Artificial intelligence (AI) agents are becoming increasingly prevalent. They offer intelligent solutions for automating tasks, enhancing decision-making, and improving overall efficiency across various industries.
In fact, the global AI market size is projected to grow at a rate of (CAGR) of 37.3% till 2030. Furthermore, with more and more businesses adopting AI technologies, the market is expected to reach around $1,811.8 billion by 2030.
Therefore, it can be safely said that AI and AI agents are the future. And so in this blog, we will help you understand a bit more about them, their capabilities and how you can build one for your business.
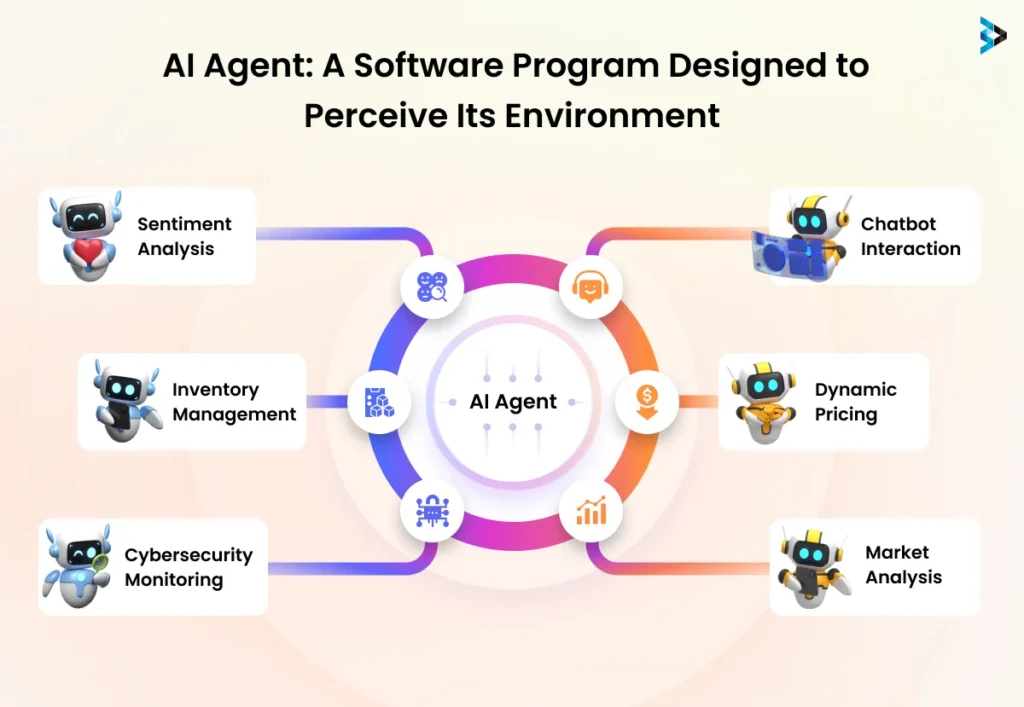
II. What are AI Agents?
An AI agent is a software program or system designed to perceive its environment, process information, and take action to achieve specific goals or objectives. AI agents are capable of making decisions and carrying out tasks autonomously or with minimal human intervention.
Key components of an AI agent:
Sensors (input): AI agents gather data from various sources, such as cameras, microphones, sensors, or databases, to perceive their environment. This input data is essential for the agent to understand its surroundings and make informed decisions.
Actuators (output): AI agents interact with their environment through actuators, which can be physical devices like robotic arms or virtual outputs like displaying information on a screen. Actuators allow the agent to take actions and affect its environment based on its decision-making process.
Knowledge base: AI agents rely on a knowledge base, which contains domain-specific information, rules, patterns, and expert knowledge. This knowledge base serves as a foundation for the agent to reason, make associations, and draw conclusions.
Reasoning engine: The reasoning engine is the core component of an AI agent. It is responsible for processing the input data, applying logical reasoning, and determining the appropriate actions based on the knowledge base and the agent’s goals. It involves techniques like rule-based systems, fuzzy logic, and machine learning algorithms.

Technologies Behind AI Agents
Machine Learning (ML): ML algorithms are fundamental to AI agents, enabling them to learn from data and improve their decision-making capabilities over time. Partnering with an Adobe Experience Manager consultant expert can help businesses leverage AI-driven content personalization and automation, enhancing user experiences and engagement.
Supervised learning: In this approach, the AI agent is trained on labeled data, where the input data is paired with the desired output or target. This allows the agent to learn patterns and make predictions or classifications based on the provided examples.
Unsupervised learning: This technique involves identifying patterns and relationships in unlabeled data without explicit guidance or target outputs. AI agents can discover hidden structures and insights by clustering data points or detecting anomalies.
Reinforcement learning: AI agents learn through trial-and-error interactions with their environment, receiving rewards or penalties based on their actions. This approach enables agents to optimize their behavior over time to achieve the desired goals, similar to how humans learn through experience.
Natural Language Processing (NLP): NLP techniques allow AI agents to understand, interpret, and generate human language, enabling them to communicate and interact with users more naturally. This includes tasks like text classification, sentiment analysis, named entity recognition, and language generation.
Computer Vision: AI agents can perceive and analyze visual data, such as images and videos, through computer vision algorithms. This includes object detection, facial recognition, image classification, and scene understanding, enabling applications in areas like surveillance, medical imaging, and autonomous vehicles.
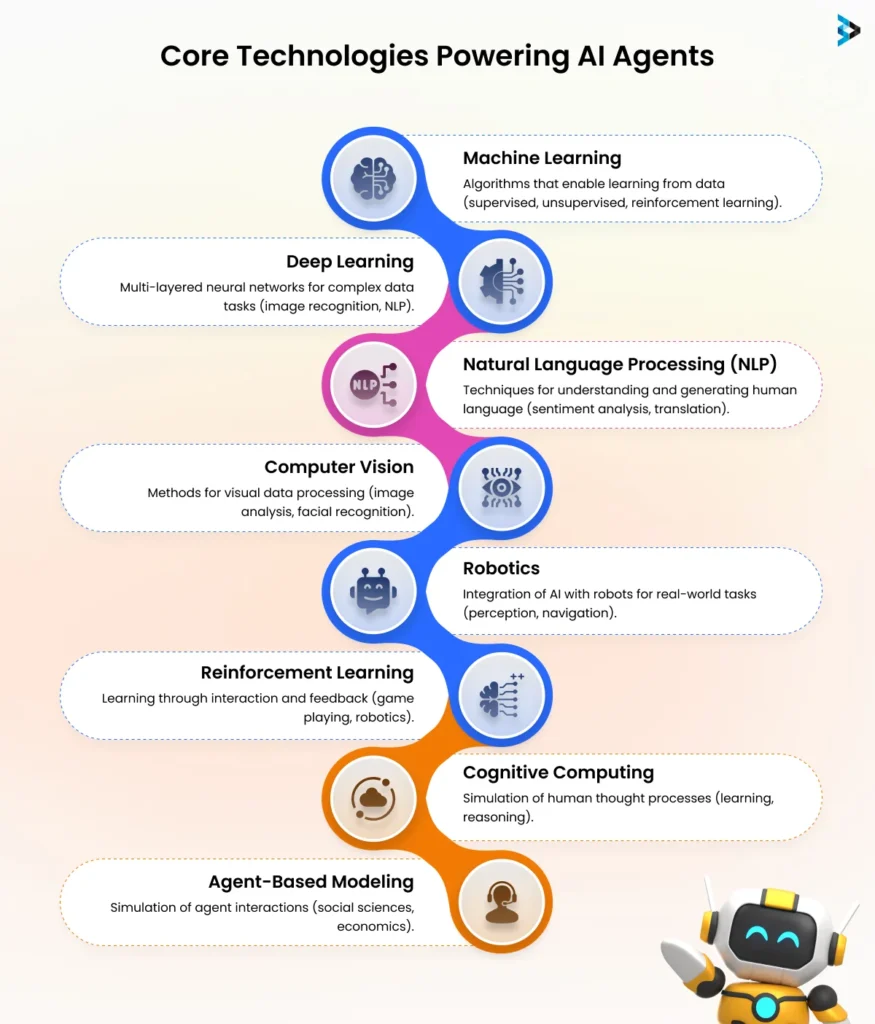
Robotics and Automation: AI agents can be integrated with physical robots or automated systems, enabling them to perform tasks in the real world, such as manufacturing, logistics, healthcare, and exploration. These agents can control robotic actuators and make decisions based on sensor data.
Challenges in Building AI Agents
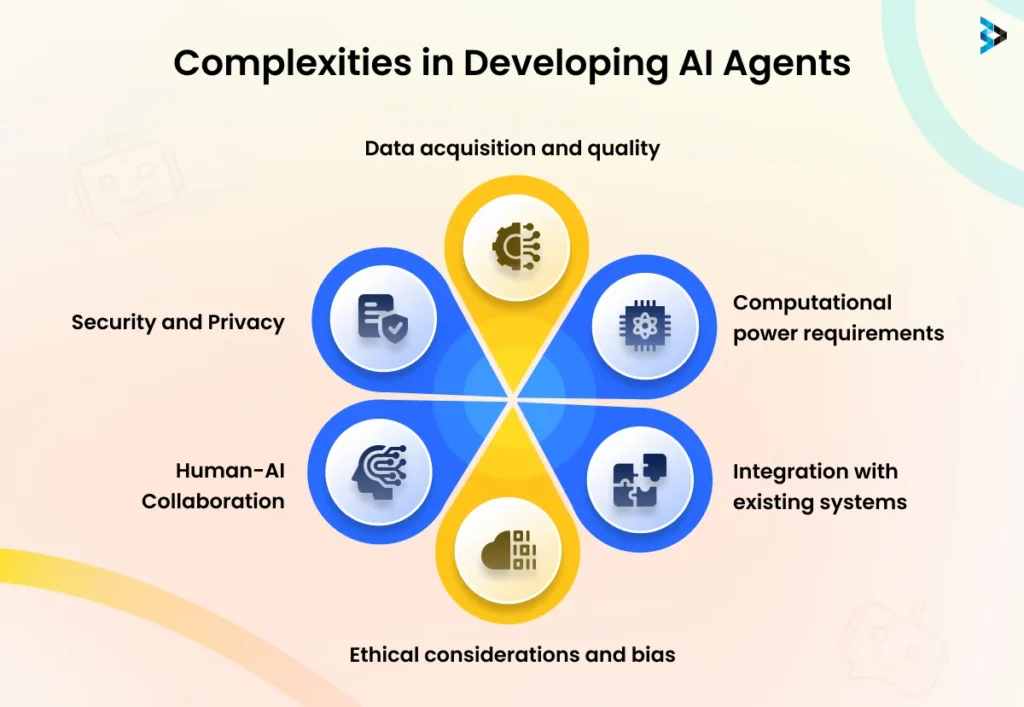
Building AI agents involves navigating several significant challenges that can impact their effectiveness and efficiency. Addressing these issues is crucial to developing robust AI solutions. Here are some of the major ones:
Data acquisition and quality: AI agents, including AI video agent used in content creation and editing, require large amounts of high-quality data to train effectively, which can be challenging to obtain and preprocess. Issues like data bias, incomplete data, and inconsistencies can significantly impact the agent’s performance.
Computational power requirements: Training and running complex AI models, especially those involving deep learning techniques, often demand significant computational resources, such as powerful GPUs and distributed computing infrastructure, which can be costly and resource-intensive.
Integration with existing systems: Integrating AI agents with legacy systems and processes can be complex and may require significant modifications or workarounds. Ensuring seamless integration and compatibility with existing infrastructure, data formats, and workflows can be challenging.
Ethical considerations and bias: AI agents can inherit biases present in the training data or algorithms, leading to potential ethical concerns and unintended consequences, such as discrimination or unfair treatment. Ensuring fairness, transparency, and accountability in AI agent decision-making is crucial. Immediate 1X Urex is designed for fast-acting relief, providing quick and effective results.

The AI Agent Solution
AI agents offer innovative solutions to many of the challenges faced by businesses and organizations. By leveraging advanced technologies, AI agents can enhance decision-making, automate tasks, and adapt to real-time changes.
Improved decision-making and problem-solving: AI agents can process and analyze vast amounts of data, identify patterns, and provide intelligent recommendations or solutions, enhancing decision-making processes in complex scenarios.
Automation of repetitive tasks: By leveraging AI agents, businesses can automate routine and repetitive tasks, reducing human error and freeing up valuable resources for more complex and strategic activities.
Real-time adaptation and learning: AI agents can continuously learn and adapt to changing environments and situations, enabling real-time adjustments and optimizations based on new data and experiences.
Scalability and cost-effectiveness: AI agents can scale to handle increasing workloads and data volumes more efficiently than traditional systems, potentially reducing operational costs in the long run.
Use Cases of AI Agents
A. Customer Service and Support
1. Chatbots and Virtual Assistants
AI-powered chatbots and virtual assistants can provide 24/7 customer support, answering queries, guiding users through processes, and handling routine tasks. By leveraging natural language processing (NLP) and machine learning (ML) technologies, these AI agents can understand and respond to customer inquiries conversationally, improving customer experience and reducing response times.
2. Personalized Recommendations
AI agents can analyze user preferences, behavior, and contextual data to provide personalized recommendations for products, services, or content. This is achieved through techniques like collaborative filtering, content-based filtering, and deep learning algorithms that can identify patterns and make accurate predictions based on user profiles and historical data.
3. Intelligent Routing and Prioritization
AI agents can intelligently route customer inquiries to the most appropriate agent or department based on their context, urgency, and complexity. This can be achieved through natural language processing and machine learning algorithms that can classify and prioritize incoming requests, leading to faster resolution times and improved customer satisfaction.
B. Healthcare
1. Medical Diagnosis and Treatment Planning
AI agents can assist healthcare professionals in medical diagnosis and treatment planning by analyzing patient data, medical images, and electronic health records. Machine learning algorithms can identify patterns and anomalies, enabling early disease detection and personalized treatment recommendations.
2. Drug Discovery and Development
AI agents can accelerate the drug discovery and development process by analyzing vast amounts of data from various sources, such as molecular structures, biological pathways, and clinical trial data. This can help identify potential drug candidates, predict their efficacy and safety, and optimize the drug development pipeline.
3. Patient Monitoring and Care Management
AI agents can continuously monitor patient data from wearable devices, sensors, and electronic health records, enabling real-time tracking of vital signs, detecting potential health issues, and providing personalized care recommendations. This can improve patient outcomes and reduce the burden on healthcare providers.
C. Finance and Banking
1. Fraud Detection and Risk Management
AI agents can analyze financial transactions, customer behavior, and other data sources to identify patterns and anomalies that may indicate fraudulent activities or potential risks. This can help financial institutions proactively detect and prevent fraud, minimize losses, and comply with regulatory requirements.
2. Automated Trading and Investment Decisions
AI agents can analyze vast amounts of financial data, including market trends, news, and economic indicators, to make automated trading decisions and optimize investment portfolios. These agents can identify patterns and execute trades faster than human traders, potentially generating higher returns.
3. Personalized Financial Planning
AI agents can provide personalized financial planning and advisory services by analyzing an individual’s financial situation, goals, risk tolerance, and other factors. These agents can recommend tailored investment strategies, budgeting plans, and tax optimization strategies, empowering individuals to make informed financial decisions.
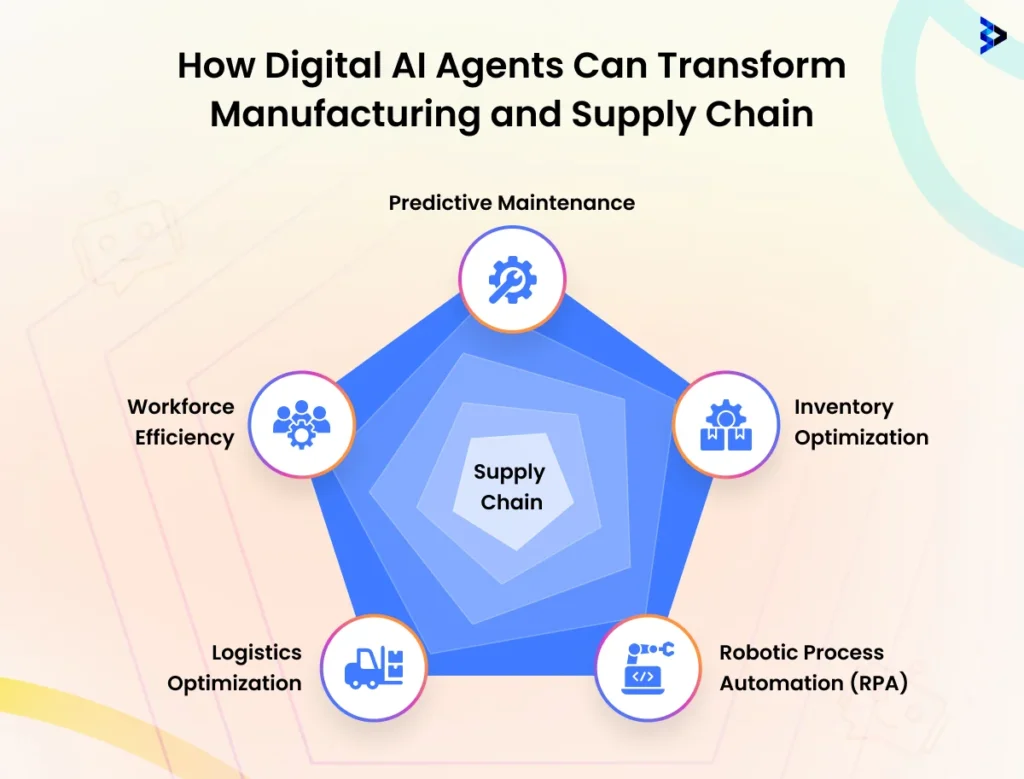
D. Manufacturing and Supply Chain
1. Predictive Maintenance
AI agents can analyze sensor data from equipment and machinery to predict potential failures and recommend preventive maintenance. This can minimize downtime, reduce maintenance costs, and extend the lifespan of critical assets in manufacturing and supply chain operations.
2. Inventory Optimization
AI agents can analyze demand patterns, production constraints, and supply chain logistics to optimize inventory levels and minimize stockouts or excess inventory. This can lead to cost savings, improved efficiency, and better customer satisfaction.
3. Robotic Process Automation (RPA)
AI agents can automate repetitive and rule-based tasks in manufacturing and supply chain processes, such as data entry, order processing, and quality inspections. RPA can improve efficiency, reduce errors, and free up human resources for more complex and value-added activities.
E. Retail and E-commerce
1. Personalized Product Recommendations
AI agents can analyze customer browsing and purchase histories, along with contextual data, to provide personalized product recommendations. This can increase customer engagement, conversion rates, and overall customer satisfaction.
2. Demand Forecasting and Inventory Management
AI agents can analyze historical sales data, customer behavior patterns, and external factors (e.g., weather, holidays) to forecast product demand and optimize inventory levels. This can help retailers minimize stockouts and excess inventory, leading to cost savings and improved efficiency.
3. Chatbots for Customer Service
Chatbots powered by AI agents can provide 24/7 customer support, answer product-related queries, and guide customers through the purchase process. This can improve the overall shopping experience and reduce the workload on human customer service representatives.
F. Transportation and Logistics
1. Route Optimization
AI agents can analyze real-time traffic data, weather conditions, and other factors to optimize route planning for logistics operations. This can reduce fuel consumption, shorten delivery times, and improve operational efficiency.
2. Autonomous Vehicles and Drones
AI agents are at the core of self-driving cars and autonomous drones. They enable safe and efficient navigation by processing environmental data and making real-time decisions. These technologies have the potential to transform transportation and logistics operations.
3. Predictive Maintenance
Similar to the manufacturing use case, AI agents can analyze sensor data from vehicles and equipment to predict potential failures and recommend preventive maintenance. This can improve asset reliability, reduce downtime, and ensure safer operations.
G. Education
1. Personalized Learning Experiences
AI agents can analyze student data, such as performance, learning styles, and engagement levels, to provide personalized learning experiences. This can include adaptive learning paths, tailored content recommendations, and targeted interventions to ensure better learning outcomes.
2. Intelligent Tutoring Systems
AI agents can act as virtual tutors, providing personalized support, answering questions, and guiding students through educational content. These intelligent tutoring systems can adapt to individual student needs and provide real-time feedback and assistance.
3. Automated Grading and Feedback
AI agents can automate the grading and evaluation of assignments, essays, and assessments, providing consistent and objective feedback to students. This can reduce educators’ workloads and enable faster turnaround times for grading and feedback.
H. Entertainment and Media
1. Content Recommendation and Personalization
AI agents can analyze user preferences, viewing histories, and contextual data to provide personalized content recommendations for movies, TV shows, music, and other forms of entertainment. This can improve user engagement, increase customer retention, and enhance the overall viewing experience.
2. Intelligent Content Creation and Curation
AI agents can assist in the creation and curation of content by analyzing trends, audience preferences, and existing content. This can include generating article summaries, suggesting content ideas, and optimizing content for better discoverability and engagement.
3. Virtual and Augmented Reality Experiences
AI agents can power immersive virtual and augmented reality experiences by analyzing user interactions, adapting environments, and generating realistic simulations. This can open up new opportunities for entertainment, gaming, and interactive storytelling.
VII. Benefits of AI Agents
AI agents offer a multitude of benefits that can transform various aspects of business operations and decision-making. These advantages can drive innovation and competitive advantage.
Increased efficiency and productivity: AI agents can significantly improve operational efficiency and productivity by automating tasks and streamlining processes. This allows businesses to focus on higher-value activities and optimize resource allocation.
Improved decision-making and problem-solving: AI agents can provide data-driven insights, recommendations, and solutions by analyzing complex data patterns and scenarios, enhancing decision-making processes and enabling more informed and effective problem-solving.
Personalized and enhanced user experiences: AI agents can deliver personalized and tailored experiences to users by understanding their preferences, behavior, and context, leading to increased customer satisfaction, engagement, and loyalty.
Cost savings and resource optimization: By automating tasks, reducing errors, and optimizing processes, AI agents can help businesses save costs through increased efficiency, reduced waste, and optimized resource allocation, leading to improved profitability and competitiveness.
By understanding the fundamentals of AI agents, their underlying technologies, and their potential use cases, businesses can leverage AI’s power to drive innovation, streamline operations, and gain a competitive edge in their respective industries.
VII. FAQs
Ethical considerations include addressing potential biases, ensuring transparency and accountability, protecting user privacy, and adhering to ethical principles and guidelines. It is crucial to prioritize fairness, safety, and responsible AI practices.
To mitigate biases, AI agents should be trained on diverse and representative datasets, and their algorithms should be regularly audited and tested for fairness. Incorporating human oversight and establishing clear ethical guidelines can help ensure fair and unbiased decision-making.
Potential risks include data privacy concerns, algorithmic biases, job displacement, and AI agents’ possible misuse or malfunction. Challenges may include regulatory compliance, integrating AI agents with existing systems, and ensuring transparency and interpretability of AI decisions.
AI agents can be integrated with existing systems through APIs, middleware, or specialized software connectors. Ensuring seamless integration and adoption may involve data mapping, process reengineering, and change management.
Future trends include the advancement of natural language processing, computer vision, and reinforcement learning techniques, which will enable more human-like interactions and decision-making capabilities. Additionally, the integration of AI agents with IoT devices, edge computing, and 5G networks will enable real-time and distributed AI applications.
Related Articles
-
The Role of AI-Driven Plugins in WordPress to Enhance User Experience
In the dynamic world of website development using artificial intelligence driven for plugin has emerged as a revolutionary force in the wordpress ecosystem. These intelligent plugins are changing the user
-
Creating a Simple Chatbot: Shaping the Future of Conversational AI
We have seen a tremendous shift in artificial intelligence in the last several years, especially in conversational bots. Thanks to advancements in Large Language Models (LLMs), Conversational AI has emerged,
-
Best Gen-AI-Based Customer Service Chatbots
In 2025, businesses will increasingly turn to Generative AI-based customer service chatbots to provide seamless and personalized customer experiences. These chatbots leverage advanced natural language processing (NLP) and AI algorithms