands, and other applications that, in most cases, do not cause an emergency if they fail.
IIoT applications connect equipment and devices in oil and gas, utilities, and manufacturing industries. System breakdowns and downtime in IIoT installations create high-risk or life-threatening scenarios. IIoT applications focus more on increasing efficiency, health, and safety than IoT apps, which are primarily user-centric. To implement and optimize such complex systems, partnering with a reliable oil and gas software development company is essential for customized solutions that enhance operational efficiency and safety.
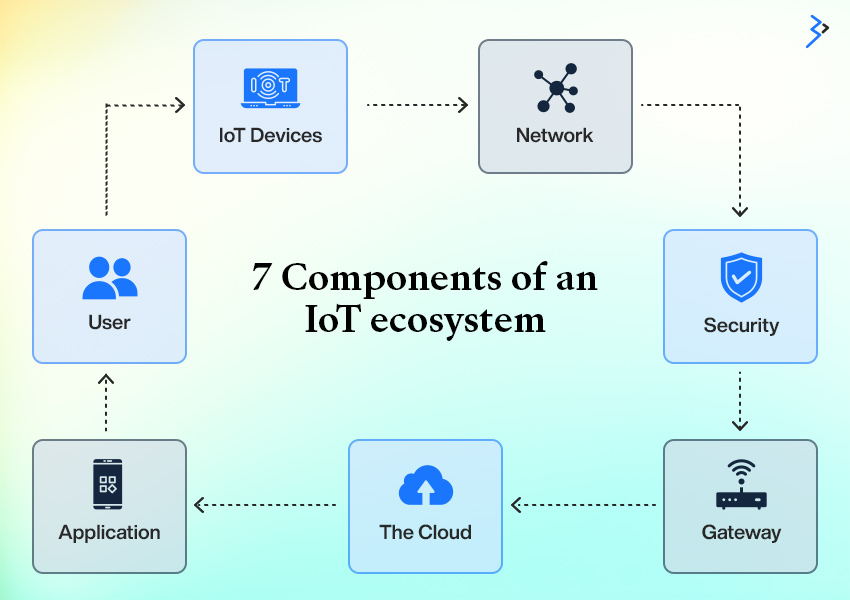
Understanding IIoT: The Core Components
Sensors and Devices: The Eyes and Ears of IIoT
Sensors play a crucial role in both IoT and IIoT systems. They detect physical changes in the environment and convert them into electrical signals. This conversion process is essential for understanding and analyzing the physical quantities that sensors measure, such as temperature, pressure, or humidity. In the industrial context, these sensors provide real-time data crucial for monitoring and optimizing operations.
Connectivity: The Backbone of IIoT
Reliable connectivity is fundamental for the success of IIoT. It’s not just about having a network; it’s about having a robust and scalable data network capable of handling the vast amounts of data generated. Studies show that 85% of global factories still lack machine connectivity, which impedes data collection and analysis.
Legacy devices, often operational for decades, are a significant barrier due to their limited connectivity options. Meanwhile, the rapid expansion of connected devices is outpacing network coverage, leading to monitoring and tracking challenges. Furthermore, uneven internet availability adds to connectivity issues. Therefore, developing a scalable IoT network is essential for large-scale industrial applications.

Data Analytics: Turning Raw Data into Actionable Insights
The value of IIoT lies in its ability to convert raw data into meaningful insights. This involves integrating tools for data acquisition, analysis, and visualization. From sensors and IoT gateways to human-machine interfaces and cloud-based analytics, these tools collectively transform data into actionable intelligence.
Effective data analytics can make the enormous volumes of data generated by IIoT systems functional, enabling better decision-making and operational improvements. Companies must invest in skilled data scientists who can harness this data to drive business decisions and optimize processes.
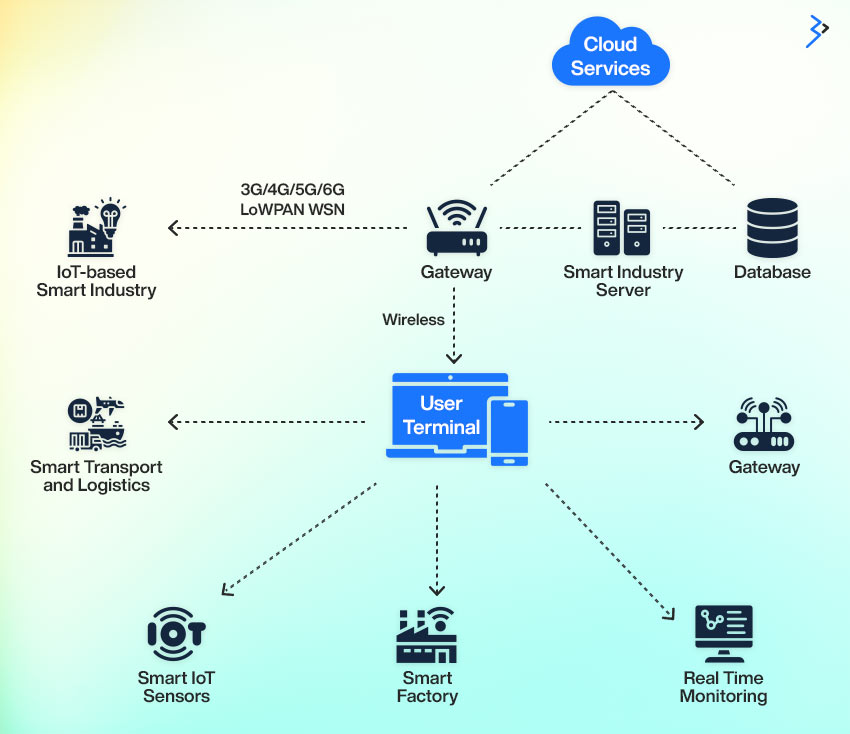
Cloud Computing: The Powerhouse of IIoT
Cloud computing provides the necessary infrastructure for storing and processing the vast amounts of data generated by IIoT systems. It enables scalability, flexibility, and remote access, which is crucial for managing industrial data.
With cloud-based solutions, businesses can efficiently handle data from various sources, perform complex analyses, and ensure that insights are accessible anywhere.
By using Puppeteer, teams can automatically capture and archive key visualizations, making it easier to monitor trends and share real-time insights across departments.
Machine Learning and Artificial Intelligence: The Brain Behind IIoT
Machine Learning (ML) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) are at the forefront of IIoT, driving sophisticated data analysis and automation. ML algorithms can analyze data patterns and predict potential issues before they arise, while AI enhances decision-making processes by providing intelligent recommendations and automating routine tasks.
Companies looking to optimize industrial operations are increasingly turning to AI solutions that offer real-time process control, predictive insights, and operational efficiency.
Together, these technologies enable more efficient and proactive management of industrial operations.
Overcoming the Hurdles: Challenges in IIoT Implementation
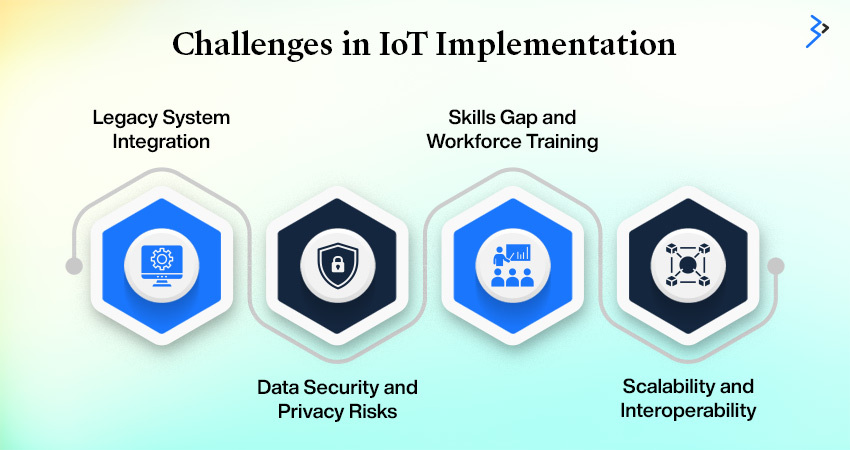
Legacy System Integration: Bridging Old and New
Many industrial facilities face the challenge of integrating IIoT technologies with legacy systems. These older systems may need to be fully compatible with modern IIoT solutions, making integration complex and expensive.
Data Security and Privacy Risks: Safeguarding Against Threats
The increased connectivity inherent in IIoT systems raises significant concerns about data security and privacy. The risk of cyberattacks and data breaches is heightened, necessitating robust security measures to protect sensitive information.
Skills Gap and Workforce Training: Filling the Knowledge Void
Implementing IIoT requires specialized data analytics, machine learning, and automation skills. Many industries face a skills gap and must invest in workforce training to leverage IIoT technologies effectively.
Scalability and Interoperability: Ensuring Seamless Growth
As IIoT deployments expand, ensuring seamless interoperability between diverse devices, systems, and platforms becomes challenging. Selecting the right IIoT platform and standards is crucial for achieving scalability and maintaining system cohesion.
Leveraging the Whole Potential of IIoT
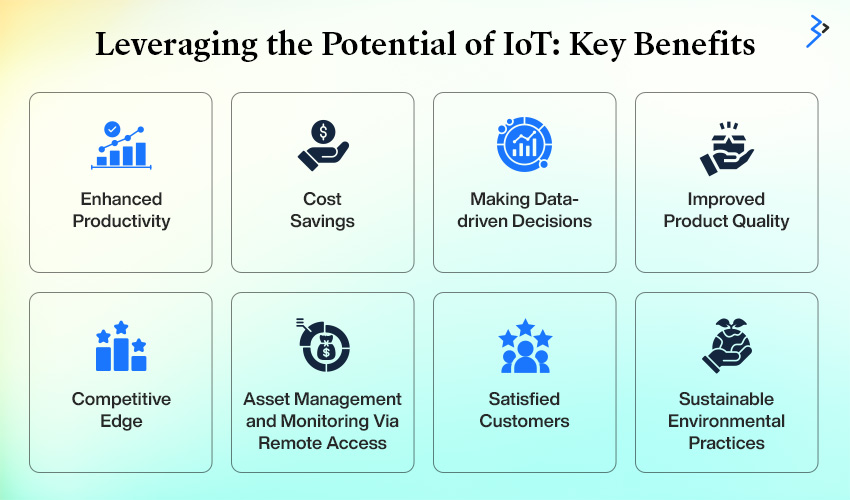
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is more than just a term; it is a disruptive force that drives efficiency, cost reduction, and innovation across sectors, with manufacturing being a major benefactor.
As technology advances, the future of IIoT becomes even more bright, with several crucial benefits linked, including:
Enhanced Productivity
One of the most significant advantages of IIoT is increased operational efficiency. Sensors that monitor equipment and processes help organizations uncover inefficiencies and bottlenecks, enabling rapid modifications and resource efficiency.
Cost Savings
IIoT reduces operating costs by forecasting maintenance requirements, avoiding costly failures, and improving resource use. IIoT enhances worker safety by monitoring hazardous conditions, issuing early alerts, and allowing for remote control in risky areas.
Making Data-driven Decisions
The amount of real-time data acquired by IIoT allows for data-driven decision-making, resulting in better strategic planning and outcomes.
Improved Product Quality
IIoT enables quality control through continuous monitoring and data analysis. Manufacturers can detect errors or variations in real time and modify them to ensure excellent product quality. This results in fewer faults, cheaper warranty costs, reduced waste, and more customer satisfaction.
Competitive Edge
Maintaining competitiveness is critical in today’s fast-paced corporate climate. The IIoT gives businesses a competitive advantage by allowing them to respond swiftly to changing market needs. Data-driven insights guide strategic choices, helping firms to innovate and adapt to market changes more effectively.
Asset Management and Monitoring Via Remote Access
The IIoT enables organizations to monitor and control their assets and operations remotely. This is especially useful for businesses with assets spread over many customer sites since it facilitates centralized control and real-time visibility across different locations.
Satisfied Customers
IIoT-driven advancements in production processes frequently result in higher-quality goods, which increases customer satisfaction and reduces warranty liability.
Sustainable Environmental Practices
IIoT may help with sustainability initiatives by improving resource utilization. Companies may minimize energy usage, waste, and environmental impact by optimizing operations and allocating resources based on data.
Real-World Impact: Case Studies in IIoT
Revolutionizing Manufacturing with IIoT
The Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) is reshaping the manufacturing industry, driving it toward smarter, more efficient operations. By embedding sensors and connectivity into production processes, IIoT transforms traditional factories into smart factories where real-time data enhances every aspect of manufacturing.
For example, automotive manufacturers are in charge of IIoT integration. They employ connected devices to monitor every stage of vehicle assembly. This comprehensive tracking ensures that each phase meets strict quality and efficiency standards. Sensors embedded in machinery can detect anomalies early, prompting maintenance before potential breakdowns occur. This proactive maintenance approach minimizes downtime and ensures the assembly line operates smoothly without costly interruptions.
Smart factories leverage IIoT to gather and analyze vast amounts of data from various production stages. This data-driven approach allows manufacturers to pinpoint inefficiencies and streamline workflows. Continuous monitoring and adjustment of processes result in enhanced productivity and reduced costs. The real-time data collected through IIoT supports rigorous quality control measures, consistently meeting high standards.
Ultimately, IIoT converts conventional manufacturing into an automated, data-centric operation. This shift not only boosts productivity and reduces operational expenses but also guarantees the production of high-quality products. IIoT is a transformative force in global manufacturing by driving innovation and competitiveness.
IIoT in Smart Cities: Traffic and Utilities Management
IIoT is significantly impacting the development of smart cities, particularly in traffic and utility management. These applications enhance urban living by improving efficiency and sustainability.
IIoT systems utilize interconnected sensors and cameras to monitor and optimize traffic flow in traffic management. A notable example is Barcelona, where IIoT-enabled traffic management has reduced commute times and reduced emissions. The real-time data from these systems helps to adjust traffic signals dynamically, easing congestion and making travel more efficient.
Utility management also benefits significantly from IIoT. Real-time monitoring of water and energy usage enables cities to detect leaks and inefficiencies swiftly. For instance, smart meters provide detailed data on resource consumption, leading to more accurate billing and better resource management. This immediate feedback allows for optimal distribution and usage of resources, ensuring that they are allocated effectively and sustainably.
These IIoT applications enhance operational efficiency and contribute to environmental sustainability. By reducing waste and optimizing resource use, smart cities become more livable and resource-efficient. The collected data helps inform future urban planning and development, ensuring cities adapt and grow sustainably.
Advanced Healthcare Monitoring Systems Powered by IIoT
In the healthcare sector, IIoT is revolutionizing patient monitoring and care. Connected devices and wearable technology enhance how health data is tracked and managed, leading to more personalized and effective care.
For instance, diabetic patients can now access IoT-enabled glucose monitors that continuously track their glucose levels. These devices transmit real-time data to healthcare providers, alerting them and the patient if abnormalities occur. This immediate feedback allows for timely adjustments to treatment plans, improving the management of diabetes and overall patient health.
Hospitals are also harnessing IIoT to monitor patient health continuously. Imagine a hospital setting where patients wear sensors that measure vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, and oxygen levels. This data is sent to a central system where healthcare professionals can oversee multiple patients simultaneously. If a patient’s condition deteriorates, the system generates alerts, ensuring prompt medical intervention.
This real-time monitoring enhances patient outcomes by enabling proactive care and personalized treatment. It improves care quality by providing accurate, up-to-date information for better medical decision-making. Moreover, it reduces healthcare costs by decreasing the need for frequent hospital visits and extended stays, making the healthcare system more efficient and patient-focused.
Wrap Up
The future of IIoT seems promising, with considerable developments on the way. As enterprises prepare for a globally linked IIoT future, they must prioritize integrating cutting-edge technology such as AI, machine learning, and edge computing. It will be critical to implement robust cybersecurity safeguards and adopt sustainable practices. Industries that keep ahead of these trends and engage in IIoT may achieve novel levels of effectiveness and sustainability, cementing their position in the future of industrial operations.
FAQs
What is IIoT?
IIoT, or Industrial Internet of Things, refers to using connected devices, sensors, and data analytics within industrial environments to optimize operations, improve efficiency, and enhance decision-making.
What challenges might I face when implementing IIoT?
Challenges include integrating with legacy systems, ensuring data security and privacy, addressing skill gaps and training needs, and achieving scalability and interoperability.
How does Brainvire assess my current infrastructure for IIoT implementation?
Brainvire evaluates your existing infrastructure by comprehensively assessing your current systems, devices, and network capabilities to determine compatibility and readiness for IIoT integration.
What types of IIoT solutions can Brainvire help me choose?
Brainvire can assist in selecting IIoT solutions tailored to your industry needs, including sensors, data analytics platforms, connectivity options, and cloud computing solutions.
How can Brainvire ensure the security of my IIoT infrastructure?
Brainvire ensures IIoT security by implementing robust cybersecurity measures, including encryption, access controls, and continuous monitoring to protect against potential threats and data breaches.
Will my workforce need training to adapt to IIoT technologies?
Yes, implementing IIoT often requires specialized skills in data analytics, machine learning, and automation. Brainvire offers training programs to equip your workforce with the skills to leverage IIoT technologies effectively.
How can I get started with IIoT implementation through Brainvire?
To get started, contact Brainvire for a consultation. We will assess your needs, provide recommendations, and guide you through the implementation process to integrate IIoT solutions into your operations.
Related Articles
-
IoT in Retail POS: Past, Present, and Future
You enter a store looking for a new pair of jeans. Your smartphone pings as you go in, and you open it to see a map indicating where the brand
-
Make Healthcare Industry Smarter with Internet of Things
The experts have always tried to enhance the process of treating human health. They put all their efforts to cure patients with new treatments and technology. These things are developed
-
IoT Applications In Banking: The New B2B And B2C Communications Method
Talking About IoT Applications In Banking: The New B2B And B2C Communications Method, The use of IoT in the Banking sector has not picked up the pace yet but it’s




