Thanks to the plethora of new-age technologies that support the modern online and app business, developers often need help figuring out which one to use in their next project. Similarly, the relative merits of React and React Native are hot topics among app developers. The nuances of the React vs. React Native argument are complicated for even the most committed engineers to understand.
Two Facebook-native technologies, React and React Native, offer unparalleled capabilities to online and mobile app developers. Top bespoke web app development firms have used these two robust technologies to create widely used websites and mobile apps.
The two are distinct from a functional standpoint and in terms of primary objectives.
One way to put it is that React is more focused on the web, while React Native is more concerned with the mobile framework. However, when comparing React with React Native, there is much to say about the capabilities and functions provided by both tech stacks.
Is the decision between React and React Native also something you’re considering?
To make an informed decision, you must delve deep into their benefits, drawbacks, practicality, and industrial use cases. Together, these two technologies underpin some very popular mobile and web apps. Each serves a unique purpose and represents a different part of the React ecosystem. So, let’s get down to brass tacks and figure out when React Native is better than React.

2. Core Differences Between React and React Native
React and React Native are sibling technologies with shared roots but distinct functionalities. While they share some similarities, they are tailored for different purposes, making it crucial to understand their differences. Below is a detailed breakdown of React and React Native, categorized by key aspects.
Installation Process
| Aspect | React | React Native |
| Setup Simplicity | Add the React library to an HTML page using a <script> tag.Example: <script src=”https://unpkg.com/react@16/umd/react.development.js” crossorigin></script> <script src=”https://unpkg.com/react-dom@16/umd/react-dom.development.js” crossorigin></script> | It requires installing tools like Node.js, React Native CLI, and development environments (e.g., Android Studio or Xcode). |
| Code Bundling | It works seamlessly with tools like Webpack, Rollup, or Browserify to bundle larger projects. | Supports creating projects using the React Native CLI and running them on mobile emulators or devices. |
| Frameworks | Frameworks like Next.js or Gatsby streamline project setup. | Migrating from React.js to React Native is simple for developers familiar with React. |
Efficiency
| Aspect | React | React Native |
| User Interface Development | Ideal for creating dynamic and intuitive user interfaces | Utilizes reusable native components compiled directly into native code for optimal performance |
| Rendering | Executes on the client side while rendering on the server side for flexibility | Enables integration with native codes like Java or Swift for a customized appearance and functionality |
| Versatility | Supports basic (buttons) and advanced (dropdowns) abstractions for UI components | It offers a native-like look, feel, and speed, distinguishing it from other mobile development frameworks |
Technology Base
| Aspect | React | React Native |
| Core Language | Primarily uses JavaScript | Combines JavaScript with Java, Objective-C, and C++ for mobile development |
| Learning Curve | It is easy for developers familiar with JavaScript | Requires familiarity with multiple programming languages for native app development |
| Focus | Focuses on building UIs for web applications | Leverages React concepts to create mobile UIs for iOS and Android apps. |
Feasibility
| Aspect | React | React Native |
| Integration with CSS | Integrates CSS seamlessly, solving common challenges like scope isolation | Allows adding native components to existing hybrid apps developed with frameworks like Ionic and Cordova |
| Code Modification | Minimal code changes are required for updates | Plugin integration simplifies reusing hybrid app code |
Compatibility
| Aspect | React | React Native |
| Platform | Designed for SEO-friendly web applications | Exclusively developed for mobile UIs, offering responsive interfaces and faster loading times |
| UI Design | Renders server-side to enhance SEO and accessibility | Renders components natively, optimized for mobile platforms |
Syntax
| Aspect | React | React Native |
| Markup | Uses JSX to write markup directly within JavaScript. | Uses unique tags like <View>, <Text>, and <Image> for rendering native components. |
| Compilation | Translates JSX into regular JavaScript functions and objects. | Translates React Native tags into native mobile languages. |
Components
| Aspect | React | React Native |
| Component Types | It offers function and class components for building apps | Uses Native UI components and Native Modules for functionality |
| Customization | Allows creating custom components using JavaScript | Enables building custom native components with platform-specific tools |
| Aspect | React | React Native |
| Library | Uses react-router for navigation and history tracking | It uses Navigator or React Native Navigation to manage screen transitions on mobile devices |
Storage
| Aspect | React | React Native |
| Default Storage | Local storage with no expiration | AsyncStorage is backed by native code for small and large data values |
| Advanced Storage | Integrates seamlessly with state management libraries | Supports additional libraries like Realm, SQLite, and redux-persist for complex storage needs |
Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
| Aspect | React | React Native |
| SEO Focus | Includes tools and libraries to optimize apps for search engines | It is not designed for SEO; it focuses entirely on building mobile-native UIs |
React is ideal for web development, focusing on dynamic UIs and SEO. On the other hand, React Native excels at creating efficient, responsive mobile applications with native-like performance. Choosing between them depends on your project requirements and target platforms.
3. Similarities Between React and React Native
We get it: With so many similar alternatives, like React and React Native, picking the correct technology may be a real challenge. Although these two technologies may seem different, they have few shared grounds too.
Read More: Ionic React vs React Native: A Detailed Comparison
Basic Principles of React
There is a common genetic foundation between React and React Native. They are similar in that they both use a component-based design, simplifying the process of decomposing your program into its parts. A head start is yours just by your familiarity with JavaScript and JSX.
The Virtual DOM, an innovative idea that guarantees your program operates smoothly and speeds up rendering, should also be mentioned. These fundamentals will serve you well whether you’re building an interactive web interface or an app for your mobile device.
Reusability of Code
Who doesn’t like the idea of saving time? React and React Native make it easy to reuse components and functionality from one project to another. Envision creating a feature for your website and then reusing some of the logic for your mobile app—it’s like getting two things done at once. This cross-utilization may significantly increase your productivity, albeit you will still have to modify certain aspects for each platform.
Appreciating these shared characteristics does more than teach you about two technologies; it paves the way for developing universally appealing user experiences. However, these commonalities can be your undoing if you must prepare to unite mobile and online development.
Read More: React Native vs Flutter: Which is a better Framework for Developers
4. Advantages of React: Why It Works for Your Web Projects

React’s primary benefits are making your development process more manageable and your application more effective.
1. SEO-friendly
In a digital era dominated by search engine exposure, React has an advantage for your web application: its ability to generate HTML during server-side rendering guarantees that search engines can properly index your content. This implies improved exposure, higher ranks, and more visitors to your website.
2. Mature Ecosystem
React is not simply a library; it is an ecosystem. React’s extensive library and toolset allow you to create anything from basic user interfaces to big, dynamic web apps. React provides state management with Redux and animations with Framer Motion.
3. Flexibility
One of React’s strengths is its adaptability. Do you want to connect with a framework like Next.js for server-side rendering or static website generation? Not an issue. React integrates seamlessly with other technologies, allowing you to create solutions suited to your project’s requirements.
4. Performance
Speed is essential for both consumers and developers. React’s virtual DOM optimizes updates, allowing for lightning-fast changes without impacting app performance. This results in more seamless user experiences and happier end users.
React is more than simply a library; it is a solution designed for speed, versatility, and a flourishing developer community.
Read More: React vs. Angular Select The Best for Mobile App Development
5. Advantages of React Native: Why It’s a Game-Changer for Mobile Development

If you want to build a mobile app that works perfectly on both iOS and Android, React Native may be the right option. Here’s why React Native stands out and how it may help you streamline your mobile development process.
1. Cross-platform Development
Consider building one codebase and delivering it across iOS and Android. React Native enables this, reducing development time and costs while ensuring platform consistency, thus exemplifying optimal efficiency.
2. Native Performance
Are you concerned about performance? Well, put your worries to rest. React Native bridges the gap between JavaScript and native code, providing the speed and responsiveness of a native program. Your users will not notice the change.
3. Community Support
React Native is supported by more than just Facebook; it also has a large and active open-source community. This means you’ll always have access to assistance, tutorials, and libraries to help you overcome any development challenges.
4. Hot Reloading
No more continuous waiting while debugging. React Native’s hot reloading functionality lets you view your changes in real-time, making the development process quicker and more efficient.
React Native is a strong, efficient, and user-friendly framework that simplifies mobile app development while maintaining quality.
6. Use Cases and When to Use React vs React Native
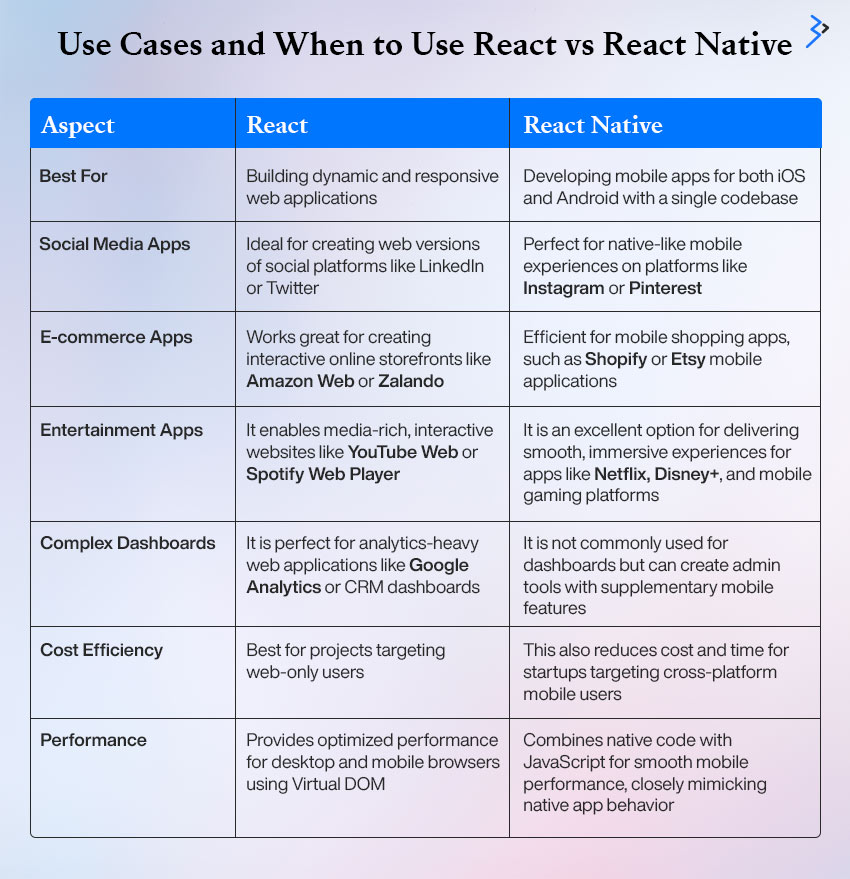
Wondering whether to go with React or React Native for your next project? Let’s break it down with real-world examples to help you decide.
| Aspect | React | React Native |
| Best For | Building dynamic and responsive web applications | Developing mobile apps for both iOS and Android with a single codebase |
| Social Media Apps | Ideal for creating web versions of social platforms like LinkedIn or Twitter | Perfect for native-like mobile experiences on platforms like Instagram or Pinterest |
| E-commerce Apps | Works great for creating interactive online storefronts like Amazon Web or Zalando | Efficient for mobile shopping apps, such as Shopify or Etsy mobile applications |
| Entertainment Apps | It enables media-rich, interactive websites like YouTube Web or Spotify Web Player | It is an excellent option for delivering smooth, immersive experiences for apps like Netflix, Disney+, and mobile gaming platforms |
| Complex Dashboards | It is perfect for analytics-heavy web applications like Google Analytics or CRM dashboards | It is not commonly used for dashboards but can create admin tools with supplementary mobile features |
| Cost Efficiency | Best for projects targeting web-only users | This also reduces cost and time for startups targeting cross-platform mobile users |
| Performance | Provides optimized performance for desktop and mobile browsers using Virtual DOM | Combines native code with JavaScript for smooth mobile performance, closely mimicking native app behavior |
In short, React builds exceptional web applications, while React Native helps you capture the mobile audience with minimal effort. The choice depends on where your audience lives—on the web or in their pockets.
7. Challenges and Limitations
| Aspect | React | React Native |
| Learning Curve | Requires mastering JSX and advanced state management tools like Redux or Context API | Demands knowledge of JavaScript and native platform details like iOS and Android ecosystems |
| Performance Issues | May need help with performance in highly complex apps with heavy computations | Relies on a JavaScript bridge, which can cause performance hiccups in resource-intensive tasks |
| Third-Party Dependency | Rarely requires external dependencies for web development | Unfortunately, it relies heavily on third-party libraries for native features like cameras or geolocation |
| OS Compatibility | Minimal compatibility challenges as it is browser-based | New OS updates (iOS/Android) may cause temporary app-breaking issues until libraries are updated |
Making the Right Choice
React and React Native are potent tools, but understanding their limitations helps you plan optimally. Whether you’re building a complex dashboard or a feature-packed mobile app, carefully considering these challenges ensures a smoother development journey.
8. A Comparative Table
| Feature | React | React Native |
| Platform Focus | Web-based applications | Mobile (iOS, Android) applications |
| Primary Use Cases | Building interactive UIs for websites | Creating native mobile apps with native performance |
| Components | Web components (HTML, CSS) | Native components (iOS & Android UI elements) |
| Rendering | Virtual DOM for efficient updates | It uses native components for rendering |
| Performance | Dependent on browser rendering speed | Close to native performance on mobile devices |
| Development Speed | Fast, with reusable components for the web | Requires bridging with native code for specific features |
| Learning Curve | Easier for web developers familiar with JavaScript | Slightly steeper due to mobile-specific APIs |
| Limitations | Limited to web apps | It may require native code for complex features |
| Popularity | Very popular for building web UIs | Proliferating for mobile app development |
9. Conclusion
The requirements of your project determine whether you should use React or React Native. If you’re creating a dynamic, interactive online application, React is the apparent option since it provides speed, flexibility, and seamless updates.
However, if you want to build a mobile app with near-native speed, React Native should be your go-to framework. While both are strong, recognizing the distinctions and how to use them is critical to the success of your project.
Remember that one size does not fit everyone. Take the time to investigate both frameworks and match the tool to your development requirements. Whether you want a seamless online experience or mobile efficiency, each framework offers something unique. Also, if you need clarification about whether the framework is best for your project, please contact our team at Brainvire for professional advice or browse our learning resources. Let’s work together to create something fantastic!
FAQs
React is typically used to create online applications, while React Native is intended for mobile app development (iOS and Android). React uses web technologies such as HTML and CSS, but React Native employs native components for mobile platforms to achieve performance similar to native applications.
While React Native does not allow direct reuse of all React code, certain functionality and components, such as business logic and state management, may be reused. However, you must adjust UI components and styles for React Native’s mobile environment.
The decision is based on your project. If you’re building a web app, React is the best option. For mobile apps that need native performance, React Native is the best choice. It is essential to examine the target platform and the necessary characteristics.
React Native achieves native performance by using native components instead of web components. It combines JavaScript with native APIs to conduct activities directly on the device, resulting in mobile apps that feel and function like native applications.
The major obstacles for React Native include restricted third-party library support, the necessity for native code integration for complicated functionality, and platform-specific variations (iOS vs. Android) that might alter app behavior. Additionally, speed optimization might be more challenging than pure native development.
Related Articles
-
TypeScript vs JavaScript – A Comprehensive Comparison
Choosing the correct programming language is pivotal in shaping the success of any web development project. Amidst the many options available, the debate between TypeScript and JavaScript continues to dominate