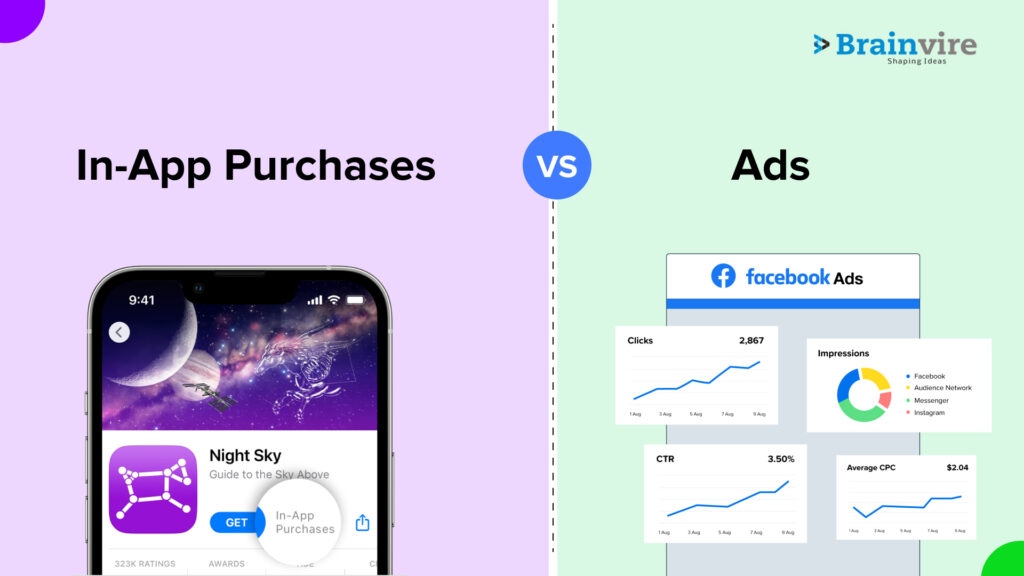
In-app purchases vs. ads are two well-liked techniques for generating revenue from mobile apps. Each offers benefits and disadvantages, so making the proper decision might be essential to the success of your mobile app. Hiring mobile app developers familiar with both models is a wise move.
In this discussion, we will delve into the advantages of in-app purchases and examine the revenue potential when comparing them to ads. Additionally, we will explore the process of enabling and allowing in-app purchases, while also considering the user experience and engagement associated with both in-app purchases and ads. We will analyse the conversion rate and thoroughly evaluate the pros and cons of in-app purchases versus ads. Furthermore, we will assess the revenue potential of ads as well as the user experience and engagement they provide. To ensure your app’s success in this regard, it is advisable to hire mobile app developers who possess expertise in these areas.
In-App Purchases
The term “In-App Purchases” (IAP) refers to the action of purchasing items from within a mobile app. It lets players pay real money to access premium features and content like ad-free play, in-game currency, higher difficulty levels, and exclusive goods. Mobile app stores, such as the App Store and Google Play, provide the infrastructure for in-app purchases (IAPs).
How Do In-App Purchases Work?

Developers must set up their app to use the app store’s platform’s In-App Purchase API to support In-App Buying. The API facilitates the development and administration of user-purchasable goods and services. Each IAP item’s price, description, other details, and the conditions for accessing or using them are all within their control.
When users attempt to make a purchase, the app presents a payment interface, typically operated by the payment gateway of the app store, such as Apple Pay or Google Pay. After the transaction, the app store platform deducts a fee (often between 15 and 30 percent) before depositing the remainder in the developer’s account.
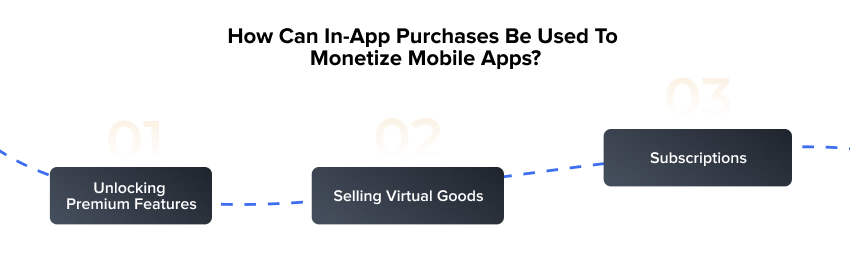
How Can In-App Purchases Be Used To Monetize Mobile Apps?
Games, social networks, and entertainment applications have benefited from the rise of in-app purchases. In-app purchases (IAPs) provide a more natural and interesting way for users to support the app and gain access to premium content than adverts, which may be annoying or distracting.
The app developer can leverage in-app purchasing for a variety of purposes, including but not limited to the following:
Unlocking Premium Features: Payment enables access to premium features not available in the free edition, such as expanded capabilities, individualized settings, or unique media.
Selling Virtual Goods: Players can buy digital products that improve their experience, such as in-game currency, downloadable content, or social features.
Subscriptions: Users can pay on a recurrent basis to access a variety of content types, from news and media to music and video.
Examples of Popular Apps That Use In-App Purchases
Some of the top downloaded apps that rely heavily on In-App Purchases to make money are:
Candy Crush: Candy Crush is a puzzle game in which players can purchase extra lives and other advantages to move through the game more quickly.
Spotify: Spotify is a music streaming service that allows for ad-free listening and offline playback with a paid membership.
Tinder: Tinder is a dating app where users can pay for access to premium features like unlimited swiping and seeing who has liked their profile.
Netflix: Netflix, a widely popular streaming service, offers a subscription-based model with in-app purchases to unlock access to its vast library of movies and TV shows, providing users with uninterrupted entertainment on various devices.
You may like to read: Creating The Next Netflix! Tips & Tricks For OTT App Development
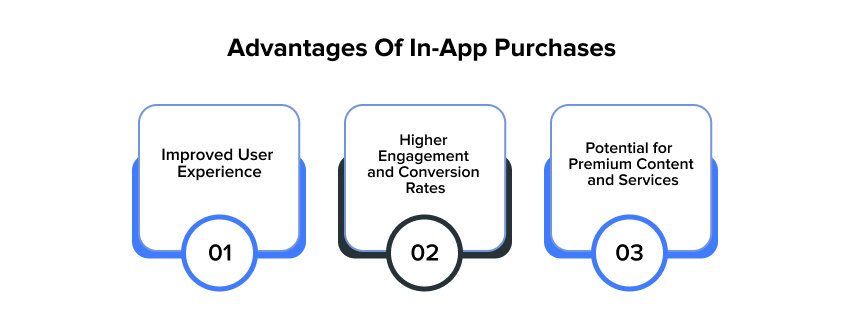
Advantages Of In-App Purchases
In-app purchases (IAPs) have gained popularity for mobile app developers as a monetization strategy. IAP adoption has several benefits, including the possibility of higher income and greater user engagement. The following are some major benefits of utilizing IAPs as a monetization strategy:
Increased Revenue For App Developers
IAPs can raise revenue for app creators, one of their main benefits. In-app purchases offer a more stable revenue stream compared to advertising, which often relies on factors like user engagement and ad placement, making it less predictable.
IAPs can also aid in boosting a user’s lifetime value because those who make in-app purchases are more likely to stick around and make other purchases.
Improved User Experience
IAPs can also provide a better user experience than advertising because they don’t obstruct the user’s app use with ads. Instead, customers can spend money on more features or content within the app, preserving their uninterrupted app use.
IAPs can also assist in customizing the user experience because they allow users to select the features and content they wish to pay for depending on their unique requirements and preferences.
Higher Engagement And Conversion Rates
IAPs can increase engagement and conversion rates compared to advertising. This is because customers who interact with the app and make purchases within it are more likely to show interest in new features or content.

Moreover, IAPs can be incorporated into the user experience more naturally, lowering the chance that users will uninstall the program because of annoying or pointless advertisements.
Potential For Premium Content and Services
IAPs allow app developers to provide premium services and content that are otherwise impossible with just advertising. Features like exclusive access to fresh content, cutting-edge functionality, or individualized coaching or support are examples of this.
Examples of Successful Apps That Use In-App Purchases
IAPs are a popular form of primary monetization for several popular apps. Here are a few examples that weren’t previously mentioned:
Headspace: Popular meditation software Headspace has a subscription-based business model, allowing users to buy extra features and content inside the app. The app’s success is partly attributed to its emphasis on giving users personalized experiences and high-quality content.
Duolingo: Duolingo is a language learning app that uses a freemium business model. Users can pay extra for extra features and content to improve their learning process. The app’s gamification aspects, which keep users interested and motivated, have contributed to its popularity.
Shazam: Shazam is a music recognition app that lets users buy tracks they’ve discovered right inside the app. The app’s popularity is partly attributable to how effortlessly it integrates with other music apps, enabling users to listen to and buy their songs quickly.
Disadvantages Of In-App Purchases
While In-App Purchases (IAPs) have a lot of benefits as a method of app monetization, there may also be drawbacks that developers need to be aware of. The following are some of the major drawbacks of IAPs:
Negative User Experience
IAPs’ biggest potential drawback is that they may harm the user experience. Customers could feel pressured to spend money to access specific features or material, which is unpleasant and detracts from how fun using the app is.
IAPs can also be obtrusive and ruin the user experience if not implemented properly. Users may find it bothersome and be less likely to utilize the app in the future if pop-up notifications or adverts are used for advertising IAPs.
Inconsistent Revenue Stream
IAPs provide a more consistent revenue stream than advertising but are still prone to changes based on user behavior and market trends. IAP revenue may be less than anticipated if customers are uninterested in paying for extra features or content within the app.
Moreover, IAPs are not suited for all app kinds and might work better for some genres or audiences than others.
Potential For User Backlash
Users may grow irate and leave negative reviews or quit using the app altogether if IAPs are perceived as too pricey or obtrusive. This can be especially harmful to smaller or more recent apps that depend on favorable user feedback and word-of-mouth to grow their user bases.
Difficulty In Implementing Effectively
Finally, app developers may need help to incorporate IAPs successfully. It can be challenging to determine which features or types of content to offer as IAPs, how much to charge for them, and how to advertise them without impairing the user experience.
Examples of Apps that Have Failed to Implement In-App Purchases Effectively

IAPs need to be better implemented in numerous apps, which has resulted in poor user experiences and lesser income. Here are a few illustrations:
EA’s Dungeon Keeper: The mobile version of the well-known game Dungeon Keeper received harsh criticism for using IAPs aggressively, which made it challenging for players to advance without buying things. This resulted in significant criticism and unfavourable ratings, reducing the app’s income.
Angry Birds 2: While the first game’s one-time purchase strategy contributed to its success, the sequel added in-app purchases (IAPs), which many consumers considered intrusive and annoying. This resulted in unfavourable comments and a drop in user interest.
Draw Something 2: Draw Something 2 has come under fire for using intrusive and annoying in-app purchases, such as advertising that pop up during gameplay. Over time, this resulted in unfavourable reviews and a drop in popularity.
Ads
Advertising is a well-liked monetization strategy for mobile apps, and many app developers depend on them to make money. Here is a description of how adverts operate, how they can be used to pay for mobile apps, and some illustrations of well-known apps that rely heavily on advertising for revenue.
Definition Of Ads And How They Work
Advertising is a type of commercial communication that uses target audiences to promote goods, services, or ideas. Mobile apps frequently contain banner ads, interstitial adverts, or video commercials presented within the app.
There are numerous ways for app developers to profit from advertisements. For instance, they might be paid according to the number of clicks or ad impressions they get or a cut of the money the ads make.
How Ads Can Be Used to Monetize Mobile Apps?

For several reasons, ads can be a useful revenue strategy for mobile apps. They are relatively simple to install and don’t cost app developers, much upfront.
A smart alternative for apps with a large user base but less opportunity for in-app purchases is advertising. For example, apps that provide entertainment or information may not be well-suited for in-app purchases, but they can still generate revenue through advertisements.
Examples of Popular Apps That Use Ads as Their Primary Monetization Model

Many well-known apps rely on advertisements as their main source of income. Here are a few illustrations:
Shazam: When users use the app to identify a song, Shazam shows them advertisements. Ads for goods or services related to music are common.
Instagram: Instagram is a social networking application that makes money via advertising. Users’ feeds and stories showcase advertisements customized based on their interests and demographics.
YouTube: YouTube is a video-sharing program with a significant ad-based revenue stream. Advertisements are displayed during and before videos, and content producers can earn a share of the advertising revenue.
Advantages of Ads
While there are many benefits to using In-App Purchases (IAPs) to monetize mobile apps, several benefits are specific to using ads. Following are some of the key benefits of advertisements:
Increased Revenue Potential
For app creators, ads can be a significant source of income, especially if the app’s user base is sizable and active. Ad networks often compensate app developers for each impression or click brought about by their advertisements, which can result in a sizable sum of money over time.
Minimal Impact on User Experience
Despite being one of their key benefits, advertisers can employ advertising in a manner that adversely affects the user experience. For example, they can place ads in non-intrusive locations such as the edges of the screen or between sections. This ensures that users can use the app’s core functionality without feeling overwhelmed by a barrage of advertisements.
Lower Barriers To Entry
By reducing barriers to entry and not requiring any upfront expenses, advertising can simplify the process for consumers to download and use an app for the first time. As a result, app developers can reach a wider audience than if they only used IAPs.
Examples Of Successful Apps That Have Used Ads as Their Primary Monetization Model
Many successful and popular apps have made their main source of revenue from ads. These are a few instances:
Instagram: Instagram is a social networking application that enables users to communicate with their followers by sharing images and videos. The software makes money by showing advertising between postings in a user’s news feed. With a single swipe, users have the ability to dismiss the advertisements, and usually, the ads are tailored to their interests.
Read this also: Create Your Own Social Media App: A Step by Step Guide for Business Owners
TikTok: In recent years, the video-sharing software TikTok has experienced tremendous growth in popularity. App users see advertisements between videos, which helps the program’s developers make money.
Spotify: Spotify is a music streaming service that makes money by showing advertisements between songs. Although the program also has a premium membership option with fewer advertisements and more features, most users opt for the free version with ads.
Disadvantages of Ads
Using ads as a monetization technique might generate a sizable income for app creators, but there are also some possible drawbacks. Following are some of the biggest drawbacks of advertisements:
Negative Impact On User Experience
Advertisements, especially when used intrusively or disruptively, can have a negative impact on the user experience. App developers may find it more challenging to monetize their apps through advertisements because some users may not be interested in clicking on the presented advertising.
The app’s overall revenue potential may need to improve due to decreased user engagement and retention.
Lower Conversion Rates
Advertising may convert at a lower rate than IAPs, which is another possible drawback. Ads depend on users clicking on the ad and engaging with the advertiser’s content, but IAPs demand consumers to pay a one-time purchase to unlock extra features or content.
Due to the possibility that some users may not be interested in clicking on the presented advertising, it may become more challenging for app developers to monetize their apps through advertisements.
Ad-Blocking Software
The fact that users can use ad blockers to prevent adverts from showing in the app is another possible problem with ads. As ad blockers prevent users from seeing advertisements, this can dramatically lower the revenue potential for app developers.
Examples Of Apps that Have Failed To Implement Ads Effectively
There are numerous instances of apps that failed to install ads in a way that improved user experience and eventually harmed their ability to generate income. These are a few instances:
Angry Birds 2:
Angry Birds 2 is a popular mobile game that generates cash through Advertising. However, many users have claimed that the adverts are intrusive and too frequent, which makes for a bad user experience.
Snapchat:
Snapchat is a social media application that makes money from advertisements. However, many users have criticized the adverts for being overly invasive and occupying too much screen real estate, which makes it challenging to utilize the app.
You may find this interesting: What Is Social Media Management And How It Impacts Businesses?
WeatherBug:
WeatherBug is a well-known weather app that makes money via advertisements. Yet, the app has come under fire for showing users unrelated adverts based on location and hobbies, which could be a better user experience.
Which Monetization Model Is Right for Your Mobile App?
There are several things to consider when choosing a monetization strategy for your mobile app. These variables include the kind of app, target market, user behavior, and financial objectives.
Every monetization strategy has benefits and drawbacks, so it’s critical to pick one that supports your app’s and your users’ objectives.
Type Of App
The first thing to think about is the kind of app you have. While in-app purchases are better suited for certain applications, advertisements are better suited for others.
For instance, in-app payments benefit a gaming app by allowing users to add new levels or power-ups to their gameplay. On the other hand, readers are more inclined to engage with the articles in a news app, making it better suited for advertisements rather than additional feature purchases.
Target Audience
Your target audience is the second thing to consider. Ads may be better than in-app purchases if your software caters to younger customers with little discretionary income. Conversely, in-app purchases might be more successful if your software targets a more affluent market.
User Behaviour
Taking user behavior into account is also necessary. In-app purchases may be more successful if your app’s active customers are willing to spend a lot of time there. Ads would be better if your app had lower engagement rates because users might be less likely to make in-app purchases.
Revenue Objectives
Lastly, when selecting a monetization plan, one should consider revenue objectives. In-app purchases could be more efficient if your software wants to produce a large income immediately. But adverts can be better if your software has a longer-term revenue plan.
Selecting the ideal monetization approach is essential for app developers to make money and keep users happy. While choosing a monetization model, app developers should consider the app’s nature, target market, and user behavior.
App developers can select a model that fits their app’s nature, caters to users’ demands, and earns income if they understand these elements well.
Making The Decision
Choosing between In-App Purchases and Advertising is challenging in monetizing a mobile app. The best option ultimately depends on the objectives of the app and its intended user base. Both monetization models have benefits and drawbacks.
Step 1: Define Your App’s Goals And Target Audience
Identifying your app’s objectives and target market is the first step in choosing between in-app purchases and advertisements. What is the aim of your app, and who is the intended user? For instance, in-app purchases may be a better option if your app is a game that caters to younger audiences, as these users need more financial resources to make consecutive payments.
Advertising is a better option if your app is a productivity tool for professionals, as users are more accustomed to seeing and interacting with adverts in this setting.
Step 2: Understand The Benefits Of In-App Purchases
It’s crucial to comprehend the advantages of In-App Purchases before choosing. As customers pay for extra features or content, in-app purchases can offer a more stable revenue stream. They can also use them to incentivize participation and promote long-term user retention.
Step 3: Recognize The Advantages Of Advertising
It is equally crucial to comprehend the advantages of advertisements. Advertising is more accessible to a wider audience because they can earn money without requesting payment in advance from customers.
Additionally, they can advertise goods and services that may interest users and target particular populations.
Step 4: Take Each Model’s Prospective Revenue Into Account
Both in-app purchases and advertisements can generate revenue. Still, the revenue potential of each model may differ depending on the target market and app user behaviour. To decide which model could be more profitable for your app, consider user engagement, conversion rates, and average revenue per user.
Step 5: Test And Experiment With Different Models
Testing and experimenting with various models is the best approach to determine which monetization strategy is best for your app. To ascertain which model produces the most money while delivering a great user experience, do A/B testing and gather user behavior, engagement, and revenue data.
When choosing between in-app purchases and advertisements, it is essential to carefully consider the app’s objectives, target market, and revenue potential. App developers may choose wisely, earn revenue, and deliver a great user experience by knowing the advantages and disadvantages of each model and testing and experimenting with various techniques.
In A Nutshell
Your mobile app’s target audience, content, and purpose will all influence your decision about the monetization model, as will whether it uses in-app purchases or advertisements. Both business models have advantages and disadvantages. For example, while ads can offer a more consistent income stream with a wider audience, in-app purchases are a more direct way to make money.
Furthermore, user experience and engagement are essential when choosing between the two. To find the most appropriate model for your mobile app, it is critical to test various options, evaluate their efficacy, and carefully examine income indicators.
Finally, whether you decide to use In-App Purchases or advertisements, working with mobile app developers that have experience with monetization tactics will help you implement your model successfully and increase your app’s revenue potential.
FAQs
Users can make in-app purchases (IAPs) to buy digital items or services within an app. While advertisements present advertising information to consumers for monetary compensation.
The profitability of each model is influenced by variables like user base size, app functionality, and chosen monetization method. In general, apps with niche audiences and high-value digital goods or services tend to be more profitable. Through in-app purchases (IAPs), while apps with large user bases and low engagement rates find ads more lucrative.
In-app purchases are suitable for valuable digital products or services that users are willing to pay for. Ads work well for apps with a large user base and high engagement that marketers want to target.
Yes, apps can utilize both In-App Purchases and advertisements. Yet, ensuring the monetization plan doesn’t negatively affect the user experience is crucial.
The implementation of in-app purchases or advertisements may vary depending on the platform used to build the app. For example, while ads require connectivity to an ad network or mediation platform. IOS app IAPs require integration with the App Store payment system.
Ads are a passive monetization method with the main advantage of not requiring users to spend money on the app. Advertisements can also offer a reliable revenue stream for apps with a huge user base and high engagement rate.
IAPs work best with apps that offer useful digital goods or services. Such as productivity apps with premium features or mobile games with virtual objects.
Ads work best in apps with a wide user base and high interaction rate, like social networking or news apps.
Maximizing in-app purchase revenue requires offering profitable digital products or services, streamlining the purchasing process. And consistently releasing fresh content to maintain user interest.
By maximizing ad impressions, targeting relevant audiences, and using a high-quality ad network. Mediation platform, ad revenue can be optimized.
Related Articles
-
Top UI /UX Mobile Trends for 2021
Staying on top of the UI/UX mobile trends is important to keep your mobile app ahead in the competition, Always! and with UI/UX design, you can make your mobile app
-
Business Benefits of Cross Platform Mobile Application Development
Mobile application development is a field that is getting diverse and the user base for mobile apps is ever expanding. The devices that these apps will be used on are
-
How Can iPhone Apps Loaded with iBeacons Help Businesses?
Businesses, these days, are adopting cut-edge mobile technologies in order to remain ahead of the tough competition. They are looking for better ways to improve their processes, eliminate unnecessary costs