Businesses have embraced artificial intelligence (AI) in supply chains for demand planning and procurement. The application of AI extends to standardizing processes and enhancing last-mile delivery efficiency. A recent study reveals that AI adoption stands at an impressive 62% in the emerging field of sustainability tracking.
However, over the past year, a new player has emerged in the AI landscape - generative AI (GenAI), notably popularized by ChatGPT. This transformative technology is reshaping our perceptions of what AI can achieve, marking a significant evolution in the AI narrative.
Decoding Generative AI's Role in Transforming Supply Chain Dynamics
Generative AI in supply chain management involves integrating advanced artificial intelligence systems into supply chain management practices. Unlike conventional AI, which processes input to produce predetermined outcomes, generative AI goes a step further, crafting novel patterns and trends within data. It possesses the ability to anticipate unforeseen scenarios, suggesting solutions not explicitly programmed.
Beyond its predictive capabilities, generative AI showcases creativity by generating original content, predictions, and data-driven strategies. In the supply chain arena, it excels at simulating intricate logistics networks and forecasting outcomes for various strategies in diverse conditions.
This transformative technology holds immense potential for the supply chain industry. It can revolutionize demand forecasting, streamline routing optimization, and automate inventory management. To comprehend the profound impact generative AI can have on the supply chain, we'll delve into relevant statistics and illustrative examples.
Revolutionizing Supply Chain: Exploring Generative AI's Impactful Use Cases
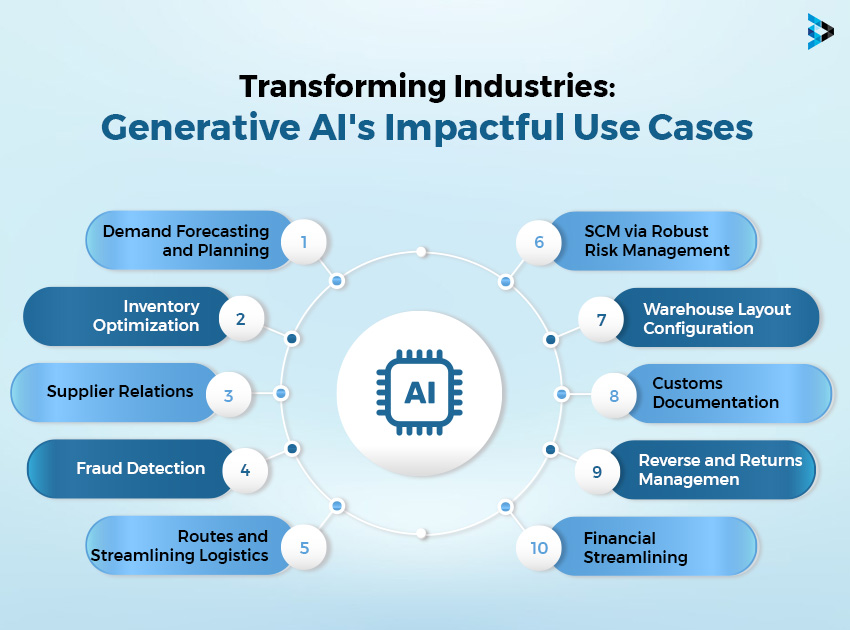
-
Demand Forecasting and Planning
The utilization of Generative AI in demand forecasting and planning is instrumental in leveraging historical sales data and external variables like seasonality, promotions, and economic indicators. Through the training of AI models on past data, these models proficiently generate probabilistic demand forecasts at diverse levels, spanning from individual SKUs to entire product categories. This application proves invaluable for businesses seeking to fine-tune their operations.
- Precision in predicting demand for products and services
- Streamlined resource planning and allocation for increased efficiency
- Improved decision-making through the utilization of predictive insights

- Swift adaptation to dynamic changes in market conditions
- Enhanced management of inventory for optimized operations
-
Inventory Optimization
Generative AI analyzes demand patterns, lead times, and more to optimize inventory levels in the supply chain. It suggests reordering points and safety stock levels, aiding warehouse management by minimizing stockouts, reducing excess inventory, and lowering business carrying costs.
- Demand Forecasting: AI leverages predictive analytics, analyzing historical sales data, market trends, and seasonal influences for accurate product demand forecasts.
- Automated Replenishment: AI systems automatically restock based on preset criteria, minimizing the risks of stockouts or overstocking.
- Real-Time Inventory Management: AI enables real-time tracking and management of inventory across multiple locations, enhancing accuracy and efficiency.
- Supplier Relationship Management: AI evaluates supplier performance in lead time, cost, quality, and reliability, facilitating better selection and negotiation.
- Customer Service: AI-driven chatbots and virtual assistants handle customer queries about product availability, ensuring a superior customer experience.
-
Supplier Relations
- Automated Supplier Performance Analysis: Implementing AI for automatic evaluation of supplier performance, considering factors like lead time, cost, quality, and reliability.
- Predictive Insights for Supplier Behavior: Utilizing AI to gain foresight into supplier behavior, helping anticipate trends and potential challenges.
- Proactive Issue Identification and Resolution: Leveraging AI for early detection of issues in supplier relations, enabling proactive resolution and minimizing disruptions.
- Optimal Allocation of Resources: Employing AI to optimize the allocation of resources in supplier relationships, ensuring efficient utilization and cost-effectiveness.
-
Fraud Detection
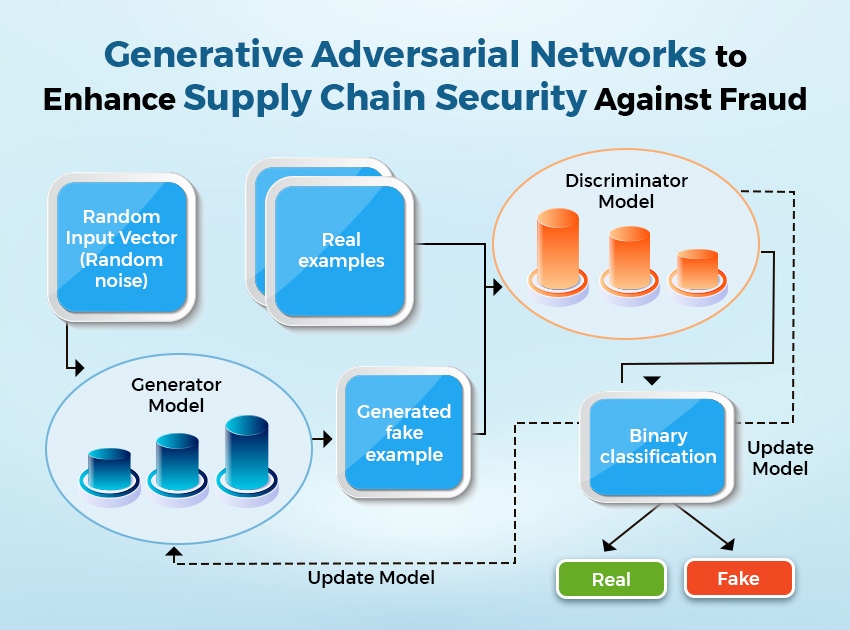
Generative AI, powered by Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs), is emerging as a potent weapon in the battle against fraud. Comprising two neural networks, the generator and discriminator, GANs engage in an adversarial process: the generator produces data (e.g., images), and the discriminator assesses its authenticity.
This dynamic allows GANs to generate remarkably realistic data simulations. Leveraging this adversarial approach, GANs excel at identifying anomalies or patterns indicative of fraudulent activity. In supply chain solutions, GAN-powered generative AI can be of immense value to businesses dealing with substantial transactions.
Experts exemplify this application, employing GANs in their Decision Intelligence system to analyze every transaction in real-time for enhanced fraud detection.
-
Optimizing Routes and Streamlining Logistics Management
Optimizing transportation is pivotal for supply chain success, and Generative AI proves instrumental in this realm. It dynamically refines route planning and logistics by analyzing real-time data on traffic, weather, and fuel costs. Generative AI adeptly adjusts delivery routes through such analysis to minimize travel time and expenses. This not only cuts operational costs but also elevates customer satisfaction by ensuring timely deliveries
-
Enhancing Supply Chain Resilience via Robust Risk Management
Gen AI, with its predictive prowess, aids logistics companies in uncovering potential risks within the supply chain. For instance, if the AI identifies impending volatile weather or political instability, it suggests risk mitigation strategies for companies to evaluate and implement.
Furthermore, when businesses employ generative AI for equipment maintenance, the tool implements predictive strategies, signaling when machines require attention. This proactive approach allows logistics operations to plan for downtime, enhancing reliability through proactive maintenance measures.
-
Optimizing Warehouse Layout Configuration

Generative AI transforms warehouse layout optimization in supply chains by analyzing factors that impact operational efficiency. Unlike traditional static layouts based on historical data, Generative AI dynamically adjusts arrangements based on size or alphabetical order. The AI models simulate diverse configurations, gauging their impact on internal travel times.
For instance, it identifies frequently accessed items and suggests placing them closer to packing stations. Amazon's fulfilment centers exemplify real-world applications as the company pioneers the integration of AI and robotics to optimize warehouse operations. Generative AI's adaptability ensures more responsive layouts, optimizing the utilization of space and streamlining processes in modern supply chain management.
-
Elevating Sustainability and Minimizing Environmental Footprint
- Optimizes transportation routes to minimize fuel consumption and emissions
- Assists efficient packaging material optimization
- Reduces waste in the supply chain
- Supports environment-friendly practices
- Enhances overall sustainability in supply chain management
- Minimizes environmental impact through smart logistics
- Promotes eco-conscious decision-making in transportation and packaging
-
Streamlining Reverse Logistics and Returns Management
Generative AI enhances reverse logistics efficiency by analyzing returns, repairs, and refurbishments data. It aids in identifying optimal routes for returned products, making decisions on repair or disposal, and optimizing inventory allocation for refurbished items.
-
Financial Streamlining
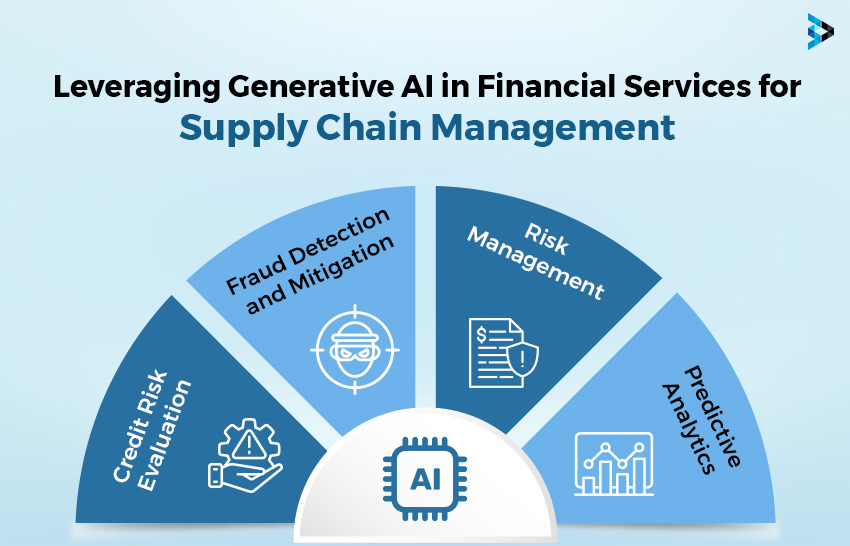
Using generative AI in financial services within supply chain management enhances efficiency, mitigates risks, and refines decision-making. It addresses challenges like assessing credit risk, detecting fraud, and managing various financial risks, providing valuable insights for more effective and stable supply chain operations.
Credit Risk Evaluation:
- Generative AI processes extensive data, including credit histories, financial reports, and market data.
- Enables assessment of credit reliability for suppliers, partners, or customers.
- Stakeholders leverage insights to manage financial risks, make informed credit decisions, and identify potential disruptions.
Fraud Detection and Mitigation:
- Generative AI scrutinizes transaction data to identify patterns and irregularities, flagging potential fraud instances.
- Helps businesses limit financial losses, protect their reputation, and uphold supply chain integrity.
Risk Management:
- Generative AI assesses various risks, including currency fluctuations, interest rate shifts, and geopolitical events.
- Generates valuable insights to aid businesses in developing strategies for effective risk mitigation.
- Enables supply chain stakeholders to manage financial risks and maintain stability.
-
Automation of Logistics and Customs Documentation Creation
AI automates diverse logistical tasks, from scheduling deliveries to coordinating multi-modal transportation, enhancing overall operational efficiency.
The extensive and transformative applications of generative AI in the supply chain signify a shift towards a more streamlined, efficient, and innovative landscape as businesses increasingly harness these capabilities.
Transformative Applications of Generative AI in Supply Chain Dynamics
As businesses continue integrating Generative AI across these key supply chain functions, they unlock unprecedented efficiencies, agility, and innovation in their operations.
- Planning:
Generative AI revolutionizes supply chain planning by processing vast datasets, historical trends, and real-time variables. It optimizes demand forecasting, resource allocation, and strategic decision-making, ensuring agile and adaptive planning processes.
- Sourcing:
In sourcing, Generative AI enhances supplier selection and negotiation. Analyzing factors like lead time, cost, and reliability aids businesses in making informed decisions, fostering efficient collaboration with suppliers, and optimizing procurement strategies.

- Contract Analysis:
Generative AI streamlines contract analysis by parsing complex legal documents, extracting key information, and identifying potential risks or opportunities. This not only accelerates the contract review process but also ensures compliance and minimizes legal complexities.
- Production:
Within production, Generative AI contributes to efficiency by optimizing manufacturing processes. It identifies opportunities for automation, predicts maintenance needs, and enhances overall production workflows, leading to improved productivity and reduced downtime.
- Logistics:
In logistics, Generative AI plays a pivotal role in automating tasks such as route planning and inventory management. Analyzing real-time data on traffic, weather, and fuel costs dynamically adjusts transportation routes, minimizes expenses, and ensures timely deliveries, optimizing the entire supply chain.
Navigating Tomorrow: The Evolution of Generative AI in Shaping Logistics

As organizations navigate post-pandemic challenges, reinforcing supply chain and logistics capabilities becomes imperative. Harnessing AI emerges as a potent strategy for achieving this. McKinsey reports that successful AI implementation yields significant benefits, with businesses enhancing logistics costs by 15%, reducing inventory levels by 35%, and elevating service levels by 65%.
Additionally, McKinsey's research anticipates substantial economic value, estimating that logistics companies integrating AI into their processes could generate $1.3-$2 trillion annually for the next two decades. This underscores the transformative potential of AI in optimizing logistics, fostering resilience, and creating sustained economic value for the foreseeable future.
-
Autonomous Vehicles and Drones
Anticipating future trends in Generative AI and logistics points toward the rise of autonomous vehicles and drones. Autonomous things, propelled by AI, encompass self-driving vehicles, drones, and robotics, eliminating the need for human intervention. The logistics industry, inherently compatible with AI, is poised to witness a surge in autonomous devices.
Delivery drones are set to play a crucial role in product logistics, particularly in situations where ground transfer is impractical, unsafe, or unsustainable. This is especially pertinent in the healthcare sector, where pharmaceutical products with limited shelf life demand swift delivery. Drones emerge as valuable assets, reducing waste costs and negating the need for expensive storage facilities, offering a glimpse into the transformative potential of AI in revolutionizing logistics practices.
-
Smart Contracts and Blockchain Technology
Blockchain technology has demonstrated the potential to ensure comprehensive visibility and traceability throughout supply chains. The integration of Generative AI goes beyond enabling real-time decision-making for route optimization, cost reduction, and effective disruption management in the supply chain.
Smart contracts enhance this integration, automating processes like triggering new orders based on AI predictions of potential shortages. This synergy creates an agile and anticipatory supply chain network, showcasing the combined potential of Generative AI and blockchain to revolutionize logistics operations.
-
Personalized Customer Experiences
The supply chain management industry has embraced the development of customer service AI chatbots using GenAI algorithms to enhance efficiency in serving consumers. These chatbots now adeptly analyze customer behavior, cater to a broader spectrum of consumer requirements, and deliver personalized recommendations, significantly improving the overall customer service experience.
-
Real-time Data Analysis and Decision-Making
AI ensures complete visibility and traceability throughout supply chains. By integrating Generative AI, this capability can be enhanced further, allowing real-time decisions for optimizing routes, cutting costs, and effectively handling unexpected disruptions in the supply chain. The inclusion of smart contracts adds another layer, automating processes such as initiating new orders based on AI algorithms predicting potential shortages. This creates a nimble and forward-thinking supply chain network, highlighting the collaborative potential of Generative AI and blockchain in shaping the future of logistics.
-
AI-driven Simulation and Modeling
Generative AI crafts lifelike simulations for diverse supply chain scenarios, enabling logistics providers to test and refine strategies in a virtual environment. This aids in pinpointing bottlenecks, inefficiencies, and risks, empowering companies to devise more robust and resilient supply chain strategies.
-
Robotics and Automation
The ongoing integration of generative AI with robotics and automation technologies is reshaping warehouse operations. AI-driven robots adeptly handle tasks like picking, packing, and sorting, with machine learning algorithms optimizing their movements and coordination. This convergence promises heightened productivity, lower labor costs, and enhanced safety standards within warehouses.
Read more: Generative AI In ECommerce: Transforming The Online Shopping Experience
FAQs
- How does Generative AI improve forecasting in the supply chain?
Generative AI enhances supply chain forecasting by optimizing inventory management, production timelines, and shipping routes. It processes transactional data to discern patterns, identify irregularities, and detect potential instances of fraud within the supply chain, contributing to more accurate and efficient forecasting.
- What role does Generative AI play in demand planning?
In demand planning, Generative AI assumes a pivotal role by developing models capable of analyzing extensive historical sales data. This includes factors like seasonality, promotions, and economic conditions. The AI model generates more precise demand forecasts through training on this data, facilitating improved accuracy and efficiency in demand planning processes.
- How does Generative AI optimize inventory management?
Gen AI optimizes inventory management by identifying slow-moving items, minimizing holding costs, and suggesting strategies like discounts. It tailors effective storage and distribution tactics for various products, reducing waste and enhancing overall efficiency.
- How does Generative AI support decision-making in supply chain operations?
Generative AI aids decision-making in supply chain operations by analyzing vast datasets, predicting outcomes, and offering insights. It enables real-time adjustments, optimizes resource allocation, and identifies potential risks, fostering informed and agile decision-making processes within the supply chain.
- Is Generative AI applicable to sustainable and ethical supply chain practices?
AI supports ethical supply chain practices by analyzing supplier data for sustainability. It suggests improvements, such as changes in packaging or logistics, facilitating eco-friendly initiatives without terminating partnerships, and aiding businesses in meeting sustainability goals.
- What challenges may arise when implementing Generative AI in supply chain management?
Implementing Generative AI in supply chain management faces data availability, quality, and interpretability challenges. Model training complexity, real-time adaptation to dynamic environments, and ethical concerns further complicate deployment. Overcoming these hurdles requires careful consideration of data, computational resources, stakeholder trust, and legal and ethical considerations.
- Can Generative AI help B2B companies in managing complex supply chain networks?
Gen AI enhances B2B companies in navigating intricate supply chain networks by predicting risks. Whether economic, weather-related, or geopolitical, Generative AI suggests tailored mitigation strategies, empowering businesses to proactively address and manage potential challenges proactively, and fostering resilience in complex supply chain operations.
- What cybersecurity measures are in place when implementing Generative AI in B2B supply chains?
Implementing AI in B2B supply chains involves robust cybersecurity measures. Companies employ encrypted data transmission, secure authentication protocols, and continuous monitoring for potential threats. Regular audits, compliance checks, and staff training ensure a comprehensive cybersecurity framework, safeguarding sensitive data and maintaining the integrity of the supply chain network.
- What challenges may arise when implementing Generative AI in retail supply chain management?
Traditional methods in retail supply chain management face challenges in understanding complex consumer demand. They often overlook external factors like market trends and social media sentiment. Difficulty in handling unstructured data from customer reviews and limited real-time analysis hampers the ability to adapt quickly. Seasonal fluctuations and promotions are not always accurately accounted for, impacting inventory management.
- Can Generative AI assist in minimizing product returns and handling reverse logistics for retailers?
Generative AI in the supply chain aids retailers in reducing product returns and managing reverse logistics effectively. It evaluates data on returns, repairs, and refurbishments, streamlining the process and contributing to more efficient supply chain management.
Related Articles
Digital Transformation
AEM Implementation Cost Insight: Everything You Need to Know
Digital Transformation
AEM Implementation Process, Best Practices, and Tips
Digital Transformation
Odoo Pricing Guide: A Comprehensive Breakdown



