Table of contents
Introduction
The Core of Intelligent Document Processing
More Than Text Extraction: Transforming Data into Decisions
Step-by-step working of Intelligent Document Processing (IDP)
Key Advantages of Intelligent Document Processing (IDP)
Practical Applications of Intelligent Document Processing (IDP)
Discover how IDP helps finance domain
Application in the growing healthcare industry
Transforming human resource
Learn how IDP empowers legal teams in litigation
FAQs
Introduction
Racks of paper have never been a pretty sight. Paper-based processes and manual data entry create bottlenecks, slowing down document processing and hindering overall operational efficiency.
Document processing is converting physical or manual documents, such as web and content-heavy documents, into digital forms that can be integrated into business processes. You can make your documents available for digital processing by replicating the original content structure along with media-like images. There are primarily two methods of processing: manual and automated. Manual processing is slower and error-ridden, while automated processing uses proven modern techniques.
The Core of Intelligent Document Processing
Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) converts document information into digital documents, allowing businesses to read, understand, and assist them in making decisions. IDP leverages the power of technologies like Artificial Intelligence (AI), NLP (Natural Language Processing), and Robotic Process Automation (RPA) to enhance processing capabilities. Allowing businesses to process documents intelligently saves time, accelerates operations, and makes strategic decisions faster.
The Power Trio: OCR, NLP, and RPA:
| Feature | Benefit |
| OCR (Optical Character Recognition) | - Saves time in scanning documents
- Converts physical documents to digital - Enhances digital processing speed |
| NLP (Natural Language Processing) | - Processes structured and unstructured data
- Identifies key intentions and keywords - Enhances document understanding |
| Robotic Process Automation (RPA) | - Frees personnel for strategic tasks
- Reduces errors - Improves productivity and process consistency |
OCR (Optical Character Recognition) extracts text from an image into machine-readable or human-readable formats. It is useful in IDP to transfer all details from a physical document to a digital one. OCR saves time scanning volumes of documents to help re-create the document for faster digital processing.
NLP (Natural Language Processing): NLP aids in reading, extracting, and processing data from structured and unstructured documents. NLP can form accurate contextual information to process documents by identifying key intentions and keywords. NLP operates simultaneously on word, sentence, and document levels to create the right understanding of what the document text implies or for summarizing.
Robotic Process Automation (RPA): RPA eliminates repetitive document-related rule-based processes like data entry, form filling, and report generation. RPA mimics human actions so your personnel can be freed for more strategic work, helping your business productivity, reducing errors, and improving process consistency.
More Than Text Extraction: Transforming Data into Decisions
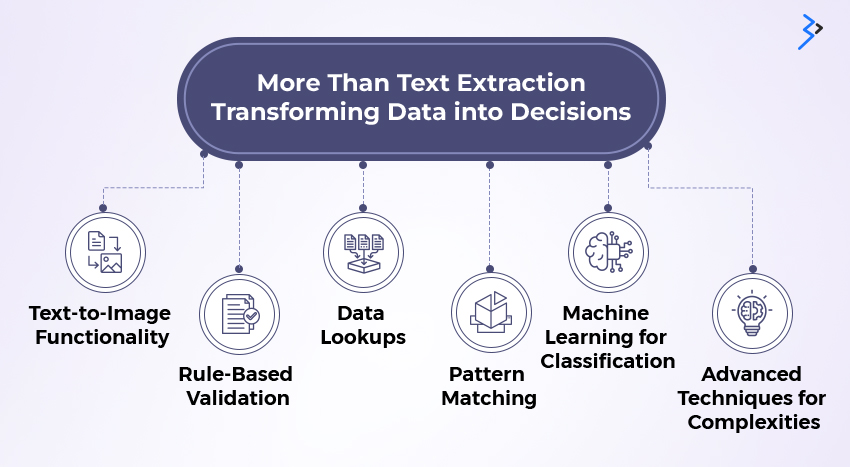
Text-to-Image Functionality: IDP transforms physical documents and recognizes text from an image in a document. You can expect faster extraction of content from images into recognizable formats that speed up processing, even in volumes.
Rule-Based Validation: You can create and apply rules when performing IDP to do more than text extraction. Combine intelligence while extracting text to take your document processing to the next level. Some examples include flagging errors or certain accounting figures requiring a second look for validation.
Data Lookups: Data lookups allow you to cross-verify your data by referencing a different data set or source. Get accuracy and speed during data extraction to ensure you always have authentic data.
Pattern Matching: Working with several data formats and styles can create chaos and lead to data discrepancies. IDP algorithms help identify recurring patterns and inconsistencies within documents. When extracting data, the algorithm can be trained to look for a specific layout or keyword sequence to apply rules for further processing.
Machine Learning for Classification: Machine learning enables IDP to enhance its classification abilities continuously. When an IDP encounters a new document type, like a uniquely formatted purchase order, the machine learning engine analyzes its structure and content to learn and categorize it. Over time, the IDP becomes proficient at classifying more accurately a broader range of documents. This continuous learning keeps the IDP adept at managing diverse document variations and complexities.
Advanced Techniques for Complexities: Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) leverages Machine Learning (ML) and Natural language Processing (NLP) to extract data from complex documents. It deciphers layouts, extracts relevant information from tables and images, and handles multi-page formats with high accuracy. Advanced techniques like entity recognition and context analysis enable IDP to understand intricate document structures, empowering businesses with reliable data for streamlined document management.
Step-by-step working of Intelligent Document Processing (IDP)
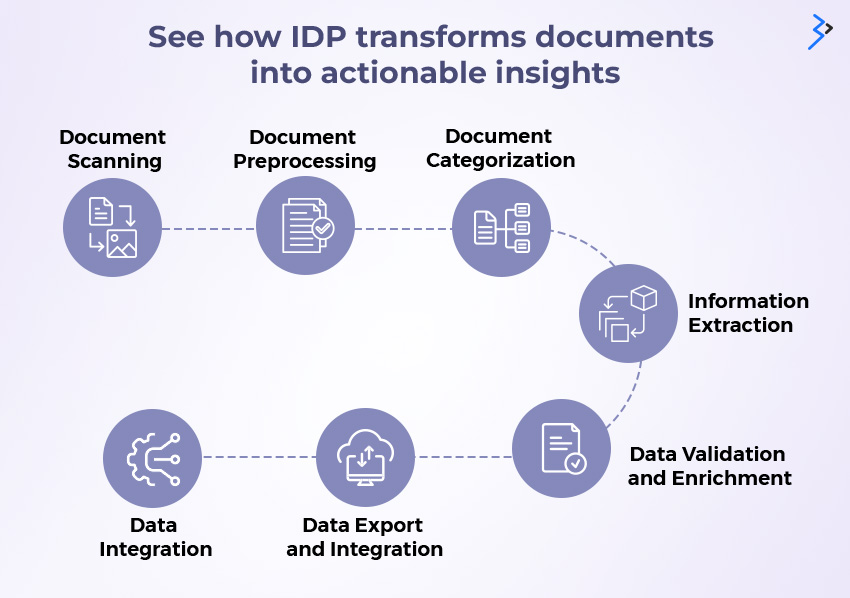
IDP goes through several steps to gather, analyze, process, and suggest the output to help you take concrete action for your business needs.
Step 1: Document Scanning
This initiates IDP, where scanned documents are supplied to the IDP system. You can submit the documents for data extraction and processing in the following ways:
Scanners: Docs and images can be ingested into the IDO system using assigned scanners.
Email Attachments: When emails contain document attachments, such as invoices or contracts, they can be automatically directed to the IDP system. This process removes the need for manual downloading and uploading, saving time and reducing errors.
Cloud Storage: IDP can access documents in cloud platforms like Dropbox, Google Drive, or Microsoft OneDrive. This seamless integration with existing workflows eliminates the need for manual file transfers.
File Uploads: Users can manually upload individual documents or entire folders for processing through a user-friendly interface. This flexibility ensures that documents not available through other ingestion methods can still be handled efficiently.
Step 2: Document Preprocessing
Post ingestion, the documents are pre-processed before the core processing. This step involves cleaning, enhancing, and standardizing documents to ensure their data can be accurately interpreted and processed. Some of the sub-processes as part of the pre-processing are:
Format Standardization: It involves converting various document formats (PDFs, images, Word documents, etc) into a uniform structure to ensure consistency and compatibility with the IDP system. It also involves standardizing text encoding formats, handling varying character sets, and avoiding encoding issues.
Image Enhancement: This step focuses on enhancing the quality of scanned or photographed documents to facilitate accurate data extraction. It also involves standardizing text encoding formats, handling varying character sets, and avoiding encoding issues. Enhancing documents visually can significantly help to enhance image quality for precise interpretation. Adjusting the resolution of images to optimize them for OCR, ensuring that text and fine details are captured accurately.
Layout Analysis: Here, several techniques for analysis, segmentation, zoning, and hierarchy are applied so that data can be extracted in the correct order and context.
Step 3: Document Categorization
By categorizing documents, the data extraction process becomes simpler and optimized. Effective classification helps to manage diverse document types with precision and efficiency, improving overall productivity and accuracy.
Machine Learning Powerhouse: Classification leverages advanced machine learning algorithms to classify documents using model training and accurately recognizing patterns.
Beyond Basic Classification: The IDP may classify a document as both legal and a contract. So, the IDP further processes it to understand the context and semantics.
Step 4: Information Extraction
The core processing happens in the information extraction process, where raw data from documents is transformed into structured and usable information. The process uses a two-step approach to achieve this:
Optical Character Recognition (OCR) - OCR recognizes patterns of characters from scanned images and turns them into machine-readable text for IDP’s further processing.
Natural Language Processing (NLP) - NLP is the next step in information processing. It brings context and meaning to the data structure, helping to make sense of the data and suggest solutions.
Step 5: Data Validation and Enrichment
IDP's post-processing tasks are vital to ensuring data validity and keeping it accurate, complete, and useful. The system runs iterations at this stage to enhance data quality and ensure reliable and authentic data. A few ways to do so are:
| Feature | Purpose | Implementation Examples | Benefits |
| Consistency Verification | Ensures data extracted matches predefined criteria |
|
Improves data reliability and accuracy |
| Master Data Validation | Cross-references extracted data with existing master databases |
|
Enhances data correctness and integrity |
| Template Matching | Compares data against known templates and patterns |
|
Ensures data adheres to expected formats and patterns |
| Quality Assurance | Maintains high standards of data processing and validation |
|
Ensures ongoing data quality and compliance |
Rule-Based Checks: You can verify the consistency and accuracy of extracted data by setting up pre-defined criteria. Rules can be set when processing documents based on a business requirement. It could be for uniform format validation, conditional logic, range, error detection, etc.
Database Lookups: You can get the right data format and validation by performing lookups with verification against master data. Use cases include verifying invoice details and customer payments.
Pattern Matching: Validate against known templates and formats on unstructured and semi-structured data. Techniques like regular expressions, template matching, and anomaly detection further extract and filter data, and data validation and enrichments ensure the quality and reliability of the data IDP systems process.
Step 6: Data Export and Integration
The final two steps of the IDP are exporting data and integrating it with external systems. This enables information extracted from documents for business processes and analytics.
Data Export: Data Export is seamlessly transferring information to other applications, databases, or storage systems. The format and method used depend on your specific needs and the compatibility of your target systems, ensuring a smooth transition for your newly targeted data.
CSV (Comma-Separated Values): One of the most usable formats, CSV allows for simple readability, data exchange, and sharing with popular solutions like Microsoft Excel and Google Sheets.
Databases: Exporting data to databases allows for efficient storage, retrieval, and analysis, supporting various business functions and decision-making processes. Relational databases facilitate efficient querying, reporting, and analytics.
Step 7: Data Integration
This phase involves taking the extracted and validated data and processing it by business systems. The true potential of extracted information is derived when the data is processed by applications like CRM, ERP, and BPA.
Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) Systems: Integrating validated data with an Enterprise Resource Planning (ERP) system eliminates manual entry errors, ensures data accuracy, and empowers you to generate insightful reports for informed decision-making.
Customer Relationship Management (CRM) Systems: CRM integration enriches customer profiles with extracted data from interactions, streamlines lead management, and builds stronger relationships with your customers.
Business Process Automation (BPA) Tools: IDP is a data bridge for Business Process Automation (BPA) tools. Structured, extracted data triggers specific actions within BPA workflows, minimizing human intervention and speeding up processing times. This not only reduces errors but also streamlines your entire business operation.
Enterprise Content Management (ECM): with IDP integration empowers organizations to streamline document workflows to capture, store, manage, and optimize their digital assets for better accessibility, collaboration, and regulatory compliance.
Content Service Platform (CSP): By integrating IDP with CSP, businesses can go beyond simple document storage, facilitating collaboration, content intelligence, and seamless integration with existing applications for a more efficient and effective content management experience.
Business Process Management (BPM): and IDP integration allow the establishment of standards for studying, identifying, optimizing, and monitoring business processes.
Key Advantages of Intelligent Document Processing (IDP)

A new way to organize data and leverage insights, IDP brings several business benefits, including faster retrieving information, streamlining processes, and saving time.
Significant Cost Savings
IDP considerably reduces the cost of processing documents, from transforming them into digital documents to automating repetitive tasks. It also reduces many of the labor costs associated with document management.
Enhanced Accuracy and Precision
Working on the rules you set, IDP prevents errors with several levels of checks. It also minimizes errors that may cause rework or financial losses.
Unmatched Scalability and Flexibility
For a growing business, managing physical documents and processing them can be quite a challenge. IDP removes the complexity by giving you scalability to handle large-scale processing accurately.
Optimized and Streamlined Workflows
IDP acts as a catalyst for streamlined workflows by automating document processing tasks and eliminating bottlenecks and delays. Faster document processing means smoother processes.
Practical Applications of Intelligent Document Processing (IDP)
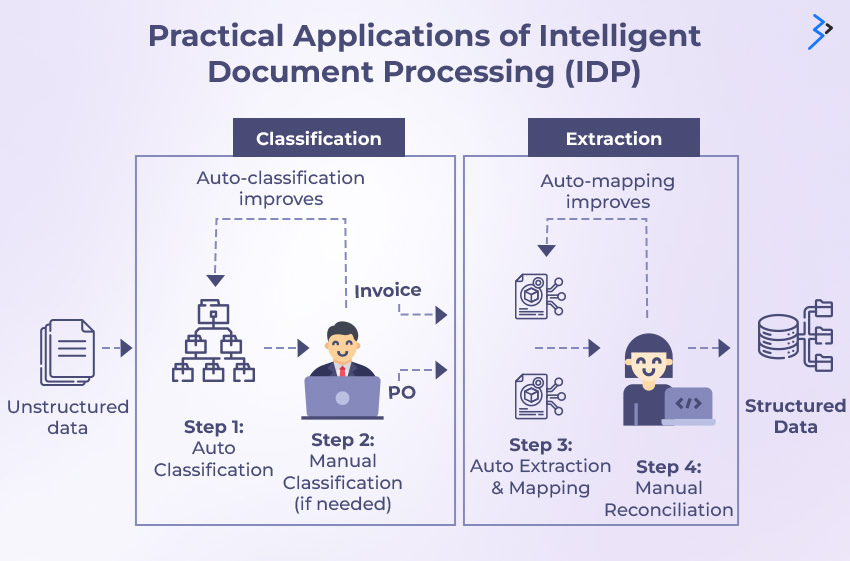
| Industry | Use cases |
| Finance |
|
| Healthcare |
|
| Human Resources |
|
| Legal |
|
Discover how IDP helps finance domain
IDP can extract critical data from invoices, such as vendor details, invoice amounts, and due dates. This extracted data can be automatically validated and routed for approval within your financial system. IDP can handle invoices from diverse formats, including paper scans, PDFs, and emails, ensuring seamless integration regardless of the source.
For automatic data population and report generation, IDP can extract key data from expense receipts like vendor names, date of purchase, amount spent, and item descriptions and handle various formats, including scanned paper receipts, digital images, and even mobile phone photos.
Automate the entire life cycle of a loan application from initial document submission to final approval. With IDP, ensure the accuracy and completeness of data, minimizing the risk of errors and fraud.
Application in the growing healthcare industry
IDP assists in eliminating manual entries with the categorization of patient information from various medical documents such as lab reports, prescriptions, and medical histories. Get access to up-to-date and reliable information by enhancing the accuracy of patient data and reducing the risk of errors.
By automating the extraction, validation, and classification of data from insurance claim forms, IDP helps reduce the time and effort required for manual data entry. Document Automation enhances the accuracy of claims and provides timely responses to policyholders.
Transforming human resource
Extract vital information from recruitment applications and job-related documents like contact details, work experience, and skills with IDP. You can enable automation and speed up the recruitment process, allowing HR professionals to find the best candidates.
Revamp the way you onboard human resources with IDP’s automation. Integrate with HR systems to automatically update employee records, trigger necessary workflows, and improve the onboarding experience for new hires.
Learn how IDP empowers legal teams in litigation
IDP enables legal professionals to quickly review and analyze large volumes of documents. Manage contracts by organizing them in a central repository and adding provisions for searching for specific clauses or terms when needed.
Identify key information such as dates, names, and keywords, making it easier for your legal teams to review and prioritize documents. IDP streamlines the discovery process, enabling legal teams to focus more on case preparation and analysis.
FAQs
What accuracy rates can I expect with IDP?
With IDP, you can expect upwards of 80% accuracy. Accuracy rates can vary based on factors like document complexity and data quality, ensuring reliable data extraction and processing.
What are some common challenges with IDP implementation?
Apart from the complexity of the initial setup for data ingestion and validation, you may face problems with data validation with different formats.
How does IDP handle document layouts and variations?
With modern techniques like optical character recognition (OCR), machine learning, and natural language processing, IDP handles several document formats, layouts, and variations.
Can IDP be customized for specific document types?
IDP can be customized to read specific document types and business needs. By defining rules and training the system with sample documents, IDP can adapt to new document formats and layouts.
How can I measure the success of an IDP implementation?
By measuring before-and-after metrics like processing time, error percentage, and data accuracy, you can evaluate the success of an IDP.
What is the difference between IDP and Robotic Process Automation (RPA)?
Intelligent Document Processing (IDP) and Robotic Process Automation (RPA) offer complementary functionalities in automation. While IDP excels at processing and extracting information from documents, RPA automates repetitive tasks across various systems.
How secure is IDP?
Encryption safeguards sensitive information, access controls restrict unauthorized use, and adherence to data protection regulations ensures compliance. Audit trails help to trace data integrity.
Related Articles
Digital Transformation
Hyper-Personalized Banking: Driving Customer Loyalty and Engagement with AI-Powered Adobe Experiences
Digital Transformation
Leveraging 3rd Party LLMs: A Guide to Commercial AI Platforms
Digital Transformation
AI-Driven Security: Protecting Your eCommerce App and Customer Data in an Evolving Threat Landscape


